Artículos SCI
2010
2010
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Structure and microstructure of EB-PVD yttria thin films grown on Si (111) substrate
Hartmanova, M; Jergel, M; Holgado, JP; Espinos, JPVacuum, 85 (2010) 535-540
Show abstract ▽
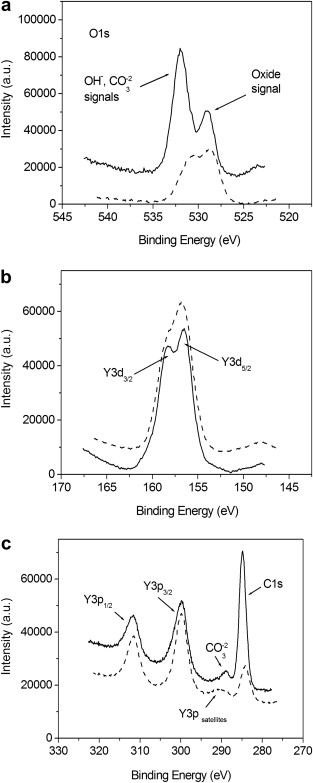
Structure and microstructure of yttria thin films grown by electron beam physical vapour deposition on a stationary Si (111) substrate at room temperature (RT), 500 degrees and 700 degrees C, were investigated by the grazing-incidence X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy, respectively. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy provided information on the surface contamination from the atmosphere and the oxidation state. A strong effect of the deposition temperature and the vapour flux incidence angle was found. The film deposited at RT is polycrystalline with very fine grains of the body-centered cubic (bcc) crystallographic symmetry. An increase of deposition temperature results in a rapid growth of bcc grains with an improved crystalline structure. Moreover, the based-centered monoclinic phase appears for the deposition temperature of 700 degrees C. Preferred grain orientation (texture) with two main components, (400) and (622), was observed in the films deposited at 500 degrees C whereas no texture was found for 700 degrees C. The microstructure exhibits the columnar feather-like structure of different degrees of perfection which can be explained by the shadowing effects caused by an oblique vapour flux incidence angle. Surface morphology of the films is governed by a combination of the triangular and four-sided (square) columns. All films were found to be dense with a little porosity between the columns.
Octubre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2010.09.003
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Wetting Properties of Polycrystalline TiO2 Surfaces: A Scaling Approach to the Roughness Factors
Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARLangmuir, 26 (2010) 15875-15882
Show abstract ▽
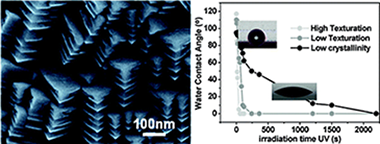
This work presents a thorough study on the wettability of polycrystalline anatase TiO2 thin films prepared at 250 degrees C in a microwave plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (MW-PECVD) reactor with Ar/O-2 plasmas. Anatase polycrystalline thin films with different microstructures, textures, and surface roughness were obtained as a function of their thickness. The water contact angle of the samples was analyzed within the assumptions of the Wenzel, Cassie, and Miwa models to ascertain the effect of roughness and other surface heterogeneities on their characteristic parameters. The roughness factors defined in the different models were calculated from the atomic force microscopy (AFM) images of the films for two different observation scales within the premises of the dynamic scaling theories. The obtained results indicate that the wetting angle of an equivalent flat anatase surface with a value of 82 degrees can only be properly estimated for observation scales of 5 x 5 mu m(2) and using the Miwa model. The analysis of the UV induced hydrophilization of the surface state of the anatase films and the posterior recovery of the partially hydrophobic character of these surfaces in the absence of UV photons suggest a clear dependence of the light induced wettability on their texture and size of crystalline domains.
Octubre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/la101975e
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Versatility and multifunctionality of highly reflecting Bragg mirrors based on nanoparticle multilayers
Olalla Sánchez-Sobrado, Mauricio E. Calvo and Hernán MíguezJournal of Materials Chemistry, 20 (2010) 8240-8246
Show abstract ▽
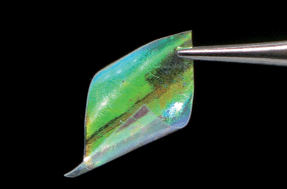
The use of both supported and flexible self-standing nanoparticle-based one dimensional photonic crystal films as effective frequency selective filters in the UV-vis-NIR is herein evaluated. The requirements to achieve a flat spectral response at the desired frequency range are analyzed and a synthetic route to realize materials with such properties presented. Strict control over the structural parameters yields multilayers in which the opening or closing of higher order photonic band gaps can be devised, thus leading to films capable of blocking the UV and NIR ranges simultaneously. Furthermore, the physico-chemical properties of the mirror can be modified to yield either moisture-repelling or, on the contrary, environmentally responsive optical filters. These materials present a great potential to be used as versatile and multifunctional optical elements.
Octubre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1039/c0jm01508c
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Microstructural study of the LiBH4-MgH2 reactive hydride composite with and without Ti-isopropoxide additive
Deprez, E; Justo, A; Rojas, TC; Lopez-Cartes, C; Minella, CB; Bosenberg, U; Dornheim, M; Borrnann, R; Fernandez, AActa Materialia, 58 (2010) 5683-5694
Show abstract ▽

An exhaustive microstructural characterization is reported for the LiBH4-MgH2 reactive hydride composite (RHC) system with and without titanium isopropoxide additive. X-ray diffraction with Rietveld analysis, transmission electron microscopy coupled to energy dispersive X-ray analysis, selected-area electron diffraction and electron energy loss spectroscopy are presented in this paper for the first time for this system for all sorption steps. New data are reported regarding average crystallite and grain size, microstrain, phase formation and morphology; these results contribute to the understanding of the reaction mechanism and the influence of the additives on the kinetics. Microstructural effects, related to the high dispersion of titanium-based additives, result in a distinct grain refinement of MgB2 and an increase in the number of reaction sites, causing acceleration of desorption and absorption reactions. Considerations on the stability of phases under electron beam irradiation have also been reported.
Octubre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2010.06.043
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Operando XAS and Raman study on the structure of a supported vanadium oxide catalyst during the oxidation of H2S to sulphur
Holgado, JP; Soriano, MD; Jimenez-Jimenez, J; Concepcion, P; Jimenez-Lopez, A; Caballero, A; Rodriguez-Castellon, E; Nieto, JMLCatalysis Today, 155 (2010) 296-301
Show abstract ▽
The modification of crystalline phases of a vanadium oxide supported on mesoporous zirconium phosphate during the partial oxidation of H2S to sulphur has been studied by using an operando Raman-GC approach and XAS in reaction conditions. The catalyst, mainly presenting crystalline V2O5, is transformed during the oxidation of H2S at 200 degrees C, presenting crystals of V4O9, which is identified by the presence of a band at ca. 900 cm(-1) in the Raman spectra (using a 785 nm line of an Argon ion laser) and by the presence of a pre-edge at 5469.8 eV (and a main-edge at 5482.2 eV) in XANES spectra. At the same time, it is observed a high conversion of H2S to sulphur (the main reaction product) and SO2 (as minority). Both activity and selectivity depend on the time on stream. In this way, the selectivity to SO2 decreases from ca. 5 to 1% with the time on stream. This change could be explained on the basis of the nature of V-species: the initial presence of V5+-O-V5+ pairs and the appearance of V5+-O-V4+ pairs at high time on stream.
Octubre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2010.02.050
- ‹ anterior
- 369 of 422
- siguiente ›














