Artículos SCI
2010
2010
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
A transparent TMPyP/TiO2 composite thin film as an HCl sensitive optochemical gas sensor
Cano, M; Castillero, P; Roales, J; Pedrosa, JM; Brittle, S; Richardson, T; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Barranco, ASensors and Actuators B-Chemical, 150 (2010) 764-769
Show abstract ▽
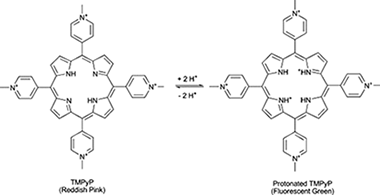
Tetracationic porphyrin (TMPyP) molecules were incorporated Into an optically transparent TiO2 thin film prepared by Glancing Angle Physical Vapour Deposition (GAPVD) by simple infiltration (at pH 6 4) The preparation of optically transparent TMPyP/TiO2 composite thin films provides a method for the integration of the porphyrin molecules Into photonic devices for direct monitoring of gases Previously UV-visible and fluorescence spectral techniques have been used to study the reversible protonation of TMPyP in aqueous solution The optical spectrum of TMPyP shows an intense Soret band at 423 nm with a 22 nm red shift upon protonation by HCl The experimental conditions for monitoring the concentration of HCl gas by absorption spectroscopy have been optimized The maximum absorbance change was observed at the Sorer band wavelength A selected temperature of 80 C and a 300 s recovery period were found to be the optimum operating parameters (response time t(50) = 16 8 7 s) The composite with smaller surface concentration of TMPyP (Gamma = 03 x 10(-9) mol cm(-2)) presented the best detection limit (0 1 ppm) The response of the composite sensor was highly stable for several months.
Octubre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2010.07.059
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Tilt angle control of nanocolumns grown by glancing angle sputtering at variable argon pressures
Garcia-Martin, JM; Alvarez, R; Romero-Gomez, P; Cebollada, A; Palmero, AApplied Physics Letters, 97 (2010) - 173103
Show abstract ▽
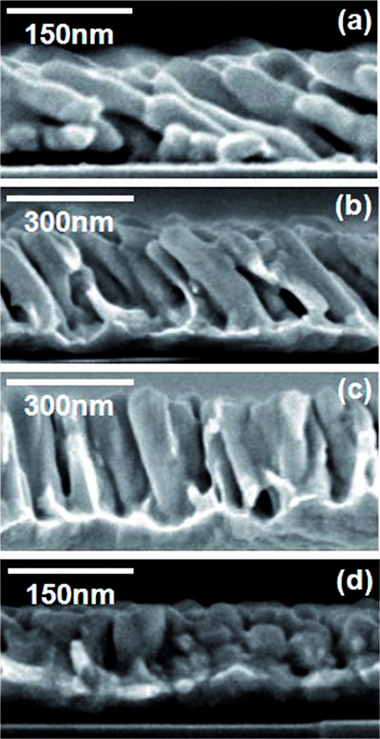
We show that the tilt angle of nanostructures obtained by glancing angle sputtering is finely tuned by selecting the adequate argon pressure. At low pressures, a ballistic deposition regime dominates, yielding high directional atoms that form tilted nanocolumns. High pressures lead to a diffusive regime which gives rise to vertical columnar growth. Monte Carlo simulations reproduce the experimental results indicating that the loss of directionality of the sputtered particles in the gas phase, together with the self-shadowing mechanism at the surface, are the main processes responsible for the development of the columns.
Octubre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1063/1.3506502
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Synthesis of biodiesel from the methanolysis of sunflower oil using PURAL (R) Mg-Al hydrotalcites as catalyst precursors
Navajas, A; Campo, I; Arzamendi, G; Hernandez, WY; Bobadilla, LF; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JA; Gandia, LMApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 100 (2010) 299-309
Show abstract ▽
A series of commercial Mg-Al hydrotalcites have been used as catalyst precursors for the methanolysis of sunflower oil.The solids were characterized by low Mg/Al molar ratios in the 0.5-2.3 range. Additionally, a solid consisting mainly of Mg(OH)(2) but containing some Al (4.2 wt.%) was also employed. The as-received materials were inactive for biodiesel synthesis so calcination and rehydration in boiling water were considered as activation treatments. Among the calcined solids, only the material consisting of MgO was significantly active, achieving about 50% oil conversion after 24h at 60 degrees C, methanol/oil molar ratio of 12 and 2 wt.% of catalyst. The effects of the calcination temperature in the 350-700 degrees C range have been investigated; calcination at 500 degrees C led to the best catalytic performance. In the case of the rehydrated materials, only the solids with the highest Mg/Al molar ratios recovered a well-ordered layered double hydroxide structure. These samples showed an improved catalytic activity compared with their calcined counterparts. A good correlation between catalytic activity and the basic properties determined using Hammett indicators and benzoic acid titration has been found. Rehydrated hydrotalcites were slightly more selective to biodiesel (75%) at intermediate levels of oil conversion than the calcined counterparts (66%). It has been verified that no Mg or Al leaching in the reaction mixture took place; however, the rehydrated samples deactivated significantly. In the case of MgO, after washing and calcination. the recycled catalyst gave 68% of the original oil conversion.
Octubre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.08.006
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Aleuritic (9,10,16-trihydroxypalmitic) acid self-assembly on mica
Heredia-Guerrero, JA; San-Miguel, MA; Sansom, MSP; Heredia, A; Benitez, JJPhysical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 12 (2010) 10423-10428
Show abstract ▽
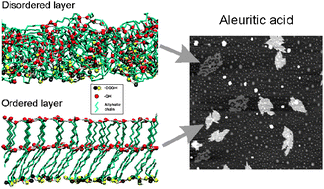
Aleuritic (9,10,16-trihydroxypalmitic) acid self-assembly on mica from solution has been studied using AFM, ATR-FTIR and MD simulations. The goal of this study is to define the role of hydroxyl groups in the interaction between molecules as reference data to understand the mechanism of formation of synthetic and natural biopolyesters from polyhydroxylated long chain carboxylic acids. In a confined structure, such as the one imposed by a vertically self-assembled layer on mica, aleuritic acid has a tendency to adopt a monolayer configuration ruled by the lateral interactions between molecules via the two secondary hydroxyl groups. This (2D) growth competes with the multilayer formation (3D), which is conditioned by the terminal primary hydroxyl group. As the self-assembly spatial constraint is relaxed, MD has shown that the structure tends to become an amorphous and crosslinked phase that can be characterized by topographic and friction force AFM data.
Septiembre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1039/c0cp00163e
Materiales Coloidales
Citrate mediated synthesis of uniform monazite LnPO(4) (Ln = La, Ce) and Ln:LaPO4 (Ln = Eu, Ce, Ce plus Tb) spheres and their photoluminescence
Nuñez, NO; Liviano, SR; Ocaña, MJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 349 (2010) 484-491
Show abstract ▽
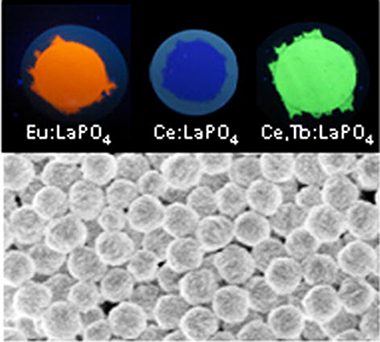
A simple method for the synthesis of spherical LaPO4 (monazite) particles with narrow size distribution and tailored size in the 150-500 nm range is reported. The procedure is based on a homogeneous precipitation process at low temperature (120 degrees C) from solutions containing La3+, citrate and phosphate ions under a very restrictive set of experimental conditions, which involves the use of La nitrate, citric acid and phosphoric acid as precursors and ethylene glycol as solvent. The growth mechanism of the spheres was investigated aiming at explaining the differences in particle size and shape observed when varying the experimental conditions. The applicability of this method for the synthesis of spherical particles of other lanthanide (Ce, Tb, Eu) phosphates is also analyzed. Finally, it is shown that the developed procedure can be used to dope the lanthanum phosphate particles with lanthanide cations, which resulted in spherical phosphors as illustrated for the Eu-doped, Ce-doped and Ce, Tb codoped systems, whose luminescent properties are also evaluated.
Septiembre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2010.05.079
- ‹ anterior
- 370 of 422
- siguiente ›














