Artículos SCI
2010
2010
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Tunable In-Plane Optical Anisotropy of Ag Nanoparticles Deposited by DC Sputtering onto SiO2 Nanocolumnar Films
Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Toudert, J; Borras, A; Lopez-Santos, C; Barranco, A; Feliu, IO; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARPlasmonics, 5 (2010) 241-250
Show abstract ▽
This work reports an easy-to-handle method for growing two-dimensional assemblies of Ag nanostructures presenting a tunable in-plane optical anisotropy. Ag is deposited by DC sputtering in an Ar plasma at room temperature onto bundled nanocolumnar SiO2 thin films grown by glancing angle physical vapor deposition. In contrast with previously reported processes involving the grazing angle deposition of the metal, DC sputtering is performed at normal incidence. By varying the deposition angle of SiO2 and the Ar pressure, it was possible to tune the deposited amount of Ag and thus the topology of the Ag deposit from isolated spherical Ag nanoparticles with isotropic optical properties to strongly dichroic Ag nanostripes oriented along the bundling direction of the SiO2 nanocolumns. Based on simple calculations taking into account the shadowing effects during metal deposition, it is proposed that the width and shape of the tip of the bundled SiO2 nanocolumns influence significantly the metal local atom flux arriving to them and thus the final structure of the deposit.
Septiembre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1007/s11468-010-9139-6
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales - Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
TiO2-SiO2 one-dimensional photonic crystals of controlled porosity by glancing angle physical vapour deposition
Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Lozano, G; Barranco, A; Miguez, H; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Materials Chemistry, 20 (2010) 6408-6412
Show abstract ▽
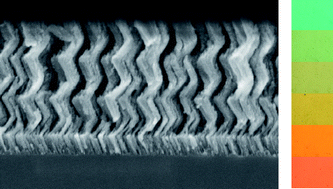
Herein we present a synthetic route to attain porous one-dimensional photonic crystals of high optical quality. The method employed, based on the alternate deposition of TiO2 and SiO2 porous layers by glancing angle physical vapour deposition, yields a highly accessible interconnected pore network throughout the entire multilayer structure. Furthermore, it allows a strict control over the average size and density of the interstitial sites, which results in the precise tuning of the refractive index of the individual layers and thus of the optical response of the ensemble. The controlled environmental response of the multilayer is confirmed by the optical monitoring of the infiltration of liquids of different refractive index.
Agosto, 2010 | DOI: 10.1039/C0JM00680G
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Characterization of Ti1-xAlxN coatings with selective IR reflectivity
Godinho, V; Philippon, D; Rojas, TC; Novikova, NN; Yakovlev, VA; Vinogradov, EA; Fernandez, ASolar Energy, 84 (2010) 1397-1401
Show abstract ▽

Ti1-xAlxN thin films were deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering. The obtained different stoichiometries give rise to different optical properties as the films change from metallic to dielectric. In this work the IR reflectivity of these coatings is investigated taking into account different application fields for IR selective Ti1-xAlxN thin films. Low Al content coatings present high reflectivity, high absorptance and low thermal emittance. High Al compositions give raise to coatings with high absorptance and high thermal emittance. The composition of the coatings was evaluated combining electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) and energy dispersive spectroscopy. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) revealed a columnar structure. Reflectance spectra for the visible and infrared spectral ranges were used to obtain the solar absorptance and thermal emittance values, used to calculate the equilibrium temperature of the coatings. The thermal stability in air from 300 to 600 degrees C was also evaluated.
Agosto, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.solener.2010.04.021
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Determination of the local structure of a highly dispersed Pd-Nanosystem located on a titanium dioxide carrier
Kriventsov, VV; Novgorodov, BN; Yakimchuk, EP; Kochubey, DI; Zyuzin, DA; Simakova, IL; Chistyakov, AV; Zhmakin, VV; Bukhtenko, OV; Tsodikov, MV; Kozitsyna, NY; Vargaftik, MN; Moiseev, II; Maksimovskii, EA; Nechepurenko, SF; Navio, JA; Nikitenko, SGJournal of Surface Investigation-X-Ray Synchrotron and Neutron Techniques, 4 (2010) 636-639
Show abstract ▽
This work is devoted to a structural study of a highly dispersed Pd nanosystem, which is stabilized in the TiO2 matrix, by XAFS spectroscopy. Nanocomposite was prepared from bimetallic PdCo(mu-OOCMe)(4)(NCMe) precursor followed by processing in several ways: calcination in air and in argon and microwave irradiation. The local structure of Pd catalysts formed by different methods was studied. Possible structural models were considered in detail.
Agosto, 2010 | DOI: 10.1134/S1027451010040166
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Tailored synthesis of nanostructured WC/a-C coatings by dual magnetron sputtering
Abad, MD; Munoz-Marquez, MA; El Mrabet, S; Justo, A; Sanchez-Lopez, JCSurface and Coatings Technology, 204 (2010) 3490-3500
Show abstract ▽

Nanostructured coatings with variable contents of tungsten carbide (WC) and amorphous carbon (a-C) are prepared by controlling the sputtering power ratio using WC and graphite targets. XRD and TEM/ED analysis shows that increasing the C incorporation. the WC nanocrystalline phases evolve from gamma-W2C to beta-WC1-x. Further C enrichment leads to a nanocomposite structure of small WC1-x crystals dispersed in a-C matrix. The a-C at.% is estimated by XPS analysis and correlated with the observed tribo-mechanical properties. The hardness and friction properties vary from hard/high friction (36-40 GPa; mu=0.6-0.8) to moderate-hard/low friction (16-20 GPa; mu similar to 0.2) coatings depending on the film composition. The transition point is found for a-C content of 10 at.%. This correlates with a change from nanocrystalline WC to nanocomposite WC1-x/a-C coatings. The overall study will help to understand the previous literature data and will serve as guide for a tailored synthesis of these WC/a-C nanocomposites.
Agosto, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2010.04.019
- ‹ anterior
- 372 of 422
- siguiente ›














