Artículos SCI
2010
2010
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical preparation of BaTiO3-Ni nanocomposites with high dielectric constant
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Dianez, MJ; Perejon, A; Criado, JMComposite Structures, 92 (2010) 2236-2240
Show abstract ▽
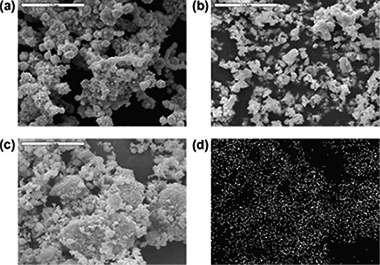
A mechanochemical procedure is proposed for an easy preparation of a BaTiO3-Ni composite in a single step. BaTiO3 and Ni powders available in the market are mixed by dry ball milling producing a decrease of particle size and an evenly distribution of both phases. In the sintered pellets the nickel particles are homogeneously distributed into the BaTiO3 matrix and isolated from others Ni particles. The dielectric constant of the composite is considerably higher than that of the barium titanate. Moreover, the temperature of the ferroelectric <-> paraelectric transition of the BaTiO3-Ni composite here prepared is much lower than the one of the pure BaTiO3 single phase.
Agosto, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2009.08.011
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Effect of surface roughness and sterilization on bacterial adherence to ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene
Kinnari, TJ; Esteban, J; Zamora, N; Fernandez, R; Lopez-Santos, C; Yubero, F; Mariscal, D; Puertolas, JA; Gomez-Barrena, EClinical Microbiology and Infection, 16 (2010) 1036-1041
Show abstract ▽
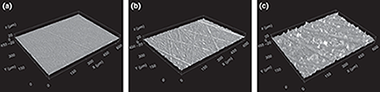
Sterilization with ethylene oxide (EO) and gas plasma (GP) are well-known methods applied to ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) surfaces in the belief that they prevent major material changes caused by gamma irradiation. However, the influence of these surface sterilization methods on bacterial adherence to UHMWPE is unknown. UHMWPE samples with various degrees of roughness (0.3, 0.8 and 2.0 mu m) were sterilized with either GP or EO. The variations in hydrophobicity, surface free energy and surface functional groups were investigated before and after sterilization. Sterilized samples were incubated with either Staphylococcus aureus or Staphylococcus epidermidis in order to study bacterial adherence to these materials. Fewer bacteria adhered to UHMWPE after sterilization with EO than after sterilization with GP, especially to the smoothest surfaces. No changes in chemical composition of the UHMWPE surface due to sterilization were observed using X-ray photoemission spectroscopy analysis. The decreased bacterial adherence to UHMWPE found at the smoothest surfaces after sterilization with EO was not directly related to changes in chemical composition. Increased bacterial adherence to rougher surfaces was associated with increased polar surface energy of EO-sterilized surfaces.
Julio, 2010 | DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02995.x/full
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Porous One-Dimensional Photonic Crystal Coatings for Gas Detection
Hidalgo, N; Calvo, ME; Colodrero, S; Miguez, HIEEE Sensors Journal, 10 (2010) 1206-1212
Show abstract ▽
Herein, we present an overview of recent progress on the development of different types of porous 1-D photonic crystal coatings which are optically responsive to gas pressure changes in the environment. Modification of the surrounding vapor pressure gives rise to adsorption and condensation phenomena within the porous networks of the photonic crystal building blocks, varying their refractive index and hence their optical features. This effect can be put into practice to precisely detect and monitor changes in the ambient through the spectral shift of either the photonic bandgap of the structure or of some other optical features. Our results demonstrate the potential of these optical coatings as new materials for gas sensing devices.
Julio, 2010 | DOI: 10.1109/JSEN.2010.2043525
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Influence of carbon chemical bonding on the tribological behavior of sputtered nanocomposite TiBC/a-C coatings
Abad, MD; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Brizuela, M; Garcia-Luis, A; Shtansky, DVThin Solid Films, 518 (2010) 5546-5552
Show abstract ▽

The tribological performance of nanocomposite coatings containing Ti-B-C phases and amorphous carbon (a-C) are studied. The coatings are deposited by a sputtering process from a sintered TiB2:TiC target and graphite, using pulsed direct current and radio frequency sources. By varying the sputtering power ratio, the amorphous carbon content of the coatings can be tuned, as observed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Raman spectroscopy. The crystalline component consists of very disordered crystals with a mixture of TiB2/TiC or TiBxCy phases. A slight increase in crystalline order is detected with the incorporation of carbon in the coatings that is attributed to the formation of a ternary TiBxCy phase. An estimation of the carbon present in the form of carbide (TiBxCy or TiC) and amorphous (a-C) is performed using fitting analysis of the C 1s XPS peak. The film hardness (22 to 31 GPa) correlates with the fraction of the TiBxCy phase that exists in the coatings. The tribological properties were measured by a pin-on-disk tribometer in ambient conditions, using 6 mm tungsten carbide balls at 1 N. The friction coefficients and the wear rates show similar behavior, exhibiting an optimum when the fraction of C atoms in the amorphous phase is near 50%. This composition enables significant improvement of the friction coefficients and wear rates (mu similar to 0.1; k < 1 x 10(-6) mm(3)/Nm), while maintaining a good value of hardness (24.6 GPa). Establishing the correlation between the lubricant properties and the fraction of a-C is very useful for purposes of tailoring the protective character of these nanocomposite coatings to engineering applications.
Julio, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2010.04.038
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Sunlight highly photoactive Bi2WO6-TiO2 heterostructures for rhodamine B degradation
Colon, G; Lopez, SM; Hidalgo, MC; Navio, JAChemical Communications, 46 (2010) 4809-4811
Show abstract ▽
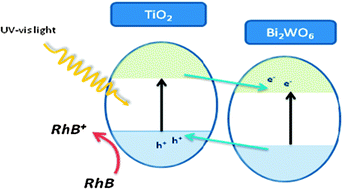
Highly efficient Bi2WO6-TiO2 heterostructures are synthesized by means of a hydrothermal method; they have high photoactivity for the degradation of rhodamine B under sunlike irradiation. An interesting synergetic effect between TiO2 and Bi2WO6 leads to an improved charge carrier separation mechanism, causing the excellent photocatalytic performance.
Julio, 2010 | DOI: 10.1039/c0cc00058b
- ‹ anterior
- 374 of 422
- siguiente ›














