Artículos SCI
2010
2010
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Steering the Self-Assembly of Octadecylamine Monolayers on Mica by Controlled Mechanical Energy Transfer from the AFM Tip
Benitez, JJ; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Salmeron, MJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 114 (2010) 12630-12634
Show abstract ▽
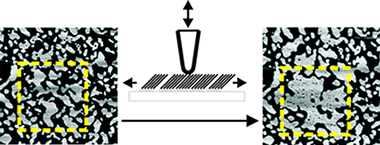
We have studied the effect of mechanical energy transfer from the tip of an atomic force microscope on the dynamics of self-assembly of monolayer films of octadecylamine on mica. The formation of the self-assembled film proceeds in two successive stages, the first being a fast adsorption from solution that follows a Langmuir isotherm. The second is a slower process of island growth by aggregation of the molecules dispersed on the surface. We found that the dynamics of aggregation can be altered substantially by the addition of mechanical energy into the system through controlled tip surface interactions. This leads to both the creation of pinholes in existing islands as a consequence of vacancy concentration and to the assembly of residual molecules into more compact islands.
Julio, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/jp102813s
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Preparation and structural properties of YBCO films grown on GaN/c-sapphire hexagonal substrate
Chromik, S; Gierlowski, P; Spankova, M; Dobrocka, E; Vavra, I; Strbik, V; Lalinsky, T; Sojkova, M; Liday, J; Vogrincic, P; Espinos, JPApplied Surface Science, 256 (2010) 5618-5622
Show abstract ▽
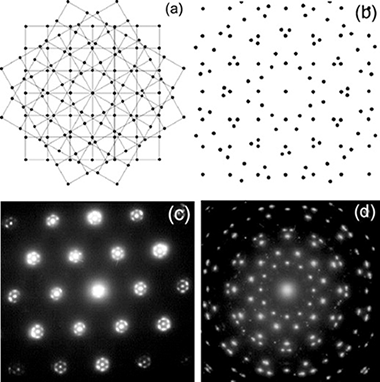
Epitaxial YBCO thin films have been grown on hexagonal GaN/c-sapphire substrates using DC magnetron sputtering and pulsed laser deposition. An MgO buffer layer has been inserted between the substrate and the YBCO film as a diffusion barrier. X-ray diffraction analysis indicates a c-axis oriented growth of the YBCO films. Φ-scan shows surprisingly twelve maxima. Transmission electron microscopy analyses confirm an epitaxial growth of the YBCO blocks with a superposition of three a–b YBCO planes rotated by 120° to each other. Auger electron spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy reveal no surface contamination with Ga even if a maximum substrate temperature of 700 °C is applied.
Julio, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.03.035
Reactividad de Sólidos - Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Microstructural Effects on the Creep Deformation of Alumina/Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes Composites
Gomez-Garcia, D; Poyato, R; Lee, Z; Castillo-Rodriguez, M; Dominguez-Rodriguez, A; Radmilovic, V; Padture, NPJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 93 (2010) 2042-2047
Show abstract ▽
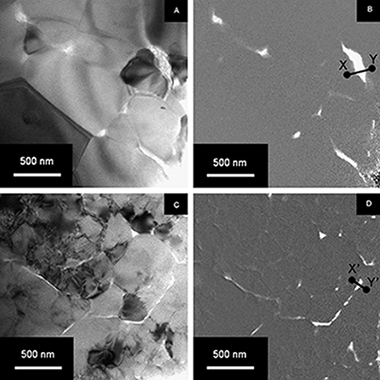
The enhanced high-temperature creep resistance in alumina/single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) composites has been attributed to the unprecedented grain-boundary structure of these composites, where the SWNTs bundles segregated at the alumina grain boundaries partially impede grain-boundary sliding. In this study, the effect of SWNTs distributions at alumina grain boundaries on the creep behavior of alumina/SWNTs composites has been investigated. Microstructures of two different alumina/10 vol% SWNTs composites, one with heterogeneous and the other with homogenous distributions of SWNTs at grain boundaries, have been characterized quantitatively. The steady-state creep rate (uniaxial compression) in the heterogeneous composite has been found to be over three times higher than that in the homogeneous composite at 1300° and 1350°C (argon atmosphere). It is argued that the less uniform distribution of SWNTs at the alumina grain boundaries in the heterogeneous composite results in less effective obstruction of grain-boundary sliding, and attendant higher creep rate. This also results in more efficient recovery in that composite.
Julio, 2010 | DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2010.03681.x
Reactividad de Sólidos
Nonisothermal calorimetric study of the precipitation processes in a Cu-1Co-0.5Ti alloy
Donoso, E; Zuniga, A; Dianez, MJ; Criado, JMJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 100 (2010) 975-980
Show abstract ▽
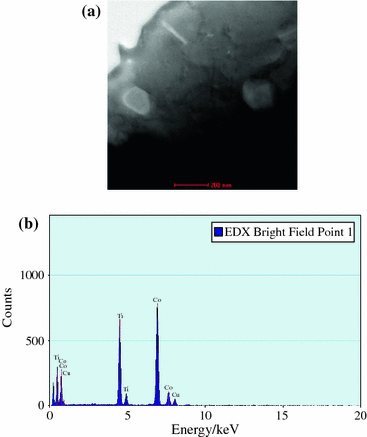
The precipitation processes in a Cu-1.0 at.%Co-0.5 at.%Ti (Cu-1.5 at.%Co2Ti) alloy were studied using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and microhardeness measurements. The analysis of the calorimetric curves from room temperature to 900 K shows the presence of two exothermic reactions attributed to the formation of CoTi and Co2Ti particles in the copper matrix. On the basis of enthalpy calculations, it was found that the decomposition begins with the precipitation of CoTi, followed by the formation of Co2Ti particles. The activation energies calculated using the modified Kissinger method were lower than the ones corresponding to diffusion of cobalt and titanium in copper. Kinetic parameters were obtained by a convolution method based on the Johnson-Mehl-Avrami (JMA) formalism. The values obtained for the parameter n were indicative of a particle nucleation process from preexistent nuclei. Microhardness measurements and TEM micrographs confirmed the formation of the mentioned phases.
Junio, 2010 | DOI: 10.1007/s10973-009-0642-y
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Self-assembly of supramolecular lipid nanoparticles in the formation of plant biopolyester cutin
Dominguez, E; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Benitez, JJ; Heredia, AMolecular Biosystems, 6 (2010) 948-950
Show abstract ▽
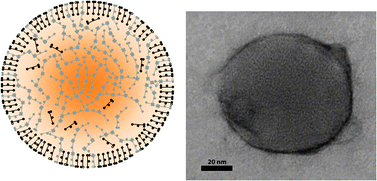
The implication of a self-assembly process in the early stages of cutin biosynthesis has been shown by means of antibodies raised against polyhydroxy fatty acid nanoparticles (cutinsomes).
Junio, 2010 | DOI: 10.1039/b927186d
- ‹ anterior
- 376 of 422
- siguiente ›














