Artículos SCI
2010
2010
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
In Situ Characterization of the Dynamic Gold-Support Interaction over Ceria Modified Eu3+. Influence of the Oxygen Vacancies on the CO Oxidation Reaction
Hernandez, WY; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 114 (2010) 10857-10865
Show abstract ▽
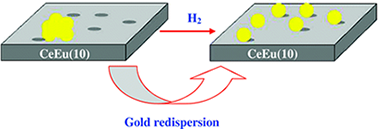
Gold-supported ceria and europium-doped ceria catalysts were prepared by the deposition-precipitation method. The influence of the pretreatment atmosphere and temperature on the concentration of oxygen vacancies and gold dispersion on the Au/CeEti(10) catalyst under actual reaction conditions was investigated by "in situ" X-ray diffraction and Raman analysis. By Raman spectroscopy, a preferential interaction of the gold with the support across the oxygen vacancies was established and correlated with the gold dispersion. The increase in the concentration of oxygen vacancies in the presence of hydrogen induces changes in the gold crystallite size by breaking-off and migration of gold nanoparticles toward the oxygen vacancies on the CeEu(10) support. The activity of the Au/CeEu(10) solid in the CO oxidation reaction was significantly improved when the catalyst was preactivated in a reducing atmosphere. This trend could be associated with the redispersion of gold together with the increase in the concentration of oxygen vacancies in the support.
Junio, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/jp1013225
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Study of the morphology of NiO nanostructures grown on highly ordered pyrolytic graphite, by the Tougaard method and atomic force microscopy: a comparative study
Preda, I; Soriano, L; Alvarez, L; Mendez, J; Yubero, F; Gutierrez, A; Sanz, JMSurface and Interface Analysis, 42 (2010) 869-873
Show abstract ▽
We studied the morphology of the deposits of NiO grown on highly ordered pyrolytic graphite (HOPG), by means of inelastic peak shape analysis and atomic force microscopy. The results obtained by both techniques show an excellent agreement. The results indicate that NiO grows on HOPG by following the Stransky-Krastanov type of growth.
Junio, 2010 | DOI: 10.1002/sia.3222
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Angular dependence of the intensity of light beams diffracted by colloidal crystals
Lozano, G; Mazzaferri, JE; Dorado, LA; Ledesma, S; Depine, RA; Miguez, HJournal of the Optical Society of America B-Optical Physics, 27 (2010) 1394-1399
Show abstract ▽
An experimental and theoretical analysis of the angular dependence of the diffracted light beams emerging from three-dimensional colloidal photonic crystals is herein presented. Diffracted beams are identified according to their associated reciprocal-lattice vectors, and their intensities are obtained as a function of the zenithal and azimuthal incidence angles. Significant changes in the beam intensities are observed for large zenithal incidence angles as the azimuthal angle is varied. This phenomenon is related to the excitation of new resonant modes inside the photonic crystal which cannot be observed under normal incidence conditions.
Junio, 2010 | DOI: 10.1364/JOSAB.27.001394
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Computational fluid dynamics study of heat transfer in a microchannel reactor for low-temperature Fischer-Tropsch synthesis
Arzamendi, G; Dieguez, PM; Montes, M; Odriozola, JA; Sousa-Aguiar, EF; Gandia, LMChemical Engineering Journal, 160 (2010) 915-922
Show abstract ▽

A three-dimensional computational fluid dynamics (CFD) study of heat transfer in a microchannel reactor for the low-temperature Fischer-Tropsch synthesis (FTS) is presented. The microreactor studied is a steel block with 80 square microchannels of 1 mm of side arranged in cross-flow configuration for the transport of syngas and cooling water. Syngas space velocities in the 5000-30,000 h(-1) (SIP) range have been considered. The microreactor exhibited good isothermicity under most simulated conditions. The FTS can be conducted with very low-temperature change between 483 and 523 K within a wide range of CO conversions using boiling water as coolant. To this end the pressure has to be set at the appropriate value between about Sand 35 atm. The pressure would have to be reduced as the CO conversion increases which might have a negative effect on the FTS selectivity to middle distillates. However, adjusting the cooling water flow rate in the range 0.25-250 g min(-1) allows maintaining the FTS temperature at suitable values while avoiding the use of low pressures. Relatively high values of the overall heat transfer coefficient in the 20-320 W m(-2) K-1 range have been obtained. A significant effect of the buoyancy forces on the thermal performance of the microreactor has been found.
Junio, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2009.12.028
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Gallium Arsenide Infiltration of Nanoporous Multi layers: A Route to High-Dielectric-Contrast One-Dimensional Photonic Crystals
Sanchez-Sobrado, O; Thomas, K; Povey, I; Pemble, ME; Miguez, HSmall, 6 (2010) 1283-1287
Show abstract ▽
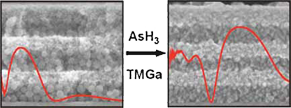
Periodic multilayers of wide photonic bandgap and high reflectance in the visible and near infrared regions are fabricated. Optical properties show that reflectance intensities close to 90% are reached for stacks of only six layers, as well as gap-to-midgap ratios of 50%. The optical response of the hybrid ensemble can be accurately tuned through the number of infiltration cycles performed.
Junio, 2010 | DOI: 10.1002/smll.200902190
- ‹ anterior
- 377 of 422
- siguiente ›














