Artículos SCI
2010
2010
Murillo's paintings revealed by spectroscopic techniques and dedicated laboratory-made micro X-ray diffraction
Duran, A; Siguenza, MB; Franquelo, ML; de Haro, MCJ; Justo, A; Perez-Rodriguez, JLAnalytica Chimica Acta, 671 (2010) 1-8
Show abstract ▽
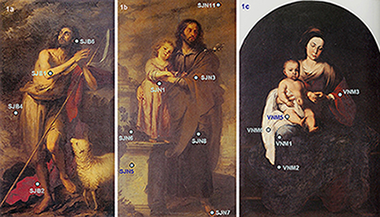
This paper describes one of the first case studies using micro-diffraction laboratory-made systems to analyse painting cross-sections. Pigments, such as lead white, vermilion, red ochre, red lac, lapis lazuli, smalt, lead tin yellow type I, massicot, ivory black, lamp black and malachite, were detected in cross-sections prepared from six Bartolome Esteban Murillo paintings by micro-Raman and micro-XRD combined with complementary techniques (optical microscopy, SEM-EDS, and FT-IR). The use of micro-XRD was necessary due to the poor results obtained with conventional XRD. In some cases, pigment identification was only possible by combining results from the different analytical techniques utilised in this study.
Junio, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2010.05.004
Materiales Coloidales - Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Environmentally responsive nanoparticle-based luminescent optical resonators
Sanchez-Sobrado, O; Calvo, ME; Nunez, N; Ocana, M; Lozano, G; Miguez, HNanoscale, 2 (2010) 936-941
Show abstract ▽
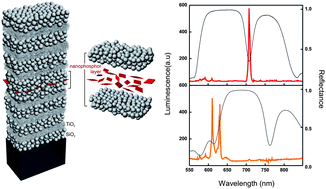
In this work, we demonstrate that optical resonators built using all-nanoparticle-based porous building blocks provide a responsive multifunctional matrix, totally different emission spectra being attained from the same embedded luminescent nanophosphors under varying environmental conditions. We show a clear correlation between modifications in the ambient surroundings, the induced changes of the resonant modes, and the resulting variations in the emission response. The method is versatile and allows nanophosphors of arbitrary shape to be integrated in the cavity. By precise control of the spectral features of the optical resonances, luminescence is strongly modulated in selected and tuneable wavelength ranges. Applications in the fields of sensing and detection are foreseen for these materials.
Junio, 2010 | DOI: 10.1039/b9nr00338j
Reactividad de Sólidos
Microstructural characterization of ceramic-intermetallic composites using TEM related techniques
Sayagues, MJ; Aviles, MA; Cordoba, JM; Alcala, MD; Gotor, FJJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 30 (2010) 1765-1774
Show abstract ▽
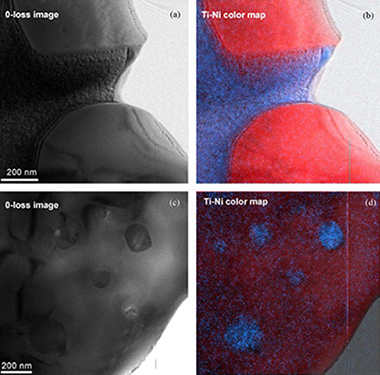
TiCxVy/Ni and TiCxNy/Ti-Co composites formed by ceramic and intermetallic binder phases were produced by pressureless sintering at 1400 degrees C from powders synthesized by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) process. Four different composites were characterized using high-resolution electron microscopic techniques, in both scanning (SEM, HRSEM) and transmission (TEM, HRTEM, ED, EDS and EELS) modes and using an energy filtered technique (EFTEM) associated with electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS). The microcharacterization showed that the ceramic phase with an fcc-cubic structure displayed a short-range order in many crystals detected by diffuse scattering in the ED patterns. This was possibly due to a sequence of C, N, and vacancies of both atoms along certain directions in the structure. On the other hand, even though the binder phase was introduced as metal in the reaction process, it was formed by Ni-Ti or Co-Ti known intermetallic compounds (NiTi2, Ni3Ti, and Co3Ti). An unknown Ni-Ti intermetallic structure with a Ni:Ti ratio close to 2:1 was only found in one of the synthesized composites and displayed a cubic structure with a lattice parameter, a, of about 8.7 angstrom.
Junio, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.01.039
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
On the microstructure of single wall carbon nanotubes reinforced ceramic matrix composites
Zapata-Solvas, E; Gomez-Garcia, D; Dominguez-Rodriguez, AJournal of Materials Science, 45 (2010) 2258-2263
Show abstract ▽
A microstructural modelling of the microstructure in single wall carbon nanotubes reinforced alumina ceramics has been developed. The model accounts for the main microstructural features, being quite useful to describe the carbon nanotube distribution along the ceramic matrix. The microstructural analysis derived from this model is found to give a deeper insight into the high-temperature creep of these composites.
Mayo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1007/s10853-009-4126-z
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
SiOxNy thin films with variable refraction index: Microstructural, chemical and mechanical properties
Godinho, V; de Haro, MCJ; Garcia-Lopez, J; Goossens, V; Terryn, H; Delplancke-Ogletree, MP; Fernandez, AApplied Surface Science, 256 (2010) 4548-4553
Show abstract ▽
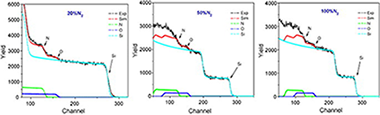
In this work amorphous silicon oxynitride films with similar composition (ca. Si0.40N0.45O0.10) were deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering from a pure Si target under different N-2-Ar mixtures. Rutherford backscattering (RBS) studies revealed that the coatings presented similar composition but different density. The mechanical properties evaluated by nanoindentation show also a dependence on the deposition conditions that does not correlate with a change in composition. An increase in nitrogen content in the gas phase results in a decrease of hardness and Young's modulus. The microstructural study by high resolution scanning electron microscopy (SEM-FEG) on non-metalized samples allowed the detection of a close porosity in the form of nano-voids (3-15 nm in size), particularly in the coatings prepared under pure N-2 gas. It has been shown how the presence of the close porosity allows tuning the refraction index of the films in a wide range of values without modifying significantly the chemical, thermal and mechanical stability of the film.
Mayo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.02.045
- ‹ anterior
- 378 of 422
- siguiente ›














