Artículos SCI
2010
2010
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Permanent magnetism in phosphine- and chlorine-capped gold: from clusters to nanoparticles
Munoz-Marquez, MA; Guerrero, E; Fernandez, A; Crespo, P; Hernando, A; Lucena, R; Conesa, JCJournal of Nanoparticle Research, 12 (2010) 1307-1318
Show abstract ▽

Magnetometry results have shown that gold NPs (similar to 2 nm in size) protected with phosphine and chlorine ligands exhibit permanent magnetism. When the NPs size decreases down to the subnanometric size range, e.g. undecagold atom clusters, the permanent magnetism disappears. The near edge structure of the X-ray absorption spectroscopy data points out that charge transfer between gold and the capping system occurs in both cases. These results strongly suggest that nearly metallic Au bonds are also required for the induction of a magnetic response. Electron paramagnetic resonance observations indicate that the contribution to magnetism from eventual iron impurities can be disregarded.
Mayo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1007/s11051-010-9862-0
Identification of cellulose fibres belonging to Spanish cultural heritage using synchrotron high resolution X-ray diffraction
Herrera, LK; Justo, A; Duran, A; de Haro, MCJ; Franquelo, M; Rodriguez, JLPApplied Physics A-Materials Science & Processing, 99 (2010) 391-398
Show abstract ▽
A complete characterisation of fibres used in Spanish artwork is necessary to provide a complete knowledge of these natural fibres and their stage of degradation. Textile samples employed as painting supports on canvas and one sample of unprocessed plant material were chosen for this study. All the samples were investigated by synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction (SR-XRD). Flax and cotton have the Cellulose I structure. The values of the crystalline index (CI) were calculated for both types of fibres. The structure of Cellulose IV was associated with the unprocessed plant material. The information obtained by SR-XRD was confirmed by laboratory techniques including scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR).
Mayo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1007/s00339-010-5626-z
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
On the microstructure of single wall carbon nanotubes reinforced ceramic matrix composites
Zapata-Solvas, E; Gomez-Garcia, D; Dominguez-Rodriguez, AJournal of Materials Science, 45 (2010) 2258-2263
Show abstract ▽
A microstructural modelling of the microstructure in single wall carbon nanotubes reinforced alumina ceramics has been developed. The model accounts for the main microstructural features, being quite useful to describe the carbon nanotube distribution along the ceramic matrix. The microstructural analysis derived from this model is found to give a deeper insight into the high-temperature creep of these composites.
Mayo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1007/s10853-009-4126-z
Reactividad de Sólidos
A new model for the kinetic analysis of thermal degradation of polymers driven by random scission
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Perejon, A; Criado, JMPolymer Degradation and Stability, 95 (2010) 733-739
Show abstract ▽
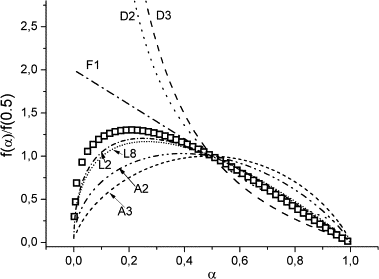
In this paper, a series of f(alpha) kinetic equations able to describe the random scission degradation of polymers is formulated in such a way that the reaction rate of the thermal degradation of polymers that go through a random scission mechanism can be directly related to the reacted fraction. The proposed equations are validated by a study of the thermal degradation of poly(butylene terephthalate) (PBT). The combined kinetic analysis of thermal degradation curves of this polymer obtained under different thermal pathways have shown that the proposed equation fits all these curves while other conventional models used in literature do not.
Mayo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2010.02.017
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Excitation transfer mechanism along the visible to the Near-IR in rhodamine J-heteroaggregates
Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Toudert, J; Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Barranco, AChemical Communications, 46 (2010) 4372-4374
Show abstract ▽
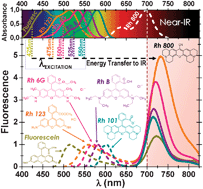
An enhanced fluorescent emission of the dye Rhodamine 800 in the Near-IR is observed in the presence of other xanthene dye molecules (RhX) when they are hosted in different matrices due to the formation of a new type of fluorescent J-heteroaggregates.
This enhanced emission of the acceptor occurs despite the low spectral overlapping and the low quantum yield of Rh800.
Mayo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1039/c0cc00087f
- ‹ anterior
- 379 of 422
- siguiente ›














