Artículos SCI
2010
2010
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Surface Functionalization, Oxygen Depth Profiles, and Wetting Behavior of PET Treated with Different Nitrogen Plasmas
Lopez-Santos, C; Yubero, F; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2 (2010) 980-990
Show abstract ▽
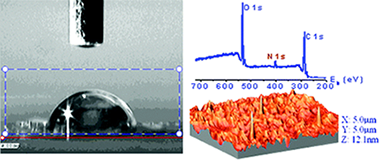
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plates have been exposed to different nitrogen containing plasmas with the purpose of incorporating nitrogen functional groups on its surface. Results with a dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) at atmospheric pressure and a microwave discharge (MW) at reduced pressure and those using an atom source working under ultrahigh vacuum conditions have been compared for N-2 and mixtures Ar + NH3 as plasma gases. The functional groups have been monitored by X-ray Photoemission Spectroscopy (XPS). Nondestructive oxygen and carbon depth profiles for the plasma treated and one month aged samples have been determined by means of the nondestructive Tougaard's method of XPS background analysis. The surface topography of the treated samples has been examined by Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM), while the surface tension has been determined by measuring the static contact angles of water and iodomethane. It has been found that the DBD with a mixture of Ar+NH3 is the most efficient treatment for nitrogen and amine group functionalization as determined by derivatization by reaction with chlorobenzaldehyde. It is also realized that the nitrogen functional groups do not contribute significantly to the observed increase in surface tension of plasma treated PET.
Abril, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/am100052w
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
One-Step Dry Method for the Synthesis of Supported Single-Crystalline Organic Nanowires Formed by pi-Conjugated Molecules
Borras, A; Groning, O; Aguirre, M; Gramm, F; Groning, PLangmuir, 26 (2010) 5763-5771
Show abstract ▽
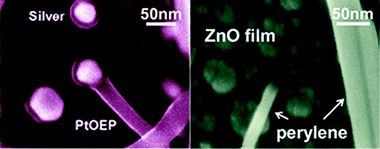
We present for the first time a general vacuum process for the growth of supported organic nanowires formed by pi-conjugated molecules, including metalloporphyrins, metallophthalocyanines, and perylenes. This methodology consists on a one-step physical vapor deposition of the pi-conjugated molecules. The synthesis is carried out at controlled temperature on substrates with tailor morphology which allows the growth or organic nanowires in the form of squared nanofibers and nanobelts. The study of the nanowires by electron diffraction and HRTEM combining with the results of a theoretical analysis of the possible arrangement of the pi-conjugated molecules along the nanowires reveals that the nanowires show a columnar structure along the fiber axis consisting of pi-stacked molecules having a herringbone-like arrangement. The formation of these nanowires on different substrates demonstrates that the growth mechanism is independent of the substrate chemical composition. An in-depth phenomenological study of the Formation of the nanowires drives us to propose a growth mechanism based on a crystallization process. Furthermore, the growth method allows the fabrication of two particular ID heterostructures: binary and open core@shell organic nanofibers.
Abril, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/la1003758
Materiales Avanzados
Physical and geotechnical properties of clay phyllites
Garzon, E; Sanchez-Soto, PJ; Romero, EApplied Clay Science, 48 (2010) 307-318
Show abstract ▽
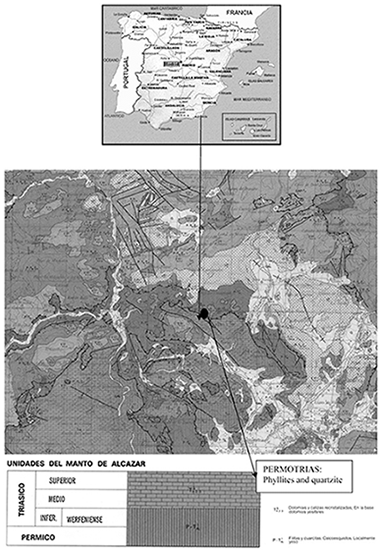
An experimental programme is presented with the aim of characterising - from physical, microstructural and geotechnical perspectives - the main properties of compacted clay phyllites. These clay phyllites are widely used as waterproofing material for roofs in the Alpujarra (Andalusia, Spain), as sealing liners in irrigation ponds, and as core material of small earthen zoned dams. An exhaustive physical-characterisation programme on the powder fraction has been followed using X-ray fluorescence (XRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), chemical analysis by energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), thermal analysis, particle-size distribution analysis, consistency limits, and density of solid particles. From a microstructural standpoint, mercury intrusion porosimetry (MIP) tests, as well as nitrogen-adsorption tests, were carried out to characterise the pore network and surface area of the material in both natural and compacted states. The geotechnical characterisation programme on the compacted material was focused on the water-permeability and water-retention properties, the volume change on soaking (swelling or collapse), the compressibility on loading, the shear-strength properties, and the mechanical-penetration properties. In this way, an important physical and hydro-mechanical data base is provided, which could help in evaluating the suitability for using this material in a wide range of earthen constructions (liners, road subgrades, embankments, core material in zoned dams). It has been found that the material contains illite, chlorite and quartz as the main components, and feldspar, iron oxide and interstratified illite-smectite as minor ones. Despite the presence of active clay minerals, the compacted material did not display an important swelling on soaking at low stresses, as a consequence of its low specific surface and low water-retention ability. The material exhibited good compaction properties and, consequently, low water permeability plus a stiff response on loading. Nevertheless, despite the low porosity attained on the dry-side compaction, the material underwent some collapse on soaking at stresses greater than 100 kPa.
Abril, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2009.12.022
Reactividad de Sólidos
Microstructural characterization of copper based alloys produced by reactive milling
Palma, R; Sepulveda, A; Zuniga, A; Donoso, E; Dianez, MJ; Criado, JMRevista de Metalurgia, 46 (1010) 197-205
Show abstract ▽
The micro and nanostructure of Cu-Al, Cu-V and Cu-Ti alloys produced by reactive milling were analyzed using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Samples with different milling times (t = 0, 10, 20 and 30 h) were considered. The grain size, dislocation density and residual microstrain were evaluated form the XRD data using the Williamson-Hall and Klug-Alexander methods. The evolution of texture as a function of milling time was also studied using XRD. It was found, using TEM, that the grain size and dispersoid size were nanometric in all three alloys considered.
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.3989/revmetalm.2010.v46.i3
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Evaluation of Different Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma Configurations As an Alternative Technology for Green C-1 Chemistry in the Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane and the Direct Decomposition of Methanol
Rico, VJ; Hueso, JL; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Physical Chemistry A, 114 (2010) 4009-4016
Show abstract ▽
Carbon dioxide reforming of methane and direct decomposition of methanol have been investigated using dielectric harrier discharges (DBD)) at atmospheric pressure and reduced working temperatures. Two different plasma reactor configurations are compared and especial attention is paid to the influence of the surface roughness of the electrodes oil the conversion yields in the first plasma device. The influence of different filling gap dielectric materials (i.e., Al2O3 of BaTiO3) in the second packed configuration has been also evaluated. Depending on the experimental conditions of applied voltage, residence time of reactants. feed ratios, or factor configuration. different conversion yields are achieved ranging front 20 to 80% in the case of methane and 7-45% for the carbon dioxide. The direct decomposition of methanol reaches 60-100% Under similar experimental conditions. Interestingly, the selectivity toward the production of hydrogen and carbon monoxide is kept almost constant under all the experimental conditions, and the formation of longer hydrocarbon chains of coke is a byproduct is not detected. The maximum efficiency yields are observed for the packed-bed reactor configuration containing alumina for both reaction processes (similar to 1 mol H-2 per kilowatt hour for dry reforming of methane and similar to 4.5 mol H-2, per kilowatt hour for direct decomposition of methanol).
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/jp100346q
- ‹ anterior
- 381 of 422
- siguiente ›














