Artículos SCI
2010
2010
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Evaluation of Different Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma Configurations As an Alternative Technology for Green C-1 Chemistry in the Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane and the Direct Decomposition of Methanol
Rico, VJ; Hueso, JL; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Physical Chemistry A, 114 (2010) 4009-4016
Show abstract ▽
Carbon dioxide reforming of methane and direct decomposition of methanol have been investigated using dielectric harrier discharges (DBD)) at atmospheric pressure and reduced working temperatures. Two different plasma reactor configurations are compared and especial attention is paid to the influence of the surface roughness of the electrodes oil the conversion yields in the first plasma device. The influence of different filling gap dielectric materials (i.e., Al2O3 of BaTiO3) in the second packed configuration has been also evaluated. Depending on the experimental conditions of applied voltage, residence time of reactants. feed ratios, or factor configuration. different conversion yields are achieved ranging front 20 to 80% in the case of methane and 7-45% for the carbon dioxide. The direct decomposition of methanol reaches 60-100% Under similar experimental conditions. Interestingly, the selectivity toward the production of hydrogen and carbon monoxide is kept almost constant under all the experimental conditions, and the formation of longer hydrocarbon chains of coke is a byproduct is not detected. The maximum efficiency yields are observed for the packed-bed reactor configuration containing alumina for both reaction processes (similar to 1 mol H-2 per kilowatt hour for dry reforming of methane and similar to 4.5 mol H-2, per kilowatt hour for direct decomposition of methanol).
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/jp100346q
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Theoretical Analysis of the Performance of One-Dimensional Photonic Crystal-Based Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
Lozano, G; Colodrero, S; Caulier, O; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 114 (2010) 3681-3687
Show abstract ▽
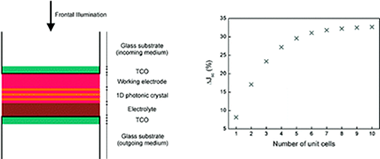
A simple analytical model that allows designing one-dimensional photonic crystal based dye sensitized solar cells of optimized performance, accounting for the actual optical features of the device, is herein presented. Based on the theoretical description of the effect of coupling such Bragg mirrors to the light harvesting electrode, recently reported experimental values of the spectral dependence of incident photon to current conversion efficiency attained for such Structures are fairly reproduced and rationalized. A thorough analysis or them in terms of the interplay between the effect of the electrode thickness and the characteristics of the Bragg reflection, such as intensity, spectral position, and width, is provided. Predictions on the maximum enhancement factors expected for realistic Structures are also presented.
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/jp9096315
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Structural characterization of polyhydroxy fatty acid nanoparticles related to plant lipid biopolyesters
Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Dominguez, E; Luna, M; Benitez, JJ; Heredia, AChemistry and Physics of Lipids, 163 (2010) 329-333
Show abstract ▽
In the present work, we report the physico-chemical properties and structural characteristics of special polyhydroxy fatty acid nanoparticles after their fusion by means of attenuated total reflection-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), scanning electronic microscopy (SEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and light microscopy. All the characteristics and properties investigated have an important degree of similarity to the native plant cutin, the main biopolymer present in the plant cuticles. The supramolecular organization of these polymerized prime nanoparticles after their interaction on cellulose substrate and isolated cuticle samples, simulating the in vivo conditions in epidermal plant cells, strongly suggests a growth of these nanoparticles after a self-assembly process.
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2010.01.006
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Room-Temperature Reaction of Oxygen with Gold: An In situ Ambient-Pressure X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Investigation
Jiang, P; Porsgaard, S; Borondics, F; Kober, M; Caballero, A; Bluhm, H; Besenbacher, F; Salmeron, MJournal of the American Chemical Society, 132 (2010) 2858-2859
Show abstract ▽
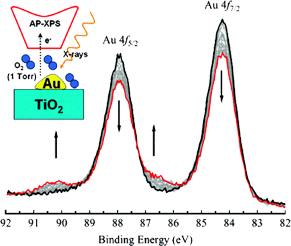
The interaction of O-2 with gold foil and gold nanoparticles grown by thermal deposition on TiO2(110) was studied by in situ ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy at room temperature. No spontaneous dissociation of O-2 was observed either on Au foil or oil Au nanoparticles up to 1 Torr of O-2. X-ray irradiation, however, is very effective in promoting gold oxidation on both surfaces in the presence of O-2. Our results help reconcile recent conflicting experimental observations regarding the activation of molecular oxygen, which is a crucial issue in Au catalyzed oxidation reactions.
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/ja909987j
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Application of Micro-X-ray Fluorescence Analysis for the Characterization of Industrial Wastes
Alba, MD; Aparicio, P; Benitez, JM; Castro, MA; Diaz, M; Orta, MMIndustrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 49 (2010) 2348-2352
Show abstract ▽
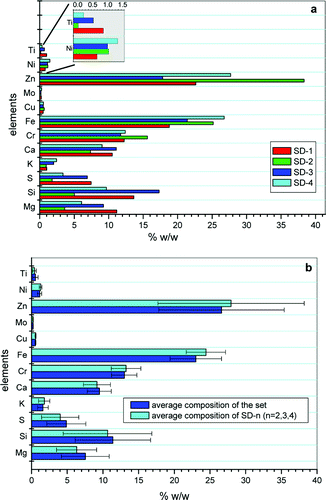
The issue of how to improve product quality and product yield in a short period of time is becoming more critical in many industries. Thus, shorter delay times between laboratory analysis and process correction are important in process control. Elimination of sample handling and operator Manipulation is desirable. The present article proposes micro-X-ray fluorescence (mu XRF) as an economical control method for industrial product quality with a minimum time cost. Samples from different industrial processes have been chosen and analyzed by XRF and mu XRF, The results show that the two techniques give similar results and that mu XRF allows the waste to be classified and is able to detect problems in the production process.
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/ie901716w
- ‹ anterior
- 382 of 422
- siguiente ›














