Artículos SCI
2010
2010
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Evaluation of Different Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma Configurations As an Alternative Technology for Green C-1 Chemistry in the Carbon Dioxide Reforming of Methane and the Direct Decomposition of Methanol
Rico, VJ; Hueso, JL; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Physical Chemistry A, 114 (2010) 4009-4016
Show abstract ▽
Carbon dioxide reforming of methane and direct decomposition of methanol have been investigated using dielectric harrier discharges (DBD)) at atmospheric pressure and reduced working temperatures. Two different plasma reactor configurations are compared and especial attention is paid to the influence of the surface roughness of the electrodes oil the conversion yields in the first plasma device. The influence of different filling gap dielectric materials (i.e., Al2O3 of BaTiO3) in the second packed configuration has been also evaluated. Depending on the experimental conditions of applied voltage, residence time of reactants. feed ratios, or factor configuration. different conversion yields are achieved ranging front 20 to 80% in the case of methane and 7-45% for the carbon dioxide. The direct decomposition of methanol reaches 60-100% Under similar experimental conditions. Interestingly, the selectivity toward the production of hydrogen and carbon monoxide is kept almost constant under all the experimental conditions, and the formation of longer hydrocarbon chains of coke is a byproduct is not detected. The maximum efficiency yields are observed for the packed-bed reactor configuration containing alumina for both reaction processes (similar to 1 mol H-2 per kilowatt hour for dry reforming of methane and similar to 4.5 mol H-2, per kilowatt hour for direct decomposition of methanol).
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/jp100346q
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Morphological evolution of pulsed laser deposited ZrO2 thin films
Alvarez, R; Palmero, A; Prieto-Lopez, LO; Yubero, F; Cotrino, J; de la Cruz, W; Rudolph, H; Habraken, FHPM; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Applied Physics, 107 (2010) 54311-54320
Show abstract ▽
Morphological evolution of ZrO2 thin films deposited during pulsed laser deposition of Zr in O-2 atmosphere has been experimentally studied at two different film deposition temperatures, 300 and 873 K. The roughness exponent, alpha, the growth exponent, beta, the coarsening exponent, 1/z, and the exponent defining the evolution of the characteristic wavelength of the surface, p, for depositions at 300 K amounted to beta = 1.0 +/- 0.1, alpha = 0.4 +/- 0.1, 1/z = 0.34 +/- 0.03, and p = 0.49 +/- 0.03, whereas for depositions carried out at 873 K amounted to beta = 0.3 +/- 0.3, alpha = 0.4 +/- 0.2, and 1/z = 0.0 +/- 0.2. Experimental error becomes important due to the flat morphology of the films inherent to the deposition technique. The change in the surface topography with the film temperature has been studied with the help of a simple Monte Carlo model which indicates the existence of two different growth regimes: a shadowing dominated growth, occurring at low temperatures, characterized by calculated values beta = 1.00 +/- 0.04, alpha = 0.50 +/- 0.04, p = 0.46 +/- 0.01, and 1/z = 0.35 +/- 0.02 and a diffusion dominated growth that takes place at high temperatures as well as at low deposition rates, characterized by calculated values beta = 0.15 +/- 0.08, alpha = 0.33 +/- 0.04, and 1/z = 0.33 +/- 0.07. The good agreement obtained between the experimental and simulated parameters is discussed within the frame of the general characteristics of the deposition method.
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1063/1.3318604
Reactividad de Sólidos
Spark Plasma Sintering of Ultrafine TiCxN1-x Powders Synthesized by a Mechanically Induced Self-Sustaining Reaction
Borrell, A; Fernandez, A; Torrecillas, R; Cordoba, JM; Aviles, MA; Gotor, FJJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 93 (2010) 2252-2256
Show abstract ▽
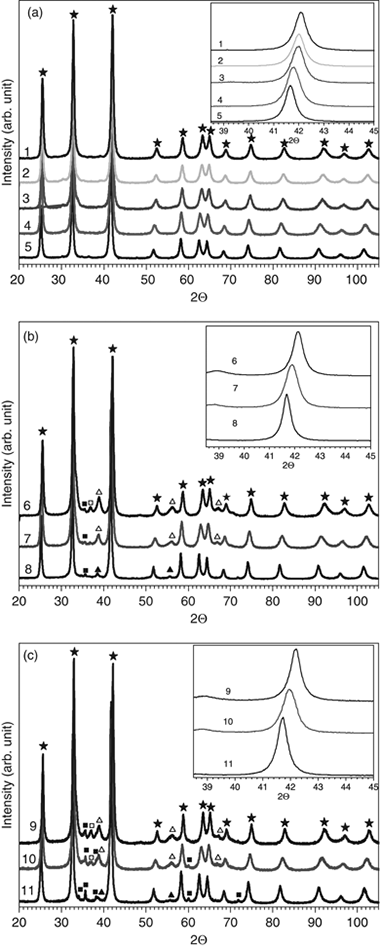
High-purity, nanometer-sized titanium carbonitride powders, TiCxN1-x, were obtained with a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) in a high-energy planetary ball mill from a mixture of titanium and different carbon precursors under a nitrogen atmosphere. A promising method for developing dense TiCxN1-x materials is the coupling of MSR with the spark plasma sintering (SPS) technique. The powders were sintered at different temperatures to provide a completely dense monolithic ceramic (> 99% theoretical density). In this work, the influence of the carbon precursor and SPS treatment on the material microstructures were studied, and the main mechanical properties of the end material were evaluated.
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2010.03735.x
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanosynthesis of Hf1-xZrxB2 Solid Solution and Hf1-xZrxB2/SiC Composite Powders
Aviles, MA; Cordoba, JM; Sayagues, MJ; Alcala, MD; Gotor, FJJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 93 (2010) 696-702
Show abstract ▽
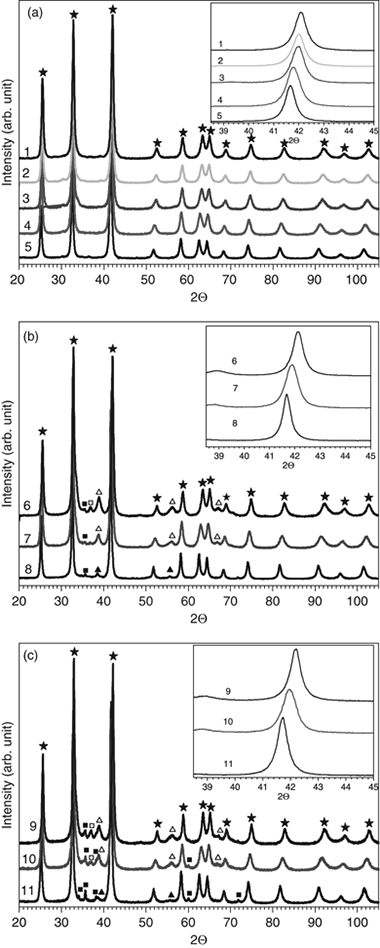
The synthesis of solid solutions in the HfB2-ZrB2 system was conducted by mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) processes under an inert atmosphere from elemental mixtures of Hf, Zr, and B. The stoichiometry of the Hf1-xZrxB2 solid solution phase was controlled by adjusting the Hf/Zr/B atomic ratio in the starting mixture. Composite materials with SiC were achieved by adding the required amount of SiC to the Hf/Zr/B reactant mixture. The presence of up to 20 vol% of SiC did not inhibit the MSR process. Longer milling times were required to ignite the mixture. Small amounts of the refractory phases ZrC or HfC were observed in the composite powders. The chemical composition, structure, and microstructure of products were studied by X-ray diffraction, scanning and transmission electron microscopy, electron diffraction, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. This complete characterization confirmed the formation of P6/mmm hexagonal diboride phases with a submicrometric microstructure. The determination of the chemical composition and lattice parameters ascertained the formation of solid solutions with good chemical homogeneity in the HfB2-ZrB2 system.
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2009.03484.x
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Active and Optically Transparent Tetracationic Porphyrin/TiO2 Composite Thin Films
Castillero, P; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Cano, M; Pedrosa, JM; Roales, J; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2 (2010) 712-721
Show abstract ▽
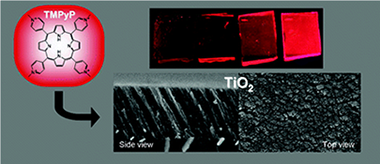
Fluorescent tetracationic porphyrin (TMPyP) molecules have been incorporated into optically transparent TiO2 thin films acting as a host material. The films, with a columnar structure and open pores, were prepared by electron evaporation at glancing angles (GAPVD). The open porosity of the films has been estimated by measuring a water adsorption isotherm with a quartz crystal monitor. TMPyP molecules were infiltrated in the host thin films by their immersion into water solutions at controlled values of pH. The state of the adsorbed molecules, the infiltration efficiency, and the adsorption kinetics were assessed by analyzing the optical response of the films by UV-vis absorption and fluorescence techniques. The infiltration efficiency was directly correlated with the acidity of the medium, increasing at basic pHs as expected from simple considerations based on the concepts of the point of zero charge (PZC) developed for colloidal oxides. By a quantitative evaluation based on the analysis of the UV spectra, the infiltration process has been described by a Langmuir type adsorption isotherm and an Elovich-like kinetics. The accessibility of the infiltrated molecules in the TMPyP/TiO2 composite films is assessed by following the changes of their optical properties when exposed to the acid vapors and their subsequent recovery with time.
Marzo, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/am900746q
- ‹ anterior
- 383 of 422
- siguiente ›














