Artículos SCI
2010
2010
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Oxidation State and Local Structure of Ti-Based Additives in the Reactive Hydride Composite 2LiBH(4) + MgH2
Deprez, E; Muñoz-Marquez, MA; Roldan, MA; Prestipino, C; Palomares, FJ; Minella, CB; Bosenberg, U; Dornheim, M; Bormann, R; Fernandez, AJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 114 (2010) 3309-3317
Show abstract ▽
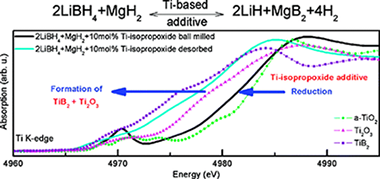
Nowadays, the technological utilization of reactive hydride composites (RHC) Lis hydrogen storage materials is limited by their reaction kinetics. However, addition of transition-metal-based additives, for instance titanium isopropoxide (Ti-iso), to the 2LiBH(4)+MgH2 system, results in a significant improvement of sorption kinetics. In this work, the evolution of chemical state and local structure of the Ti-based additive has been investigated by means of X-ray absorption (XAS) and photoemission (XPS) spectroscopy. X-ray absorption near-edge Structure (XANES) its well as extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) analysis have been Undertaken at the Ti K-edge. The measurements reveal the formation of a highly dispersed and disordered TiO2-like phase during ball milling. During first desorption reduced titanium oxide and titanium boride are formed and remain stable upon cycling. The Surface analysis performed by XPS shows that the reduction processes of the Ti-based additive during first desorption IS Coupled to the migration of the Ti species front the surface to the bulk of the material. Several factors, related to favoring heterogeneous nucleation of MgB2 and the increase of interfacial area through grain refinement are proposed as potential driving force, among other effects, for the observed kinetic improvement.
Febrero, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/jp910955r
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
In situ spectroscopic detection of SMSI effect in a Ni/CeO2 system: hydrogen-induced burial and dig out of metallic nickel
Caballero, A; Holgado, JP; Gonzalez-delaCruz, VM; Habas, SE; Herranz, T; Salmeron, MChemical Communications, 46 (2010) 1097-1099
Show abstract ▽
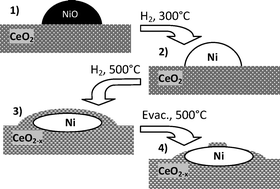
In situ APPES technique demonstrates that the strong metal support interaction effect (SMSI) in the Ni-ceria system is associated with the decoration and burial of metallic particles by the partially reduced support, a phenomenon reversible by evacuation at high temperature of the previously absorbed hydrogen.
Febrero, 2010 | DOI: 10.1039/b920803h
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Lanthanide sorption on smectitic clays in presence of cement leachates
Galunin, E; Alba, MD; Santos, MJ; Abrao, T; Vidal, MGeochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 74 (2010) 862-875
Show abstract ▽
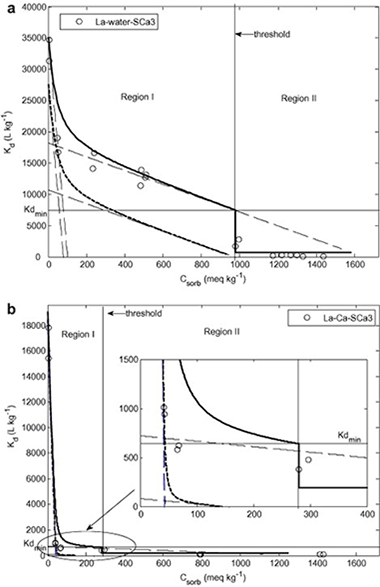
Due to their potential retention capacity, clay minerals have been proposed for use in the engineered barriers for the storage of high-level radioactive actinides in deep geological waste repositories. However, there is still a lack of data on the sorption of actinides in clays in conditions simulating those of the repositories. The present article examines the sorption of two lanthanides (actinide analogues) in a set of smectitic clays (FEBEX bentonite, MX80 bentonite, hectorite, saponite, Otay montmorillonite, and Texas montmorillonite). Distribution coefficients (K-d) were determined in two media: water and 0.02 mol L-1 Ca, the latter representing the cement leachates that may modify the chemical composition of the water in contact with the clay. The K-d values of the lanthanides used in the experiments (La and Lu) varied greatly (25-50 000 L kg(-1)) depending on the ionic medium (higher values in water than in the Ca medium), the initial lanthanide concentration (up to three orders of magnitude decrease inversely with lanthanide concentration), and the examined clay (up to one order of magnitude for the same lanthanide and sorption medium). Freundlich and Langmuir isotherms were used to fit sorption data to allow comparison of the sorption parameters among smectites. The model based on the two-site Langmuir isotherms provided the best fit of the sorption data, confirming the existence of sorption sites with different binding energies. The sites with higher sorption affinity were about 6% of the total sorption capacity in the water medium, and up to 17% in the Ca medium, although in this latter site sorption selectivity was lower. The wide range of K-d values obtained regarding the factors examined indicated that the retention properties of the clays should also be considered when selecting a suitable clay for engineered barriers.
Febrero, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.gca.2009.11.003
Seville City Hall Chapter Room ceiling decoration
Duran, A; Robador, MD; de Haro, MCJ; Herrera, LK; Gimena, P; Perez-Rodriguez, JLMateriales de Construcción, 60 (2010) 83-95
Show abstract ▽
El objetivo de este trabajo es el estudio de diferentes aspectos, como el color, la composición química y las fases mineralógicas presentes en los diferentes materiales que forman la ornamentación del techo de la Sala Capitular del Ayuntamiento de Sevilla, mediante métodos físicos y químicos. Nuestros resultados muestran que el dorado fue realizado sobre una capa de bol previamente depositada sobre una lámina de blanco de plomo que cubría un estrato de calcita. Posteriormente, y probablemente debido a alteraciones en el dorado original, el techo fue de nuevo dorado usando una técnica similar. En el siglo XIX, casi todo el techo, excepto las zonas con inscripciones, fue blanqueado usando una mezcla de calcita y blanco de plomo. Se empleó plata para cubrir la espada del rey Juan I (casetón 27). Finísimas láminas de oro se usaron para decorar los atributos reales: coronas, cinturones, cetros, espadas y rosarios. En diferentes partes de la decoración fueron detectados pigmentos como azurita, malaquita, bermellón y negro de humo. La composición del mortero de la estructura era a base de cal y dolomita molida.
Febrero, 2010 | DOI: 10.3989/mc.2010.45107
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Air- and Light-Stable Superhydrophobic Colored Surfaces Based on Supported Organic Nanowires
Borras, A; Groning, P; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Barranco, A; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARLangmuir, 26 (2010) 1487-1492
Show abstract ▽

In this work, we report oil it new type of superhydrophobic material consisting of supported organic nanowires prepared by vacuum deposition, Different intensely colored surfaces with water contact angles its high its 180 degrees call be Fabricated depending oil the composition. morphology, and density of the nanowires. These surfaces are stable in air and under intense light irradiation. The wettability properties of coatings made of metalloporphyrins and metallophthalocyanines nanowires as well as other heterostructured binary and open core@shell nanowires are studied.
Febrero, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/la903701j
- ‹ anterior
- 384 of 422
- siguiente ›














