Artículos SCI
2010
2010
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Complete n-hexane oxidation over supported Mn-Co catalysts
Todorova, S; Kolev, H; Holgado, JP; Kadinov, G; Bonev, C; Pereniguez, R; Caballero, AApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 94 (2010) 46-54
Show abstract ▽

Two series of Co-Mn samples were prepared by impregnation of silica with aqueous solutions or Co(NO3)(2)center dot 6H(2)O and/or Mn(NO3)(2)center dot 6H(2)O. Cobalt oxide was the predominant phase in one of the series and manganese was used as the promoter. The major component in the second series was manganese oxide and Co was the promoter. The prepared samples were characterized by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), temperature-programmed reduction (TPR), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and tested in the reaction of complete n-hexane oxidation. The catalytic activity of both single component cobalt and manganese samples was similar, however, a combination between the two elements changed significantly the activity and this depended on the method of preparation. Catalysts prepared by a common solution of Co- and Mn nitrates manifested a considerable increase in activity as a result of very low crystallinity of the supported metal oxide phases, partial enrichment of the surface with cobalt and uniform distribution of oxide agglomerates on the support.
Febrero, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.10.019
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Synthesis, characterization, and photoactivity of InTaO4 and In0.9Ni0.1TaO4 thin films prepared by electron evaporation
Rico, VJ; Frutos, F; Yubero, F; Espinos, JP; Gonzales-Elipe, ARJournal of Vacuum Science & Technology A, 28 (2010) 127-134
Show abstract ▽
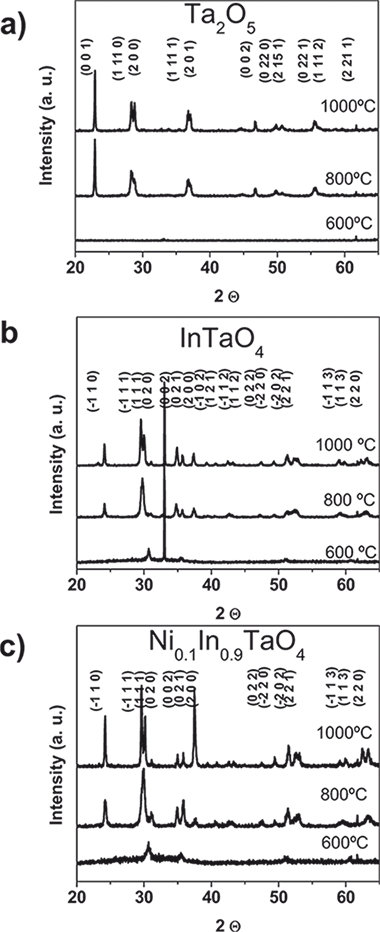
InTaO4 and In0.9Ni0.1TaO4 thin films have been prepared by electron evaporation of successive layers of the single oxide components and posterior annealing at T > 800 degrees C. The annealed thin films presented the monoclinic crystallographic structure typical of these mixed oxides. The electrical and optical behaviors of the films, assessed by C-V measurements, surface conductivity as a function of temperature, and UV-vis absorption spectroscopy, indicate that these oxides are wide band gap semiconductors with a variable dielectric constant depending on the annealing conditions. By reflection electron energy loss spectroscopy some electronic states have been found in the gap at an energy that is compatible with the activation energy deduced from the conductivity versus 1/T plots for these oxides. The photoactivity of these materials has been assessed by looking to the evolution of the wetting contact angle as a function of the irradiation time. All the films became superhydrophilic when irradiated with UV light, while the In0.9Ni0.1TaO4 thin films also presented a small partial decrease in wetting angle when irradiated with visible photons.
Enero, 2010 | DOI: 10.1116/1.3273597
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Doping level effect on sunlight-driven W,N-co-doped TiO2-anatase photo-catalysts for aromatic hydrocarbon partial oxidation
Kubacka, A; Bachiller-Baeza, B; Colon, G; Fernandez-Garcia, MApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 93 (2010) 274-281
Show abstract ▽
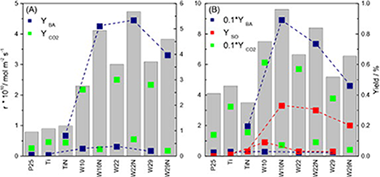
A series of nanosized W,N-co-doped anatase TiO2 catalysts with different dopant contents has been prepared by a microemulsion method and examined in the sunlight selective photo-oxidation of toluene and styrene. The activity results have been correlated with structural, electronic, and surface examinations of the catalysts done with the help of XRD-Rietveld, N-2 physisorption and NH3 chemisorption-calorimetry, XPS, Infrared, and UV-visible spectroscopies. Irrespective of the reaction, a consistent reaction rate enhancement with respect to titania (nano-TiO2, P25) references and W-doped TiO2 systems is observed for single-phase anatase W,N-co-doped samples. This is likely linked with the decrease of the band gap energy decrease and results from a combined W-N cooperative effect on structural properties of the anatase network. W,N simultaneous presence also makes a drastic effect on selectivity, maximizing the yield to partial oxidation products. This appears related with surface properties of the materials.
Enero, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.09.039
Microscopic and spectroscopic techniques for the study of paper supports and textile used in the binding of hispano-arabic manuscripts from Al-Andalus: A transition model in the 15th century
Espejo, T; Duran, A; Lopez-Montes, A; Blanc, RJournal of Cultural Heritage, 11 (2010) 50-58
Show abstract ▽

This work focuses on the study of paper and textiles used in the binding of a series of manuscripts that share some specific characteristics that lead us to speculate on the possibility of a transitional codicological typology from the Arabic to the Christian book in Al-Andalus during the 15th century. The books we analyzed belong to the collection of the Historical Archive of Malaga, the Archive of Sacromonte Abbey, in Granada, the School of Arabic Studies and the Library of P.P. Escolapios, also in Granada. Paper physical study was performed by microscopic and spectroscopic techniques. A routine and objective method, Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, was employed and proved to be a useful technique for the characterization of cellulosic fibres, main component of paper from the boards and the envelope flap pasteboards, and the fabric lining from the cover. The results of our research will help us to date, identify and study the evolution of the techniques, proving that the materials and innovations of the Italian paper manufacturing processes were perfectly known in the south of modern day Spain, before the Christian Reconquest.
Enero, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.culher.2009.01.007
Reactividad de Sólidos - Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
The Multistep Nature of the Kaolinite Dehydroxylation: Kinetics and Mechanism
Ortega, A; Macias, M; Gotor, FJJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 93 (2010) 197-203
Show abstract ▽
The thermal dehydroxylation of kaolinite has been reexamined using small sample weights, a homogeneous particle size distribution and high-vacuum conditions in order to reduce the influences of heat and mass-transfer phenomena. The controlled rate thermal analysis (CRTA) technique, which was specially developed to minimize the pressure and temperature gradients through the sample, was employed to carry out meaningful kinetic experiments. Two advanced isoconversional methods, the Vyazovkin and the Galwey methods, were used complementarily to determine the dependence of the activation energy on the degree of conversion. For this purpose, the Vyazovkin method has been adapted to CRTA experiments. It was demonstrated that there are at least two different stages, revealing the multistep nature of this reaction. The activation energy for the first step, which is assigned to nucleation and the growth of nuclei, decreases from 100 to 75 kJ/mol. The second stage corresponds to a diffusion process and the activation energy rises to 120 kJ/mol because of the metakaolinite formation, which closes the interlamellar channels and leaves isolated patches of kaolinite from which the water escapes with difficulty.
Enero, 2010 | DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2009.03328.x
- ‹ anterior
- 385 of 422
- siguiente ›














