Artículos SCI
2009
2009
Reactividad de Sólidos
Synthesis of complex carbonitride powders TiyMT1−yCxN1−x (MT: Zr, V, Ta, Hf) via a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Cordoba, JM; Aviles, MA; Sayagues, MJ; Alcala, MD; Gotor, FJJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 482 (2012) 349-355
Show abstract ▽
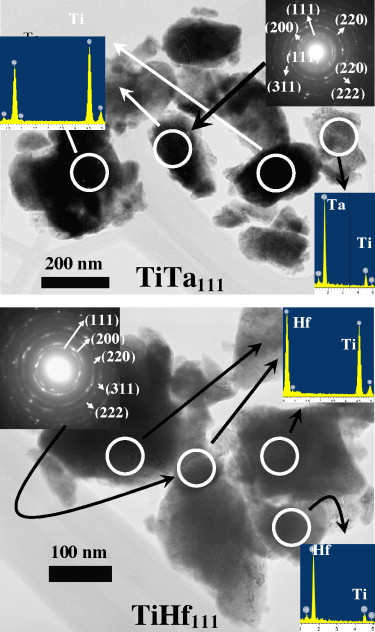
The machinability of materials is a dynamic field with enormous implications in different industrial sectors because manufacturers are constantly looking for improvements that can increase the overall productivity. Manufacturers of cutting tool inserts need to develop products that can perform at higher speeds and last longer under increasingly rigorous operating conditions. It has been revealed that cermets may exhibit better properties and performances when solid solution of multiple hard compounds is added instead of a mixture of several binary ones. In this work, a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) is described as a suitable synthesis method to obtain a wide range of different new quaternary carbonitride systems by milling mixtures of elemental powders of transition metals and graphite in a nitrogen atmosphere. Characterization was carried out using X-ray powder diffraction, elemental analysis, energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX), scanning and transmission electron microscopy and electron diffraction (ED).
Agosto, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.04.012
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Incorporation and Thermal Evolution of Rhodamine 6G Dye Molecules Adsorbed in Porous Columnar Optical SiO2 Thin Films
Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Blaszczyk-Lezak, I; Espinos, JP; Hamad, S; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Barranco, ALangmuir, 25 (2009) 6869-6874
Show abstract ▽

Rhodamine 6G (Rh6G) dye molecules have been incorporated into transparent and porous SiO2 thin films prepared by evaporation at glancing angles. The porosity of these films has been assessed by analyzing their water adsorption isotherms measured for the films deposited on a quartz crystal monitor. Composite Rh6G/SiO2 thin films were prepared by immersion of a SiO2 thin film into a solution of the dye at a given pH. It is found that the amount of Rh6G molecules incorporated into the film is directly dependent on the pH of the solution and can be accounted for by a model based on the point of zero charge (PZC) concepts originally developed for colloidal oxides. At low pHs, the dye molecules incorporate in the form of monomers, while dimers or higher aggregates are formed if the pH increases. Depending on the actual preparation and treatment conditions, they also exhibit high relative fluorescence efficiency. The thermal stability of the composite films has been also investigated by characterizing their optical behavior after heating in an Ar atmosphere at increasing temperatures up to 275 °C. Heating induces a progressive loss of active dye molecules, a change in their agglomeration state, and an increment in their relative fluorescence efficiency. The obtained Rh6G/SiO2 composite thin films did not disperse the light and therefore can be used for integration into optical and photonic devices.
Agosto, 2009 | DOI: 10.1021/la900695t
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Effect of Sulfate Pretreatment on Gold-Modified TiO2 for Photocatalytic Applications
Hidalgo, MC; Maicu, M; Navio, JA; Colon, GJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 113 (2009) 12840-12847
Show abstract ▽

The influence of sulfated pretreatment of TiO2 on the structure, morphology, and dispersion of gold and photocatalytic properties of Au/TiO2 were studied. Notable enhancements in the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 were achieved by deposition of gold onto samples that had previously undergone sulfate treatment followed by high temperature calcination. The enhancement in activity can be attributed to the stronger bonding and improved electronic communication between gold particles and TiO2 on defect rich surfaces as are found on sulfated samples after calcination at 700 °C. Two different methods for gold deposition were evaluated: chemical reduction by citrate and photodeposition. The citrate method produced more homogeneous and smaller gold particles with a better dispersion than photodeposition, which lead to greater increases in activity in the photocatalytic degradation of phenol when the former method was used for deposition on both sulfated and nonsulfated TiO2. The combination of sulfate pretreatment and gold deposition by chemical reduction was shown to be a good strategy to obtain gold/titania catalysts possessing homogeneous particle size and dispersion of the metal and a strong bonding between the Au and the TiO2 surface.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1021/jp903432p
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
ZnO activation by using activated carbon as a support: Characterisation and photoreactivity
Melian, EP; Diaz, OG; Rodriguez, JMD; Colon, G; Arana, J; Melian, JH; Navio, JA; Pena, JPApplied Catalysis A-General, 364 (2009) 176-181
Show abstract ▽

The effect of the mixing ZnO with different portions of activated carbon (AC) has been studied. The resulting catalysts were characterised and evaluated in the photocatalytic decomposition of aqueous pollutants. Changes in the catalyst colour and in the FTIR vibration bands of the surface hydroxyl groups were recorded. νOH vibrations were shifted to lower wavenumbers as AC loading increased, demonstrating modification of the acid-base character of the catalysts. Laser scattering studies showed that AC loading leads to smaller ZnO particles. BET surface area measurements and scanning electron micrograph (SEM) analysis showed agglomeration of ZnO particle pores in the AC structure.
Results showed that in addition to a synergistic effect of the AC-ZnO combination, AC content modifies the ZnO particle properties and consequently photocatalytic behaviour. This was evident in phenol degradation experiments where changes in the concentration profiles of the catechol and hydroquinone degradation intermediates, were observed. However, the AC-ZnO catalysts were less efficient than pure ZnO in the degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol (DCP). This seems to be due to the strong adsorption of the DCP molecule on AC, resulting in lower diffusion to the catalytic ZnO and thus a lower rate of photocatalysis.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2009.05.042
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Electrical characteristics of mixed Zr–Si oxide thin films prepared by ion beam induced chemical vapor deposition at room temperature
Ferrer, FJ; Frutos, F; Garcia-Lopez, J; Jimenez, C; Yubero, FThin Solid Films, 517 (2009) 5446-5452
Show abstract ▽
Mixed Zr–Si oxide thin films have been prepared at room temperature by ion beam decomposition of organometallic volatile precursors. The films were flat and amorphous. They did not present phase segregation of the pure single oxides. A significant amount of impurities (–C–, –CHx, –OH, and other radicals coming from partially decomposed precursors) remained incorporated in the films after the deposition process. This effect is minimized if the Ar content in the O2/Ar bombarding gas is maximized. Static permittivity and breakdown electrical field of the films were determined by capacitance–voltage and current–voltage electrical measurements. It is found that the static permittivity increases non-linearly from ~ 4 for pure SiO2 to ~ 15 for pure ZrO2. Most of the dielectric failures in the films were due to extrinsic breakdown failures. The maximum breakdown electrical field decreases from ~ 10.5 MV/cm for pure SiO2 to ~ 45 MV/cm for pure ZrO2. These characteristics are justified by high impurity content of the thin films. In addition, the analysis of the conduction mechanisms in the formed dielectrics is consistent to Schottky and Poole-Frenkel emission for low and high electric fields applied, respectively.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2009.01.099
- ‹ anterior
- 394 of 422
- siguiente ›














