Artículos SCI
2009
2009
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Nanoindentation of TiO2 thin films with different microstructures
Gaillard, Y; Rico, VJ; Jimenez-Pique, E; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 42 (2009) 145305
Show abstract ▽
A series of nanoindentation tests has been carried out with TiO2 films produced by physical vapour deposition (PVD) under different conditions. Films with different microstructures and crystallographic structures have been prepared by changing experimental parameters such as the temperature of the substrate, the deposition angle (by the so-called glancing angle physical vapour deposition, GAPVD) or by exposing the growing film to a beam of accelerated ions. The obtained results of hardness and Young's modulus depict interesting correlations with the microstructure and structure of the films providing a general picture for the relationships between these characteristics and their mechanical properties. Different models have been used to extract Young's modulus and hardness parameters from the experimental nanoindentation curves. The obtained results are critically discussed to ascertain the ranges of validity of each procedure according to the type of sample investigated.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1088/0022-3727/42/14/145305
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Degradation of n-Butyl tin Chlorides in Waters. A Comparative Assessment of the Process by Photo-assisted and Chemical- treatment Methods
Navio, JA; Cerrillos, C; Macias, MJournal of Advanced Oxidation Technologies, 12 (2009) 158-163
Show abstract ▽
Study of degradation processes of metals used in some artworks from the cultural heritage of Andalusia, Spain
Duran, A; Herrera, LK; de Haro, MCJ; Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Justo, ARevista de Metalurgia, 45 (2009) 277-286
Show abstract ▽
The study of the alteration processes of metals, such as lead, bronze, iron and tin-mercury alloys, used in some of the
most important chosen artefacts of Andalusian Cultural Heritage is the main objective of this paper. Hydrocerussite
and cerussite were detected in lead seals stored in a hole of cardboard. Bronze is altered to atacamite by environmental
contamination, which is also responsible for the formation of rust from iron. Corrosion of the tin-mercury surface
of amalgam mirrors produces tin monoxide and tin dioxide and releases liquid mercury from the solid phase.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.3989/revmetalm.0827
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Stability of phyllosilicates in Ca(OH)2 solution: Influence of layer nature, octahedral occupation, presence of tetrahedral Al and degree of crystallinity
Mantovani, M; Escudero, A; Alba, MD; Becerro, AIApplied Geochemistry, 24 (2009) 1251-1260
Show abstract ▽
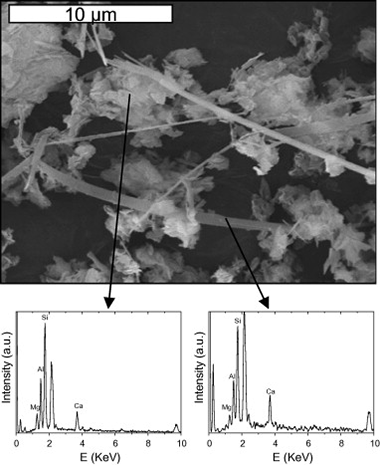
This paper presents the results of a comprehensive investigation of the interaction of layered silicates with Ca(OH)2 in hydrothermal conditions. The study is intended to evaluate the stability of the clay buffer in radioactive waste repositories, at the intermediate stages of concrete leaching, when the pH is controlled by the dissolution of portlandite. The influence of layer nature, octahedral occupation, presence of tetrahedral Al and degree of crystallinity will be assessed by analysing the behaviour of a set of well-selected phyllosilicates and using the combined capabilities of 29Si and 27Al MAS-NMR spectroscopy, powder X-ray diffraction and SEM/EDX. The results show that the main factor affecting the stability of the clay is the octahedral occupation, so that trioctahedral phyllosilicates are much more stable than dioctahedral ones. The nature and expandability of the layer does not seem to much influence the stability of the clay, so that a 2:1 expandable phyllosilicate shows the same stability as a chemically analogous 1:1 non-expandable phyllosilicate. However other factors like the poor crystallinity of the starting material or the presence of Al in the tetrahedral sheet of trioctahedral phyllosilicates weaken the clay structure in alkaline conditions and favour the transformation towards other phases.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.03.012
Study of the gilding technique used in polychromed stones and ceramics by dedicated laboratory-made micro X-ray diffraction and complementary techniques
Duran, A; Perez-Rodriguez, JL; de Haro, MCJAnalytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 394 (2009) 1671-1677
Show abstract ▽
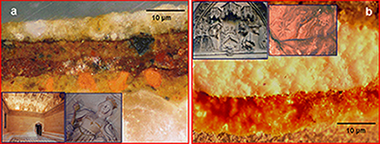
This work describes the use of a new dedicated laboratory-made micro X-ray diffraction system for detecting the phases present in cross-sections of artworks. As an example, the phases present in samples from gilding ceramics and stone sculptures from the heritage of Seville (Spain) were successfully detected using this new system, which takes advantage of various devices developed for synchrotron radiation, and is complemented by the information provided by other techniques.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1007/s00216-009-2836-3
- ‹ anterior
- 395 of 422
- siguiente ›














