Artículos SCI
2009
2009
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Stability of phyllosilicates in Ca(OH)2 solution: Influence of layer nature, octahedral occupation, presence of tetrahedral Al and degree of crystallinity
Mantovani, M; Escudero, A; Alba, MD; Becerro, AIApplied Geochemistry, 24 (2009) 1251-1260
Show abstract ▽
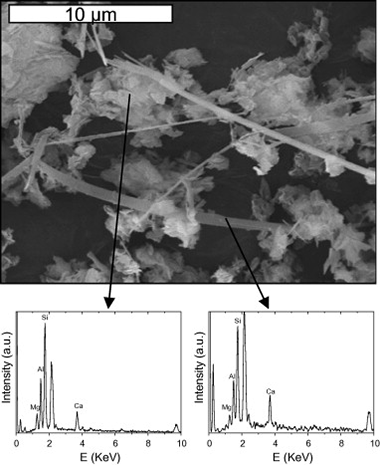
This paper presents the results of a comprehensive investigation of the interaction of layered silicates with Ca(OH)2 in hydrothermal conditions. The study is intended to evaluate the stability of the clay buffer in radioactive waste repositories, at the intermediate stages of concrete leaching, when the pH is controlled by the dissolution of portlandite. The influence of layer nature, octahedral occupation, presence of tetrahedral Al and degree of crystallinity will be assessed by analysing the behaviour of a set of well-selected phyllosilicates and using the combined capabilities of 29Si and 27Al MAS-NMR spectroscopy, powder X-ray diffraction and SEM/EDX. The results show that the main factor affecting the stability of the clay is the octahedral occupation, so that trioctahedral phyllosilicates are much more stable than dioctahedral ones. The nature and expandability of the layer does not seem to much influence the stability of the clay, so that a 2:1 expandable phyllosilicate shows the same stability as a chemically analogous 1:1 non-expandable phyllosilicate. However other factors like the poor crystallinity of the starting material or the presence of Al in the tetrahedral sheet of trioctahedral phyllosilicates weaken the clay structure in alkaline conditions and favour the transformation towards other phases.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.03.012
Study of the gilding technique used in polychromed stones and ceramics by dedicated laboratory-made micro X-ray diffraction and complementary techniques
Duran, A; Perez-Rodriguez, JL; de Haro, MCJAnalytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 394 (2009) 1671-1677
Show abstract ▽
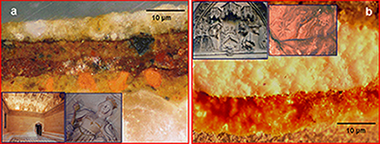
This work describes the use of a new dedicated laboratory-made micro X-ray diffraction system for detecting the phases present in cross-sections of artworks. As an example, the phases present in samples from gilding ceramics and stone sculptures from the heritage of Seville (Spain) were successfully detected using this new system, which takes advantage of various devices developed for synchrotron radiation, and is complemented by the information provided by other techniques.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1007/s00216-009-2836-3
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Light generation at the anomalous dispersion high energy range of a nonlinear opal film
Botey, M; Maymo, M; Molinos-Gomez, A; Dorado, L; Depine, RA; Lozano, G; Mihi, A; Miguez, H; Martorell, JOptics Express, 17 (2009) 12210-12216
Show abstract ▽
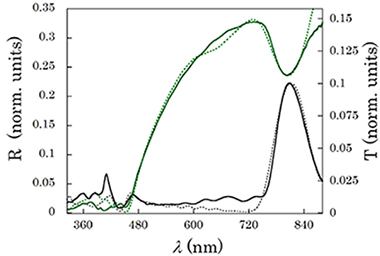
We study experimentally and theoretically light propagation and generation at the high energy range of a close-packed fcc photonic crystal of polystyrene spheres coated with a nonlinear material. We observe an enhancement of the second harmonic generation of light that may be explained on the basis of amplification effects arising from propagation at anomalous group velocities. Theoretical calculations are performed to support this assumption. The vector KKR method we use allows us to determine, from the linear response of the crystal, the behavior of the group velocity in our finite photonic structures when losses introduced by absorption or scattering by defects are taken into account assuming a nonzero imaginary part for the dielectric constant. In such structures, we predict large variations of the group velocity for wavelengths on the order or smaller than the lattice constant of the structure, where an anomalous group velocity behavior is associated with the flat bands of the photonic band structure. We find that a direct relation may be established between the group velocity reduction and the enhancement of a light generation processes such as the second harmonic generation we consider. However, frequencies for which the enhancement is found, in the finite photonic crystals we use, do not necessarily coincide with the frequencies of flat high energy bands.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1364/OE.17.012210
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Deposition of Al-Fe pillared bentonites and gold supported Al-Fe pillared bentonites on metallic monoliths for catalytic oxidation reactions
Martinez, LM; Dominguez, MI; Sanabria, N; Hernandez, WY; Moreno, S; Molina, R; Odriozola, JA; Centeno, MAApplied Catalysis A-General, 364 (2009) 166-173
Show abstract ▽

Al-Fe pillared bentonite and gold supported on Al-Fe pillared bentonite catalysts deposed on Fecralloy monoliths have been prepared, characterized and tested in two oxidation reactions: gaseous oxidation of CO and phenol oxidation in aqueous medium. The deposition of the solid on the metallic substrate does not alter its structural characteristics. The use of monoliths improves the activity in both reactions and offers the additional advantage to facilitate the separation of the catalyst from the reaction medium.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2009.05.046
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Chemical State of Nitrogen and Visible Surface and Schottky Barrier Driven Photoactivities of N-Doped TiO2 Thin Films
Romero-Gomez, P; Rico, V; Borras, A; Barranco, A; Espinos, JP; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 113 (2009) 13341-13351
Show abstract ▽
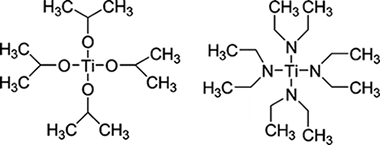
N-doped TiO2 thin films have been prepared by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition and by physical vapor deposition by adding nitrogen or ammonia to the gas phase. Different sets of N-doped TiO2 thin films have been obtained by changing the preparation conditions during the deposition. The samples have been characterized by X-ray diffraction, Raman, UV−vis spectroscopy, and X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (XPS). By changing the preparation conditions, different structures, microstructures, and degrees and types of doping have been obtained and some relationships have been established between these film properties and their visible light photoactivity. The N1s XP spectra of the samples are characterized by three main features, one tentatively attributed to Ti−N (i.e., nitride with a binding energy (BE) of 396.1 eV) and two others with BEs of 399.3 and 400.7 eV, tentatively attributed to nitrogen bonded simultaneously to titanium and oxygen atoms (i.e., Ti−N−O like species). By controlling the deposition conditions it is possible to prepare samples with only one of these species as majority component. It has been shown that only the samples with Ti−N−O like species show surface photoactivity being able to change their wetting angle when they are illuminated with visible light. The presence of these species and an additional complex structure formed by a mixture of anatase and rutile phases is an additional condition that is fulfilled by the thin films that also present photocatalytic activity with visible light (i.e., surface and Schottky barrier driven photoactivities). The relationships existing between the reduction state of the samples and the formation of Ti−N or Ti−N−O like species are also discussed.
Julio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1021/jp9024816
- ‹ anterior
- 396 of 422
- siguiente ›














