Artículos SCI
2009
2009
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
W,N-Codoped TiO2-Anatase: A Sunlight-Operated Catalyst for Efficient and Selective Aromatic Hydrocarbons Photo-Oxidation
Kubacka, A; Bachiller-Baeza, B; Colon, G; Fernandez-Garcia, MJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 113 (2009) 8553-8555
Show abstract ▽
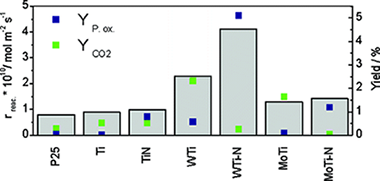
New W,N-doped TiO2 anatase-based materials are synthesized having both unprecedent high activity and selectivity in the gas-phase partial oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons using sunlight as excitation energy and molecular oxygen as oxidant.
Mayo, 2009 | DOI: 10.1021/jp902618g
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Integration of methanol steam reforming and combustion in a microchannel reactor for H2 production: A CFD simulation study
Arzamendi, G; Dieguez, PM; Montes, M; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JA; Gandia, LMCatalysis Today, 143 (2009) 25-31
Show abstract ▽

A computational fluid dynamics (CFD) study of the thermal integration of the steam reforming of methanol (SRM) and the combustion of methanol in a catalytic microchannel reactor is presented. This issue is of interest for in situ H2 production for portable power units based on low-temperature PEM fuel cells. Three-dimensional simulations have been carried out under relevant conditions for the SRM reaction that have shown that microreactors allow achieving complete methanol reforming and combustion at space velocities as high as 50,000 h−1, with selectivities for H2 above 99% at relatively low temperatures in the 270–290 °C range.
Mayo, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2008.09.034
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Cationic (V, Mo, Nb, W) doping of TiO2–anatase: A real alternative for visible light-driven photocatalysts
Kubacka, A; Colon, G; Fernandez-Garcia, MCatalysis Today, 143 (2009) 286-292
Show abstract ▽

In this article we investigate the structure–activity link of anatase-type Ti–M (M = V, Mo, Nb, and W) mixed oxides used for toluene photo-oxidation under sunlight-type excitation. An analysis of the local and long-range structural and electronic characteristics of the mixed oxides show that only structurally highly homogeneous anatase-type oxides with electronic properties exclusively leading to a band gap decrease drive to efficient visible light-driven photocatalysts. Within our microemulsion preparation method, this only occurs for Ti–V and Ti–W series of samples. The isoelectronic (V4+) substitution of Ti4+ ions at the anatase lattice is characterized by a low solubility limit (ca. 2.5 at. %), and drives to a limited modification of the band gap and to a moderate enhancement of the photo-activity with respect to bare titania reference systems. W presence at anatase cation positions occurs with concomitant presence of cation vacancies derived by the charge imbalance between the W6+ and Ti4+ species. A unique W-vacancy local arrangement is detected by the structural characterization, leading to both an important band gap decrease and enhancement of the photo-activity upon sunlight excitation.
Mayo, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2008.09.028
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Wetting angles and photocatalytic activities of illuminated TiO2 thin films
Rico, V; Romero, P; Hueso, JL; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARCatalysis Today, 143 (2009) 347-354
Show abstract ▽

TiO2 thin films have been prepared by physical vapour deposition (PVD) and plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition (PECVD) to study the UV-induced photo-activity of this material. Wetting angle variations and photo-catalytic activity for the degradation of dyes upon UV illumination have been compared for thin films with different crystalline structure (amorphous, rutile and anatase), microstructure (columnar, compact, etc.) and porosities as estimated from the values of their refraction indices and their direct assessment with a quartz crystal monitor. The surface of the thin films became superhydrophilic upon UV light irradiation and then it recovered its original state by keeping the samples in the dark. Wetting angle decays follow very similar kinetics for amorphous and crystalline films, independently of their actual porosities. By contrast the photo-catalytic activity was very dependent on the crystalline structure of the films (anatase > rutile > amorphous) and on their porosities. The different behaviour depicted by the films with regard to these two properties suggests that they respond to different though related mechanisms and that they cannot be considered as equivalent when trying to prove the photo-activity of TiO2.
Mayo, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2008.09.037
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
High deposition rates of uniform films in tetramethylsilane-based plasmas generated by elementary microwave sources in matrix configuration
Latrasse, L; Lacoste, A; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Bes, A; Rayar, M; Pelletier, JSurface and Coatings Technology, 203 (2009) 2343-2349
Show abstract ▽
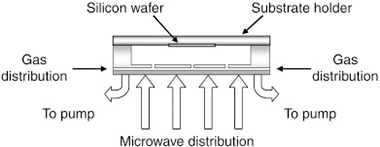
Plasma scaling up can be achieved by distributing elementary microwave plasma sources on planar rectangular networks. These so-called matrix plasmas can generate uniform sheets of plasma over a wide argon pressure range, from 7.5 to 750 Pa, with densities between 1012 and 1013 cm− 3. In order to estimate the capabilities of matrix plasmas for PACVD processing in terms of deposition rate and uniformity, SiOCH and SiNCH films were deposited using TMS (tetramethylsilane), as the organic gas precursor of silicon, mixed with oxygen or nitrogen flows. Plasmas of O2 / TMS and N2 / TMS gas mixtures can be sustained between 5 and 25 Pa. Variations in the deposition rate as a function of microwave power and nitrogen partial pressure are reported. Thickness uniformity of SiOCH and SiNCH films was measured across a silicon wafer. The obtained deposition rates exceed 1.3 μm/min and the films present a uniformity better than 5% on 75 mm diameter silicon wafers. Composition of the films has also been analyzed by XPS as a function of process parameters: microwave input power, composition of gas mixture, and N2 partial pressure. In particular, these analyses have shown a very low yield of nitrogen incorporation when using N2 gas as nitrogen precursor and high Si and Si–Si bonding contents in the films, probably due to a strong fragmentation of the TMS precursor in the high density plasma.
Mayo, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2009.02.121
- ‹ anterior
- 399 of 422
- siguiente ›














