Artículos SCI
2009
2009
Materiales Coloidales
M-Doped Al2TiO5 (M=Cr, Mn, Co) Solid Solutions and their Use as Ceramic Pigments
Dondi, M; Lyubenova, TS; Carda, JB; Ocaña, MJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 92 (2009) 1972-1980
Show abstract ▽
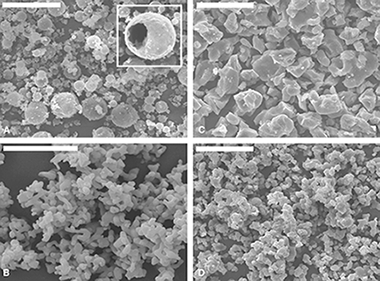
New ceramic pigments based on the tialite (Al2TiO5) structure, doped with Co (pink), Cr (green), or Mn (brown), were prepared through the pyrolysis of aerosols followed by calcination of the obtained powders at 1400°C. The expected decomposition of Al2TiO5 into a mixture of Al2O3 and TiO2 on refiring was inhibited by Cr-doping and also by co-doping with Mg the Mn- or Co-doped samples. Microstructure and phase evolution during pigment preparation were monitored by scanning electron microscopy and XRPD. Unit cell parameters of tialite were determined by Rietveld refinement of the X-ray diffraction patterns, revealing in all cases the formation of solid solutions where the solubility of dopants in the Al2TiO5 lattice followed the trend Co<Mn<Cr. The valence state and possible location of dopants in the tialite lattice were investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectra and diffuse reflectance spectroscopies, which suggested the presence of Cr3+ ions in a large interstitial site of the tialite lattice with a distorted octahedral geometry, and of Mn3+ and Co2+ ions in the Al3+ octahedral sites of the tialite lattice in the former case, and in both Al3+ and Ti4+ octahedral sites in the latter. Testing the ceramic glazes assessed the technological behavior of pigments, which found that the color stability was reasonably good for the Mn-doped tialite and the Cr-doped pigment, although the latter suffered a small loss of green hue. The Co-doped pigment was found to be not stable in glazes, undergoing a cobalt-leaching effect.
Junio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2009.03172.x
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Chemical Reactions in 2D: Self-Assembly and Self-Esterification of 9(10),16-Dihydroxypalmitic Acid on Mica Surface
Heredia-Guerrero, JA; San-Miguel, MA; Sansom, MSP; Heredia, A; Benitez, JJLangmuir, 25 (2009) 6869-6874
Show abstract ▽
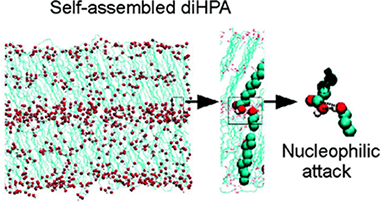
9(10),16-Dihydroxypalmitic acid (diHPA) is a particularly interesting polyhydroxylated fatty acid (1) because it is the main monomer of cutin, the most abundant biopolyester in nature, and (2) because the presence of a terminal and a secondary hydroxyl group in midchain positions provides an excellent model to study their intermolecular interactions in a confined phase such as self-assembled layers. In this study we have combined atomic force microscopy (AFM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FT-IR) spectroscopy, as well as molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to conclude that the self-assembling of diHPA molecules on mica is a layer by layer process following a Brunauer−Emmett−Teller (BET) type isotherm and with the first layer growing much faster than the rest. Interactions between secondary hydroxyls reinforce the cohesive energy of the monolayer, while the presence of the terminal hydroxyl group is necessary to trigger the multilayered growth. Besides, XPS and ATR-FT-IR spectroscopies clearly indicate that spontaneous self-esterification occurs upon self-assembling. The esterification reaction is a prerequisite to propose a self-assembly route for the biosynthesis of cutin in nature. Molecular dynamics simulations have shown that internal molecular reorganization within the self-assembled layers provides the appropriate intermolecular orientation to facilitate the nucleophilic attack and the release of a water molecule required by the esterification reaction.
Junio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1021/la9001412
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Growth of Crystalline TiO2 by Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
Borras, A; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Widmer, R; Rico, VJ; Justo, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARCrystal Growth & Design, 9 (2009) 2868-2876
Show abstract ▽

TiO2 thin films in the form of anatase have been prepared by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) at 523 K as the substrate temperature and a low working pressure. The study of the microstructure and texture of the films at different stages of deposition show that their growth follows the Kolmogorov’s model developed to describe the evolution of crystalline films from a saturated homogeneous medium. An additional characteristic feature of the growth process by PECVD is the formation of different crystalline domains, particularly at low deposition rates. The effects of this parameter and of the characteristics of the substrate on the growing process are also addressed.
Junio, 2009 | DOI: 10.1021/cg9001779
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Molding with nanoparticle-based one-dimensional photonic crystals: a route to flexible and transferable Bragg mirrors of high dielectric contrast
Calvo, ME; Sobrado, OS; Lozano, G; Miguez, HJournal of Materials Chemistry, 19 (2009) 3144-3148
Show abstract ▽
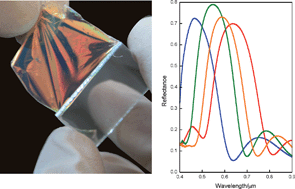
Self-standing, flexible Bragg mirror films of high refractive index contrast and showing intense and wide Bragg peaks are herein presented. Nanoparticle-based one-dimensional photonic crystals are used as templates to infiltrate a polymer, which provides the multilayer with mechanical stability while preserving the dielectric contrast existing in the mold. Such films can be lifted off the substrate and used to coat another surface of arbitrary shape.
Mayo, 2009 | DOI: 10.1039/B902090J
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
W,N-Codoped TiO2-Anatase: A Sunlight-Operated Catalyst for Efficient and Selective Aromatic Hydrocarbons Photo-Oxidation
Kubacka, A; Bachiller-Baeza, B; Colon, G; Fernandez-Garcia, MJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 113 (2009) 8553-8555
Show abstract ▽
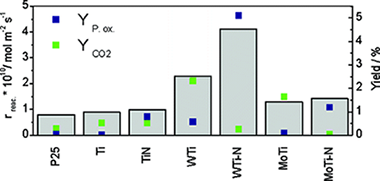
New W,N-doped TiO2 anatase-based materials are synthesized having both unprecedent high activity and selectivity in the gas-phase partial oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons using sunlight as excitation energy and molecular oxygen as oxidant.
Mayo, 2009 | DOI: 10.1021/jp902618g
- ‹ anterior
- 398 of 422
- siguiente ›














