Artículos SCI
2009
2009
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Self-lubricating Ti–C–N nanocomposite coatings prepared by double magnetron sputtering
Martinez-Martinez, D; Lopez-Cartes, C; Justo, A; Fernandez, A; Sanchez-Lopez, JCSolid State Sciences, 11 (2009) 660-670
Show abstract ▽
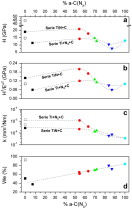
This paper is devoted to the development of Ti(C,N)-based nanocomposite protective coatings consisting of nanocrystals of a hard phase (TiN or TiCxNy) embedded in an amorphous carbon-based matrix (a-C or a-CNx). The objective here is the achievement of a good compromise between the mechanical and tribological properties by the appropriate control of the hard/soft phase ratio and the microstructural characteristics of the film. To achieve this purpose, dual magnetron sputtering technique was employed following two different strategies. In the first one, we use Ti and graphite targets and Ar/N2 gas mixtures, while in the second case, TiN and graphite targets are sputtered in an Ar atmosphere. By changing the sputtering power applied to each magnetron, different sets of samples are prepared for each route. The effect of the bias voltage applied to the substrate is also studied in some selected cases. The mechanical and tribological properties of the films are characterized and correlated with the microstructure, crystallinity and phase composition. The establishment of correlations enables the development of advanced coatings with tailored mechanical and tribological properties for desired applications.
Marzo, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2008.10.017
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Cutin synthesis: A slippery paradigm
Heredia, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Dominguez, E; Benitez, JJBiointerphases, 4 (2009) P1-P3
Show abstract ▽
Despite its biological importance, the mechanism of construction of cutin, the polymer matrix of plant cuticles, has not yet been elucidated. Recently, progress on lipid barrier formation of polymers such as cutin and suberin has been recently reviewed by Pollard et al. In their review the authors state that the ubiquitous cutin is the least understood of the plant extracellular polymers and that major questions about cutin structure and its macromolecular assembly remain to be resolved. At the time this paper was being published our research group has developed a new hypothesis on plant cutin synthesis.
Marzo, 2009 | DOI: 10.1116/1.3063816
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Study by grazing incident diffraction and surface spectroscopy of amalgams from ancient mirrors
Herrera, LK; Duran, A; Franquelo, ML; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Espinos, JP; Rubio-Zuazo, J; Castro, GR; Justo, A; Perez-Rodriguez, JLCentral European Journal of Chemistry, 7 (2009) 47-53
Show abstract ▽

Characterization of four amalgam surfaces, with different alteration degrees from Andalusia historical mirrors, has been carried out by grazing-incidence X-ray diffraction (GIXRD), and other spectroscopic techniques (SEM/EDX, XPS, and REELS). The combination of all these techniques allows determining the corrosion state of the amalgams. The results show that the amalgams are composed in all cases of a binary alloy of tin and mercury. As mercury has high vapour pressure at RT, it slowly segregates and eventually evaporates, it leaves finely divided particles of tin that easily can be oxidize, forming tin monoxide (SnO) and tin dioxide (SnO2). In one of the samples, most of the amalgam remains unoxidized, since Hg0.1Sn0.9 and metallic Sn phases are the major components; in two other samples, Hg0.1Sn0.9 and Sn phases are not detected while SnO2 and SnO phases appear. Finally, in the last studied sample, only SnO2 phase is detected. The surface analyses of these samples by XPS show that, for most of them an unique chemical species (Sn4+) is found.
Marzo, 2009 | DOI: 10.2478/s11532-008-0089-1
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Pillared clays with Al–Fe and Al–Ce–Fe in concentrated medium: Synthesis and catalytic activity
Sanabria, NR; Centeno, MA; Molina, R; Moreno, SApplied Catalysis A-General, 356 (2009) 243-249
Show abstract ▽

This paper proposes a new methodology for the modification of clays with the mixed Al–Fe and Al–Ce–Fe systems, which involves the synthesis of solid polymeric precursors and their use as pillaring agents in the modification of clays. The process of intercalation of clay with Al13, Al13 + Fe and Al13 + Ce + Fe nitrate was performed using ultrasound. The pillaring agents Al13, Al13 + Fe and Al13 + Ce + Fe were characterized by XRF, XRD, SEM and 27Al NMR techniques, and pillared clays were characterized by XRF, XRD and N2 adsorption to 77 K. The catalytic properties of pillared clays were evaluated using catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of phenol in dilute aqueous medium, demonstrating activity comparable to that of solids modified by the conventional method.
Marzo, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2009.01.013
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Water plasmas for the revalorisation of heavy oils and cokes from petroleum refining
Hueso, JL; Rico, VJ; Cotrino, J; Jimenez-Mateos, JM; Gonzalez-Elipe, AREnvironmental Science & Technology, 43 (2009) 2557-2562
Show abstract ▽

This work investigates the possibility of using plasmas to treat high boiling point and viscous liquids (HBPVL) and cokes resulting as secondary streams from the refining of oil. For their revalorisation, the use of microwave (MW) induced plasmas of water is proposed, as an alternative to more conventional processes (i.e., catalysis, pyrolysis, combustion, etc.). As a main result, this type of energetic cold plasma facilitates the conversion at room temperature of the heavy aromatic oils and cokes into linear hydrocarbons and synthesis gas, commonly defined as syngas (CO + H2 gas mixture). The exposure of the coke to this plasma also facilitates the removal of the sulfur present in the samples and leads to the formation on their surface of a sort of carbon fibers and rods network and new porous structures. Besides, optical emission measurements have provided direct evidence of the intermediates resulting from the fragmentation of the heavy oils and cokes during their exposure to the water plasma. Furthermore, the analysis of the mass spectra patterns suggests a major easiness to break the aromatic bonds mainly contained in the heavy oils. Therefore, an innovative method for the conversion of low value residues from oil-refining processes is addressed.
Marzo, 2009 | DOI: 10.1021/es900236b
- ‹ anterior
- 403 of 422
- siguiente ›














