Artículos SCI
2009
2009
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Redox chemistry of gold in a Au/FeOx/CeO2 CO oxidation catalyst
Penkova, A; Chakarova, K; Laguna, OH; Hadjiivanov, K; Saria, FR; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JACatalysis Communications, 10 (2009) 1196-1202
Show abstract ▽

Calcination and evacuation of a Au/FeOx/CeO2 catalyst at 573 K leads to reduction of the deposited gold to metal. This metal state is stable under oxygen and only at 573 K some metal atoms are oxidized to Auδ+ sites (Au+ cations situated on metal gold particles). However, even at room temperature, gold is readily oxidized in a CO + O2 mixture producing, in addition to the Auδ+ sites, some isolated Au+ cations.
Marzo, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.catcom.2009.01.014
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Control over the Structural and Optical Features of Nanoparticle-Based One-Dimensional Photonic Crystals
Calvo, ME; Sanchez-Sobrado, O; Colodrero, S; Miguez, HLangmuir, 25 (2012) 2443-2448
Show abstract ▽
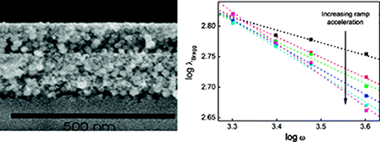
Herein we present a detailed analysis of the effect of the spin-coating protocol over the optical properties of nanoparticle-based one-dimensional photonic crystals. Based on these results, we provide a reliable synthetic route to attain high-quality porous multilayers in which the effect of imperfections is minimized and whose Bragg diffraction can be precisely tuned over the entire visible and near-infrared spectrum. We present a systematic study of the effect of the acceleration ramp and final rotation speed over the structural and optical quality of these materials. This allows us to relate the structural variations observed with the different relative importance of fluid flow and solvent evaporation on the thinning of each layer in the stack for the different deposition conditions employed.
Febrero, 2009 | DOI: 10.1021/la8030057
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
WC/a-C nanocomposite thin films: Optical and electrical properties
Abad, MD; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Cusnir, N; Sanjines, RJournal of Applied Physics, 105 (2009) 033510
Show abstract ▽

WC/amorphous carbon (a-C) thin films were deposited by dual magnetron sputtering from individual WC and graphite targets. The influence of film composition and microstructure on the optical and electrical properties was investigated. As evidenced by x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and grazing angle x-ray diffraction measurements, the WC/a-C films are composite materials made of hexagonal W2C and/or cubic β-WC1−X nanocrystallites embedded in (a-C) matrix. The optical properties were studied by spectroscopic ellipsometry and the electrical resistivity was measured by the van der Pauw method between 20 and 300 K. Both the optical and the electrical properties of the WC/a-C films are correlated with the chemical composition and microstructure evolution caused by a-C addition. The optical properties of W2C/a-C and β-WC1−x/a-C films with a-C content ≤ 10 at. % are explained by modeling their dielectric functions by a set of Drude–Lorentz oscillators. Further increase in a-C content leads only to the formation of β-WC1−x/a-C nanocomposite structures and their optical properties progressively evolve to those of a-C single phase. The electrical resistivity as a function of the temperature of all the films exhibits a negative temperature coefficient of resistivity. Theoretical fitting using the grain-boundary scattering model shows that the transport properties are mainly limited by the grain size and electron mean free path parameters.
Febrero, 2009 | DOI: 10.1063/1.3060717
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Fabrication of ordered crystalline zirconium nanoporous membranes by an one-step procedure
Marquez, F; Morant, C; Pirota, KR; Borras, A; Sanz, JM; Elizalde, ENano Today, 4 (2009) 21-26
Show abstract ▽
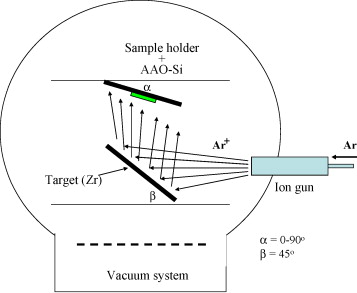
Crystalline porous zirconium membranes were obtained by physical vapor deposition on AAO templates at room temperature. These membranes were found to have similar hexagonal nanohole arrays as the template and high crystallinity. The pore size of the synthesized metallic membranes could be controlled during the synthesis through appropriate parameters in the experimental procedure.
Febrero, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.nantod.2008.10.012
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Synthesis, Rietveld Analysis, and Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance of X2-Sc2SiO5
Alba, MD; Chain, P; Gonzalez-Carrascosa, TJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 92 (2009) 487-490
Show abstract ▽
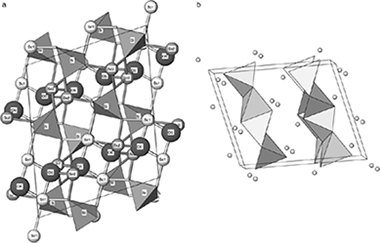
Compounds containing rare earths are of increasing technological interest especially because of their unique mechanical, magnetic, electrical, and optical properties. Among them, rare earth oxyorthosilicates are attractive scintillators for γ- and X-ray spectroscopy and detection. However, there are many structural aspects of those compounds that are not clear. In this research, the structure parameters for Sc2Si2O5, X2-polymorph, have been refined from powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) data and the 29Si MAS NMR spectrum is reported for the first time. X2-Sc2SiO5 polymorph was synthesized by the sol–gel method and characterized by XRD and 29Si MAS NMR. The XRD pattern was indexed in a monoclinic unit cell with space group I2/c; the resulting unit cell parameters were a=9.9674(2) Å, b=6.4264(9) Å, c=12.0636(2) Å, and β=103.938(1)°. The 29Si MAS NMR spectrum showed a unique signal at −79.5 ppm, compatible with the unique Si crystallographic site in the unit cell. Finally, the band valence method has been applied to the calculation of a “shift parameter,” which is correlated with the NMR chemical shift.
Febrero, 2009 | DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2008.02877.x
- ‹ anterior
- 404 of 422
- siguiente ›














