Artículos SCI
2009
2009
Materiales Coloidales - Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Porous One-Dimensional Photonic Crystals Improve the Power-Conversion Efficiency of Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
Colodrero, S; Mihi, A; Haggman, L; Ocana, M; Boschloo, G; Hagfeldt, A; Miguez, HAdvanced Materials, 21 (2009) 764-770
Show abstract ▽
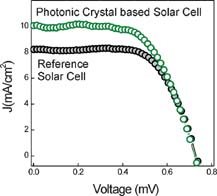
A device for solar-energy conversion was introduced in which a porous and highly reflecting 1D photonic crystal (1D PC) was coupled to a dye-sensitized nanocrystals anatase (NC-TiO2) electrode. The results show that the transparency of the PC-based dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSC) in the visible range of the electromagnetic spectrum is very similar to that of the reference cell. The multilayer whose photonic bandgap has a larger overlap with the absorption band of the ruthenium dye, gives rise to a larger enhancement of the photocurrent. It is also seen that the porous 0.5μm thick PC, whose deleterious effect is compensated by the large increment in photocurrent. The spectral photoelectric response of the cell clearly shows the effect that coupling to a PC has on the current photogenerated in the dye-sensitized electrode.
Febrero, 2009 | DOI: 10.1002/adma.200703115
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Control over the Structural and Optical Features of Nanoparticle-Based One-Dimensional Photonic Crystals
Calvo, ME; Sanchez-Sobrado, O; Colodrero, S; Miguez, HLangmuir, 25 (2012) 2443-2448
Show abstract ▽
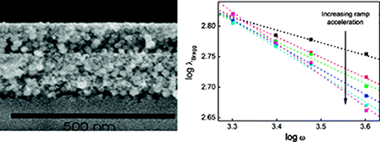
Herein we present a detailed analysis of the effect of the spin-coating protocol over the optical properties of nanoparticle-based one-dimensional photonic crystals. Based on these results, we provide a reliable synthetic route to attain high-quality porous multilayers in which the effect of imperfections is minimized and whose Bragg diffraction can be precisely tuned over the entire visible and near-infrared spectrum. We present a systematic study of the effect of the acceleration ramp and final rotation speed over the structural and optical quality of these materials. This allows us to relate the structural variations observed with the different relative importance of fluid flow and solvent evaporation on the thinning of each layer in the stack for the different deposition conditions employed.
Febrero, 2009 | DOI: 10.1021/la8030057
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Phase separation of carboxylic acids on graphite surface at submonolayer regime
Alba, MD; Bickerstaffe, AK; Castro, MA; Clarke, SM; Medina, S; Millan, C; Orta, MM; Pavon, E; Perdigon, ACThe European Physical Journal Special Topics, 167 (2009) 151-156
Show abstract ▽
Mixing behaviour of solid crystalline monolayers adsorbed onto graphite from different mixtures of undecanoic and dodecanoic acids at submonolayer coverage has been investigated. X-ray diffraction measurements have been collected from a variety of compositions as a function of temperature. An extensive phase separation is found for all the compositions – the scattering patterns characteristic of the pure material crystalline structures being preserved across the entire composition range. The temperature dependence of the monolayer melting points and their depression is also clearly indicative of separation of the two surface components, in clear contrast to that expected if the two carboxylic acids mixed ideally in the monolayer.
Febrero, 2009 | DOI: 10.1140/epjst/e2009-00951-6
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Preferential Adsorption from Binary Mixtures on Graphite: The n-Decane−n-Heptan-1-ol System
Alba, MD; Castro, MA; Clarke, S; Medina, S; Messe, L; Millan, C; Orta, MM; Perdigon, ACJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 113 (2009) 3176-3180
Show abstract ▽
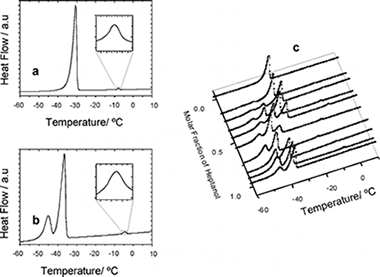
The competitive adsorption of n-decane and n-heptan-1-ol adsorbed from the binary liquid mixture onto graphite has been studied using differential scanning calorimetry, incoherent quasielastic neutron scattering, and 1H and 2H nuclear magnetic resonance. A solid monolayer is identified at all bulk solution compositions with a melting temperature that varies with bulk composition in a manner resembling the bulk behavior. Incoherent elastic neutron scattering, IQNS, and nuclear magnetic resonance, NMR, data indicate that decane is preferentially adsorbed onto the surface over most of the composition range, heptanol being the principal surface component only at very high heptanol concentrations. NMR is proved, for the first time, to be an efficient tool to provide independent information on each component of the system.
Febrero, 2009 | DOI: 10.1021/jp8072014
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Synthesis of MCM-22 zeolites of different Si/Al ratio and their structural, morphological and textural characterisation
Delitala, C; Alba, MD; Becerro, AI; Delpiano, D; Meloni, D; Musu, E; Ferino, IMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 118 (2009) 1-10
Show abstract ▽
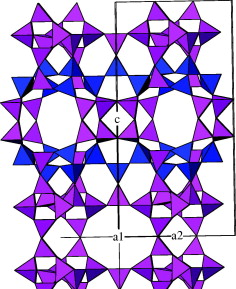
MCM-22 zeolites with Si/Al in the 9–46 range were synthesised in rotating autoclave and characterised by X-ray diffraction, 1H, 29Si and 27Al magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance, scanning electron microscopy and nitrogen physisorption. For the Si/Al = 21, 30 and 46 samples both X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy revealed the crystallisation of pure MCM-22. Besides the latter, crystals of ferrierite also formed during the synthesis of the Si/Al = 9 sample. Based on the 1H MAS NMR spectra of dehydrated samples, the different proton species present on the MCM-22 samples were determined and quantified. Information about the incorporation of Al ions into the zeolite framework, as well as on the preferential crystallographic sites occupied in dependence on the Si/Al ratio of the sample, was obtained by 27Al MAS NMR spectroscopy. From 29Si MAS NMR spectra, differences in the degree of crystallinity of the samples were assessed, the results being in agreement with the diffraction data. Nitrogen physisorption runs revealed the microporous nature of the adsorbents, with a supermicropore to ultramicropore volume ratio in good agreement, for the best crystallised samples, with the porous structure with supercages and sinusoidal channels of the ideal MCM-22 crystal.
Febrero, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2008.07.047
- ‹ anterior
- 405 of 422
- siguiente ›














