Artículos SCI
2009
2009
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Preferential Adsorption from Binary Mixtures on Graphite: The n-Decane−n-Heptan-1-ol System
Alba, MD; Castro, MA; Clarke, S; Medina, S; Messe, L; Millan, C; Orta, MM; Perdigon, ACJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 113 (2009) 3176-3180
Show abstract ▽
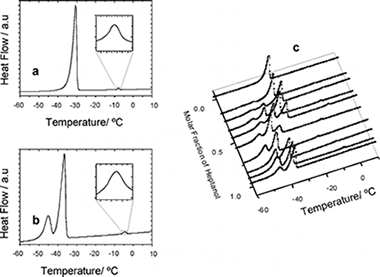
The competitive adsorption of n-decane and n-heptan-1-ol adsorbed from the binary liquid mixture onto graphite has been studied using differential scanning calorimetry, incoherent quasielastic neutron scattering, and 1H and 2H nuclear magnetic resonance. A solid monolayer is identified at all bulk solution compositions with a melting temperature that varies with bulk composition in a manner resembling the bulk behavior. Incoherent elastic neutron scattering, IQNS, and nuclear magnetic resonance, NMR, data indicate that decane is preferentially adsorbed onto the surface over most of the composition range, heptanol being the principal surface component only at very high heptanol concentrations. NMR is proved, for the first time, to be an efficient tool to provide independent information on each component of the system.
Febrero, 2009 | DOI: 10.1021/jp8072014
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Porosity and microstructure of plasma deposited TiO2 thin films
Borras, A; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Garrido-Molinero, J; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 118 (2009) 314-324
Show abstract ▽

The microstructure of TiO2 thin films prepared by plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition has been assessed by using water adsorption–desorption isotherms measured by means of a quartz crystal monitor (QCM). Thin films have been deposited by using titanium tetraisopropoxide as a precursor and by changing different experimental parameters of the deposition procedure such as temperature of the substrate, pressure, and gas composition in the plasma. The films were characteristic of different microstructures that, according to their scanning electron micrographs, have been categorized as columnar, homogeneous and crystalline. They also have different refraction indices with values between 1.95 and 2.41. Water and toluene adsorption isotherms have been measured by means of a QCM monitor for the films heated in vacuum to remove the water previously adsorbed in their pores. The analysis of the adsorption-desorption isotherms by means of the so called “t-plots” and the determination of the pore size distribution curves rendered that the three kinds of microstructures presented different kinds of isotherms and water adsorption behaviours. Columnar films consisted of micro- and meso-pores had a very high adsorption hystheresis at low pressures. Homogeneous films only had micropores and presented no adsorption hystheresis. Crystalline films consisted of both micro- and meso-pores but had no adsorption hystheresis at low pressures. A zone scheme has been proposed to account for the microstructure of the films depending on the plasma conditions utilized. The implications of the different water adsorption behaviours of the films for the determination of their refraction indices are discussed.
Febrero, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2008.09.002
Materiales Coloidales - Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Experimental Demonstration of the Mechanism of Light Harvesting Enhancement in Photonic-Crystal-Based Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
Colodrero, S; Mihi, A; Anta, JA; Ocaña, M; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 113 (2012) 1150-1154
Show abstract ▽
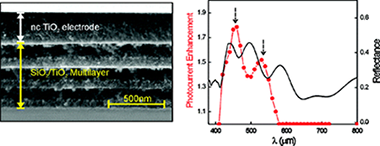
Herein, we report an experimental analysis of the photogenerated current of very thin and uniform dye-sensitized nanocrytalline titanium oxide (nc-TiO2) electrodes coupled to high-quality one-dimensional photonic crystals. The effect of well-defined optical absorption resonances are detected both in optical spectroscopy and photogenerated current experiments, a clear correspondence between them being established. Our study demonstrates that light trapping within absorbing electrodes is responsible for the absorption enhancement that has previously been reported and unveils the mechanism behind it. We prove that this effect improves significantly the power conversion efficiency of very thin electrodes.
Enero, 2009 | DOI: 10.1021/jp809789s
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Influence of the microstructure on the mechanical and tribological behavior of TiC/a-C nanocomposite coatings
Martinez-Martinez, D; Lopez-Cartes, C; Fernandez, A; Sanchez-Lopez, JCThin Solid Films, 517 (2009) 1662-1671
Show abstract ▽
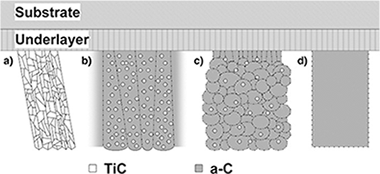
The performance of protective thin films is clearly influenced by their microstructure. The objective of this work is to study the influence of the structure of TiC/a-C nanocomposite coatings with a-C contents ranging from ~ 0% to 100% on their mechanical and tribological properties measured by ultramicroindentation and pin-on-disks tests at ambient air, respectively. The microstructure evolves from a polycrystalline columnar structure consisting of TiC crystals to an amorphous and dense TiC/a-C nanocomposite structure when the amount of a-C is increased. The former samples show high hardness, moderate friction and high wear rates, while the latter ones show a decrease in hardness but an improvement in tribological performance. No apparent direct correlation is found between hardness and wear rate, which is controlled by the friction coefficient. These results are compared to the literature and explained according to the different film microstructures and chemical bonding nature. The film stress has also been measured at the macro and micro levels by the curvature and Williamson–Hall methods respectively. Other mechanical properties of the coating such as resilience and toughness were evaluated by estimating the H3/E⁎2 and H/E⁎ ratios and the percentage of elastic work (We). None of these parameters showed a tendency that could explain the observed tribological results, indicating that for self-lubricant nanocomposite systems this correlation is not so simple and that the assembly of different factors must be taken into account.
Enero, 2009 | DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2008.09.091
Materiales Avanzados
Application of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in the search for and characterization of raw materials of interest in ceramics and glass
Garzon, E; Garcia, IG; Ruiz-Conde, A; Sanchez-Soto, PJBoletín de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio, 48 (2009) 39-44
Show abstract ▽
- ‹ anterior
- 406 of 422
- siguiente ›














