Artículos SCI
2022
2022
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Ultrathin Plasma Polymer Passivation of Perovskite Solar Cells for Improved Stability and Reproducibility
Obrero-Perez, JM; Contreras-Bernal, L; Nuñez-Galvez, F; Castillo-Seoane, J; Valadez-Villalobos, K; Aparicio, FJ; Anta, JA; Borras, A; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Barranco, AAdvanced Energy Materials, (2022) 2200812
Show abstract ▽
Despite the youthfulness of hybrid halide perovskite solar cells, their efficiencies are currently comparable to commercial silicon and have surpassed quantum-dots solar cells. Yet, the scalability of these devices is a challenge due to their low reproducibility and stability under environmental conditions. However, the techniques reported to date to tackle such issues recurrently involve the use of solvent methods that would further complicate their transfer to industry. Herein a reliable alternative relaying in the implementation of an ultrathin plasma polymer as a passivation interface between the electron transport layer and the hybrid perovskite layer is presented. Such a nanoengineered interface provides solar devices with increased long-term stability under ambient conditions. Thus, without involving any additional encapsulation step, the cells retain more than 80% of their efficiency after being exposed to the ambient atmosphere for more than 1000 h. Moreover, this plasma polymer passivation strategy significantly improves the coverage of the mesoporous scaffold by the perovskite layer, providing the solar cells with enhanced performance, with a champion efficiency of 19.2%, a remarkable value for Li-free standard mesoporous n-i-p architectures, as well as significantly improved reproducibility.
Julio, 2022 | DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202200812
Reactividad de Sólidos
Albero: An alternative natural material for solar energy storage by the calcium-looping process
Moreno, V; Arcenegui-Troya, J; Sanchez-Jimenez, P; Perejon, A; Chacartegui, R; Valverde, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAChemical Engineering Journal, 440 (2022) 135707
Show abstract ▽
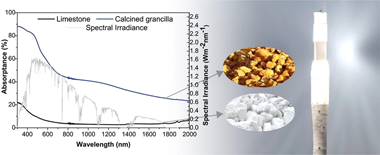
Large-scale thermochemical energy storage (TCES) is gaining relevance as an alternative to current thermal energy storage systems in Concentrated Solar Power plants. Among the different systems, the reversible reaction between CaO and CO2 stands out due to the wide availability and low cost of the raw material: limestone. Direct solar absorption of the storage media would improve the efficiency of solar-to-thermal energy storage due to reduced thermal transfer barriers, but the solar optical absorption of CaCO3 is poor. In this work, we propose the use of a Ca-rich calcarenite sedimentary rock so-called albem as an alternative to limestone. We demonstrate that this reddish material exhibits an average solar absorptance that is approximately ten times larger than limestone. Moreover, the multicycle carbonation/calcination performance under different experimental conditions has been studied by thermogravimetry, and similar values to those exhibited for limestone have been obtained. Besides, the material is cheap (6 Elton), and simulations showed that the use of this material would significantly improve the overall CaL-CSP efficiency at the industrial level.
Julio, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.135707
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photocatalytic oxidation of pollutants in gas-phase via Ag3PO4-based semiconductor photocatalysts: Recent progress, new trends, and future perspectives
Y. Naciri; A. Hsini; A. Bouziani; R. Djellabi; Z. Ajmal; M. Laabd; J.A. Navío; A. Mills; C.L. Bianchi; H.Li; B. Bakiz; A. AlbourineCritical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 52 (2022) 2339-2382
Show abstract ▽
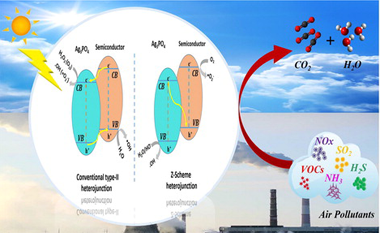
Air pollution has become a significant challenge for both developing and developed nations. due to its close association with numerous fatal diseases such as cancer, respiratory, heart attack, and brain stroke. Over recent years, heterogeneous semiconductor photocatalysis has emerged as an effective approach to air remediation due to the ease of scale-up, ready application in the field, use of solar light and ready availability of a number of different effective photocatalysts. To date, most work in this area has been conducted using UV-absorbing photocatalysts, such as TiO2 and ZnO; However, recent studies have revealed Ag3PO4 as an attractive, visible-light-absorbing alternative, with a bandgap of 2.43 eV. In particular, this material has been shown to be an excellent photocatalyst for the removal of many types of pollutants in the gas phase. However, the widespread application of Ag3PO4 is restricted due to its tendency to undergo photoanodic corrosion and the poor reducing power of its photogenerated conductance band electrons, which are unable to reduce O2 to superoxide •O2 −. These limitations are critically evaluated in this review. In addition, recent studies on the modification of Ag3PO4 via combination with the conventional heterojunctions or Z-scheme junctions, as well as the photocatalytic mechanistic pathways for enhanced gas-pollutants removal, are summarized and discussed. Finally, an overview is given on the future developments that are required in order to overcome these challenges and so stimulate further research into this promising field.
Julio, 2022 | DOI: 10.1080/10643389.2021.1877977
Reactividad de Sólidos
Thermal behavior of ammonium fluorosilicates complexes: Obtaining and kinetic analysis
Resentera, AC; Perejon, A; Esquivel, MR; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Rodriguez, MHChemical Engineering Research amd Design, 182 (2022) 490-501
Show abstract ▽
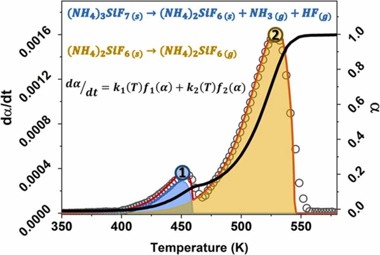
In this work, a mixture of (NH4)3SiF7/(NH4)2SiF6 powders was obtained as a by-product of the Li extraction process from alpha-spodumene aluminosilicate with NH4HF2. The thermal behavior of the powders was analyzed by non-isothermal thermogravimetric experiments. The kinetic parameters that describe the processes involved were obtained using mathematical deconvolution, Friedman's method, combined kinetic analysis, and nonlinear regression optimization. The results show that the process occurs in two partially overlapping steps, the thermal decomposition of (NH4)3SiF7 into (NH4)2SiF6 and the subsequent sublimation of (NH4)2SiF6. The apparent activation energies were 72.6 and 79.8 kJ/ mol for steps 1 and 2, respectively. The apparent pre-exponential factors were 1.19 x 106 and 2.50 x 105 s-1, respectively. The kinetic models indicated that Step 1 follows an A2 model, while Step 2 follows an F0 model. Finally, the resulting kinetic parameters allowed the reconstruction of the original experimental curves and obtaining predictions of curves recorded under other heating programs.
Junio, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cherd.2022.04.021
Materiales Avanzados
Thermal behaviour of the different parts of almond shells as waste biomass
Garzon, E; Arce, C; Callejon-Ferre, AJ; Perez-Falcon, JM; Sanchez-Soto, PJJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 147 (2022) 5023-5035
Show abstract ▽
The main aim of this study is to investigate the thermal behaviour of the different parts of almond shells produced in an almond industry as a waste biomass. For this purpose, several experiments have been conducted under laboratory conditions. After removing the mature almonds, the waste raw materials subject of this study were treated with distilled water (10 min) and separated in several parts. Taking into account their physical characteristics, they were: (a) complete shells: exocarp, mesocarp and endocarp without grinding (Sample C); (b) ground samples of complete shells, sieved under 0.2 mm (Sample M); (c) hard layers of the endocarp (Sample E); (d) internal layers of the endocarp (Sample I); and (e) mature drupes (Sample P) or skin, being constituted by the flexible part of green colour (fresh form) or yellow (after drying). The thermal behaviour of all these sample materials has been investigated using a laboratory furnace, with determination of ash contents and mass loss by progressive heating (120 min of holding time). Elemental and DTA-TG/DTG analyses of selected sample materials have been carried out. Although a complete study can be very complex, a first approach has been performed in this investigation. Results on thermal decomposition of this biomass waste have been presented to emphasize the main differences between sample materials of almond shells. These results have demonstrated the influence of several parameters, such as the particle size, and previous treatments in the thermal behaviour of the different parts of the almond shells, as showed in this investigation. Structural analysis of almond shells allowed to determine lignin, cellulose and hemicellulose. From the lignin content, it has been predicted the higher heating value (18.24 MJkg(-1)) of this waste as by-product of industrial interest. Other linear correlations to calculate this parameter have been applied with similar results in all these samples.
Junio, 2022 | DOI: 10.1007/s10973-021-10940-x
- ‹ anterior
- 56 of 420
- siguiente ›














