Artículos SCI
2022
2022
Reactividad de Sólidos
Predictions of polymer thermal degradation: relevance of selecting the proper kinetic model
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Arcenegui-Troya, J; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 147 (2022) 2335-2341 DOI: 10.1007/s10973-021-10649-x
Abstract
Making predictions, such as lifetime estimations, is one of the main objectives of kinetic studies. Thus, from conventional thermal analysis experiments, the behavior of polymeric materials under processing or application conditions, usually far away from those used in the laboratory experiments, could be estimated. Conventional prediction procedures usually make use of oversimplified equations based on simple approaches. One of the most common approaches is the assumption of a first, or n-order, kinetic model for the process. However, recent studies have shown, for a number of polymers, that random scission kinetic models are not only physically sound, but more reliable in terms of describing the degradation kinetics. In this paper, the consequences of selecting an erroneous kinetic model on lifetime predictions is discussed. It is demonstrated, using both simulated and experimental data, that any kinetic analysis of a chain scission driven reaction performed assuming a first-order model entails enormous deviations in predictions. This occurs despite the fact that the first-order kinetic model can fit experimental data from chain scission driven reactions with significant correlation coefficients, and even lead to a reasonably good reconstruction of the original experimental curves.
Febrero, 2022 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-021-10649-x
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Performance of AISI 316L-stainless steel foams towards the formation of graphene related nanomaterials by catalytic decomposition of methane at high temperature
Cazana, F; Latorre, N; Tarifa, P; Royo, CJ; Sebastian, V; Romeo, E; Centeno, MA; Monzon, ACatalysis Today, 383 (2022) 236-246 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2020.12.003
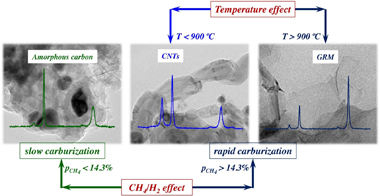
Abstract
This work explores the preparation of graphene-related materials (GRMs) grown on stainless steel foams via catalytic decomposition of methane (CDM). The main active phases for the reaction are the Fe nanoparticles segregated from the stainless-steel after the activation stage of the foam. The effect of the feed composition and reaction temperature has been studied in order to maximize the productivity, stability and selectivity to GRMs. The maximum productivity attained was 0.116 g(C)/g(foam) h operating at 950 degrees C with a feed ratio of CH4/H-2 = 3 (42.9 %CH4:14.3 %H-2). The carbonaceous nanomaterials (CNMs) obtained were characterized by X-Ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy and by transmission and scanning electron microscopy. The parameters of the kinetic model developed are directly related to the relevant stages of the process, including carburization, diffusion-precipitation and deactivation-regeneration. The balance among these sequential stages determines the overall performance of the activated foam. In conditions of rapid carburization of the Fe NPs (p(CH4) > 14 %), the productivity to CNMs is favoured, avoiding an initial deactivation of the active sites by fouling with amorphous carbon. After a rapid carburization, the selectivity to the different CNMs is governed by the ratio CH4/H-2, and mainly by the temperature. Thus, the formation of GRMs, mainly Few Layer Graphene (FLG) and even graphene, is favoured at temperatures above 900 degrees C. At lower temperatures, carbon nanotubes are formed.
Enero, 2022 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2020.12.003
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Enhanced catalytic activity and stability of nanoshaped Ni/CeO2 for CO2 methanation in micro-monoliths
Garcia-Moncada, N; Navarro, JC; Odriozola, JA; Lefferts, L; Faria, JACatalysis Today, 383 (2022) 205-215 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2021.02.014
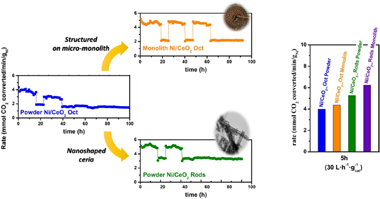
Abstract
Coupling inherently fluctuating renewable feedstocks to highly exothermic catalytic processes, such as CO2 methanation, is a major challenge as large thermal swings occurring during ON- and OFF- cycles can irreversible deactivate the catalyst via metal sintering and pore collapsing. Here, we report a highly stable and active Ni catalyst supported on CeO2 nanorods that can outperform the commercial CeO2 (octahedral) counterpart during CO2 methanation at variable reaction conditions in both powdered and mu-monolith configurations. The long-term stability tests were carried out in the kinetic regime, at the temperature of maximal rate (300 degrees C) using fluctuating gas hourly space velocities that varied between 6 and 30 L h- 1.gcat- 1. Detailed catalyst characterization by mu-XRF revealed that similar Ni loadings were achieved on nanorods and octahedral CeO2 (c.a. 2.7 and 3.3 wt. %, respectively). Notably, XRD, SEM, and HR-TEM-EDX analysis indicated that on CeO2 nanorods smaller NiClusters with a narrow particle size distribution were obtained (- 7 +/- 4 nm) when compared to octahedral CeO2 (- 16 +/- 13 nm). The fast deactivation observed on Ni loaded on commercial CeO2 (octahedral) was prevented by structuring the reactor bed on mu-monoliths and supporting the Ni catalyst on CeO2 nanorods. FeCrAlloy (R) sheets were used to manufacture a multichannel mu-monolith of 2 cm in length and 1.58 cm in diameter, with a cell density of 2004 cpsi. Detailed catalyst testing revealed that powdered and structured Ni/ CeO2 nanorods achieved the highest reaction rates, c.a. 5.5 and 6.2 mmol CO2 min- 1.gNi - 1 at 30 L h- 1.gcat- 1 and 300 degrees C, respectively, with negligible deactivation even after 90 h of fluctuating operation.
Enero, 2022 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2021.02.014
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Unravelling the role of Fe in trimetallic Fe-Cu-Pt/Al2O3 catalysts for CO-PROX reaction
Palma, S; Gonzalez-Castano, M; Romero-Sarria, F; Odriozola, JAMolecular Catalysis, 517 (2022) 112015 DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2021.112015
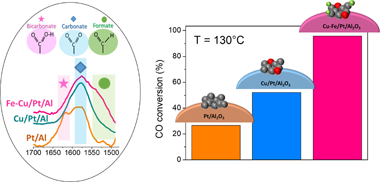
Abstract
This work proposes a trimetallic Fe-Cu/Pt/Al2O3 catalyst as an appealing system for preferential oxidation of CO (CO-PROX) reaction. The excellent conversion rates achieved by the Fe-Cu/Pt/Al2O3 catalysts under realistic reforming-surrogated feed streams along with the catalyst stability, reproducibility, and scalability showcase a very competitive system for CO-PROX reaction units. Furthermore, the systematic analysis conducted for Pt/Al2O3, Cu/Pt Al2O3, and Fe-Cu/Pt/Al2O3 catalysts enabled establishing meaningful relationships between catalytic behaviour and the catalyst surface to reactants interactions. Thus, the enhanced CO oxidation performances attained by the incorporation of Fe species into bimetallic Cu/Pt/Al2O3 catalysts were associated to superior surface electron densities and inhibited CO adsorption process over Pt surfaces. Remarkably, operando-DRIFTS spectroscopy evidenced significantly larger H-containing surface species developed over the trimetallic system. The enhanced abilities for developing thermally instable intermediates favoured by small amounts of Fe should indeed determine the enhanced catalysts behaviours displayed by the trimetallic Fe-Cu/Pt/Al2O3 catalyst.
Enero, 2022 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2021.112015
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Compositional gradients at the nanoscale in substoichiometric thin films deposited by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles: A case study on SiOx thin films
Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Alcaide, AM; Rico, V; Ferrer, FJ; Alcala, G; Rojas, TC; Alvarez, R; González-Elipe, AR; Palmero, APlasma Processes and Polymers (2022) e2100116 DOI: 10.1002/ppap.202100116
Abstract
We demonstrate the existence of stoichiometric variations at the nanoscale when growing nanocolumnar SiOx thin films by reactive magnetron sputtering deposition at oblique angles. Results show stoichiometric variations in the range 0.3 < x < 1.3 when growing a SiO0.5 thin film. This agrees with results from a numerical growth model that obtains a shift of the stoichiometry in all nanocolumns from lower values at the side facing the Si target to higher values at the opposite side. The different momentum distribution of the gaseous reactive and sputtered species results in preferential incorporation of the latter at a particular side of the nanocolumns. The general occurrence of this mechanism during the reactive magnetron sputtering deposition of substoichiometric thin films at oblique angles is discussed.
Enero, 2022 · DOI: 10.1002/ppap.202100116
Reactividad de Sólidos
Flash Sintering Research Perspective: A Bibliometric Analysis
Gil-Gonzalez, E; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, AMaterials, 15 (2022) 416 DOI: 10.3390/ma15020416
Abstract
Flash Sintering (FS), a relatively new Field-Assisted Sintering Technique (FAST) for ceramic processing, was proposed for the first time in 2010 by Prof. Rishi Raj's group from the University of Colorado at Boulder. It quickly grabbed the attention of the scientific community and since then, the field has rapidly evolved, constituting a true milestone in materials processing with the number of publications growing year by year. Moreover, nowadays, there is already a scientific community devoted to FS. In this work, a general picture of the scientific landscape of FS is drawn by bibliometric analysis. The target sources, the most relevant documents, hot and trending topics as well as the social networking of FS are unveiled. A separate bibliometric analysis is also provided for Reaction or Reactive Flash Sintering (RFS), where not only the sintering, but also the synthesis is merged into a single step. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study of this nature carried out in this field of research and it can constitute a useful tool for researchers to be quickly updated with FS as well as to strategize future research and publishing approaches.
Enero, 2022 · DOI: 10.3390/ma15020416
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Molecular Interface Engineering via Triazatruxene-Based Moieties/NiOx as Hole-Selective Bilayers in Perovskite Solar Cells for Reliability
Hemasiri, NH; Calio, L; Pegu, M; Kazim, S; Ahmad, SSolar RRL (2022) 2100793 DOI: 10.1002/solr.202100793
Abstract
Interface engineering is an effective approach to decrease nonradiative recombination and the energy barrier at the perovskite/hole transporting layer (HTL) interfaces. To overcome such limitations, an organic semiconductor (DTT-EHDI2) is proposed, which is, composed of dithienothiophene (DTT) as the core and a planar triazatruxene incorporating an alkyl chain as the side group. This is noted to be an effective interfacial layer for inverted planar perovskite solar cells (PSCs). The altered interface effectively minimizes the detrimental charge recombination and tailors the photoinduced charge transfer dynamics at the interface of the inorganic HTL/perovskite. The pi-conjugation in DTT-EHDI2 induces high hole mobility and electrical conductivity via electron-donating properties and strong pi-pi intermolecular interaction. The synergetic approach leads to a substantial performance enhancement in dopant-free DTT-EHDI2-based inverted planar PSCs, achieving 18.15% power conversion efficiency with negligible hysteresis effect. The present approach provides an effective direction of the cost-effective thiophene derivative as an interfacial agent to escalate the optoelectronic performances in photovoltaics.
Enero, 2022 · DOI: 10.1002/solr.202100793
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Coarse-grained approach to amorphous and anisotropic materials in kinetic Monte Carlo thin-film growth simulations: A case study of TiO2 and ZnO by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition
Budagosky, J; Garcia-Casas, X; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Barranco, A; Borras, APlasma Processes and Polymers (2022) e2100179 DOI: 10.1002/ppap.202100179
Abstract
The growth of TiO2 and ZnO thin films is studied by means of coarse-grained kinetic Monte Carlo simulations under conditions typically encountered in plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition experiments. The basis of our approach is known to work well to simulate the growth of amorphous materials using cubic grids and is extended here to reproduce not only the morphological characteristics and scaling properties of amorphous TiO2 but also the growth of polycrystalline ZnO with a good approximation, including the evolution of the film texture during growth and its dependence on experimental conditions. The results of the simulations have been compared with available experimental data obtained by X-ray diffraction, analysis of the texture coefficients, atomic force microscopy, and scanning electron microscopy.
Enero, 2022 · DOI: 10.1002/ppap.202100179
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Optoelectronic Devices Based on Scaffold Stabilized Black-Phase CsPbI3 Nanocrystals
Romero-Perez, C; Rubino, A; Calio, L; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HAdvanced Optical Materials (2022) 2102112 DOI: 10.1002/adom.202102112
Abstract
The optoelectronic properties of lead halide perovskites are intimately related to their crystalline phase. For the case of cesium lead iodide (CsPbI3) several polymorphs meet the Goldschmidt tolerance factor, which determines their stability, and form broad band absorber and luminescent phases. However, at room temperature none of them are stable, which prevents their use in optoelectronics. In this work, bare CsPbI3 nanocrystals are synthesized in the sub-10 nm range in the "black", light emitting, crystalline phase, using a pore controlled SiO2 matrix that limits crystal size and confers a certain degree of strain that favors their stability. Quantum confinement effects allow the tuning of the optical properties of the CsPbI3 nanocrystals by means of the crystal size. Their suitability as optoelectronic materials is demonstrated by building scaffold supported CsPbI3 quantum dot based photovoltaic and light emitting devices.
Enero, 2022 · DOI: 10.1002/adom.202102112
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Structured and micro-structured catalysts: A fascinating future for a sustainable world – A special issue in tribute to the careers of Professors Mario Montes and José Antonio Odriozola
M.A.Centeno; L.M.Gandía; F.Romero-Sarria; O.SanzCatalysis Today, 383 (2022) 1-4 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2021.09.034
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of Steam Injection during Carbonation on the Multicyclic Performance of Limestone (CaCO3) under Different Calcium Looping Conditions: A Comparative Study
Troya, JJA; Moreno, V; Sánchez-Jiménez, PE; Perejon, A; Valverde, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAACS Sustanaible Chemistry & Engineering, 10 (2022) 850-859 DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c06314
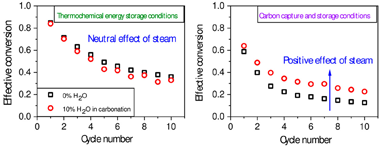
Abstract
This study explores the effect of steam addition during carbonation on the multicyclic performance of limestone under calcium looping conditions compatible with (i) CO2 capture from postcombustion gases (CCS) and with (ii) thermochemical energy storage (TCES). Steam injection has been proposed to improve the CO2 uptake capacity of CaO-based sorbents when the calcination and carbonation loops are carried out in CCS conditions: at moderate carbonation temperatures (similar to 650 degrees C) under low CO2 concentration (typically similar to 15% at atmospheric pressure). However, the recent proposal of calcium-looping as a TCES system for integration into concentrated solar power (CSP) plants has aroused interest in higher carbonation temperatures (similar to 800-850 degrees C) in pure CO2. Here, we show that steam benefits the multicyclic behavior in the milder conditions required for CCS. However, at the more aggressive conditions required in TCES, steam essentially has a neutral net effect as the CO2 uptake promoted by the reduced CO2 partial pressure but also is offset by the substantial steam-promoted mineralization in the high temperature range. Finally, we also demonstrate that the carbonation rate depends exclusively on the partial pressure of CO2, regardless of the diluting gas employed.
Enero, 2022 · DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c06314
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of the Processing Parameters on the Porosity and Mechanical Behavior of Titanium Samples with Bimodal Microstructure Produced via Hot Pressing
Chavez-Vasconez, R; Lascano, S; Sauceda, S; Reyes-Valenzuela, M; Salvo, C; Mangalaraja, RV; Gotor, FJ; Arevalo, C; Torres, YMaterials, 15 (2022) 136 DOI: 10.3390/ma15010136
Abstract
Commercially pure (c.p.) titanium grade IV with a bimodal microstructure is a promising material for biomedical implants. The influence of the processing parameters on the physical, microstructural, and mechanical properties was investigated. The bimodal microstructure was achieved from the blends of powder particles with different sizes, while the porous structure was obtained using the space-holder technique (50 vol.% of ammonium bicarbonate). Mechanically milled powders (10 and 20 h) were mixed in 50 wt.% or 75 wt.% with c.p. titanium. Four different mixtures of powders were precompacted via uniaxial cold pressing at 400 MPa. Then, the specimens were sintered at 750 degrees C via hot pressing in an argon gas atmosphere. The presence of a bimodal microstructure, comprised of small-grain regions separated by coarse-grain ones, was confirmed by optical and scanning electron microscopies. The samples with a bimodal microstructure exhibited an increase in the porosity compared with the commercially available pure Ti. In addition, the hardness was increased while the Young's modulus was decreased in the specimens with 75 wt.% of the milled powders (20 h).
Enero, 2022 · DOI: 10.3390/ma15010136
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Plasma engineering of microstructured piezo-Triboelectric hybrid nanogenerators for wide bandwidth vibration energy harvesting
García-Casas, X; Ghaffarinehad, A; Aparicio, FJ; Castillo-Seoane, J; López-Santos, C; Espinós, JP; Cotrino, J; Sánchez-Valencia, JR; Barranco, A; Borrás, ANano Energy, 91 (2022) 106673 DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.106673
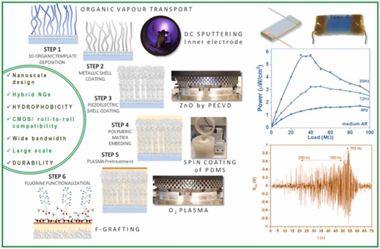
Abstract
We introduce herein the advanced application of low-pressure plasma procedures for the development of piezo and triboelectric mode I hybrid nanogenerators. Thus, plasma assisted deposition and functionalization methods are presented as key enabling technologies for the nanoscale design of ZnO polycrystalline shells, the formation of conducting metallic cores in core@shell nanowires, and for the solventless surface modification of polymeric coatings and matrixes. We show how the perfluorinated chains grafting of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) provides a reliable approach to increase the hydrophobicity and surface charges at the same time that keeping the PDMS mechanical properties. In this way, we produce efficient Ag/ZnO convoluted piezoelectric nanogenerators supported on flexible substrates and embedded in PDMS compatible with a contact-separation triboelectric architecture. Factors like crystalline texture, ZnO thickness, nanowires aspect ratio, and surface chemical modification of the PDMS are explored to optimize the power output of the nanogenerators aimed for harvesting from low-frequency vibrations. Just by manual triggering, the hybrid device can charge a capacitor to switch on an array of color LEDs. Outstandingly, this simple three-layer architecture allows for harvesting vibration energy in a wide bandwidth, thus, we show the performance characteristics for frequencies between 1 Hz and 50 Hz and demonstrate the successful activation of the system up to ca. 800 Hz.
Enero, 2022 · DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.106673
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Boosting water activation determining-step in WGS reaction on structured catalyst by Mo-doping
Garcia-Moncada, N; Jurado, L; Martinez-Tejada, LM; Romero-Sarria, F; Odriozola, JACatalysis Today, 383 (2022) 193-204 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2020.06.003
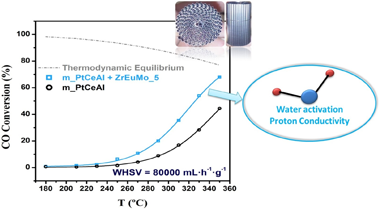
Abstract
Proton conductors Mo-Eu-Zr mixed oxide systems were synthesized and further mixed with a conventional Pt/CeO2/Al2O3 catalyst to develop a highly efficient water-gas-shift (WGS) catalyst. The designed catalyst, once structured, allows reach the equilibrium conversion at medium temperatures (similar to 350 degrees C) at 80 L.g(-1) h(-1) space velocity. The ability of the proton conductor to maintain an elevated water concentration at the metal-support interface by Grotthuss' mechanism boosts the catalytic activity in WGS reaction.
The Mo-containing proton conductor is extensively characterized allowing to establish the formation of molybdenum oxide phases nucleating on top of the Eu sites in Eu-Zr oxide solid solution. [MoO4](2-) to [Mo7O24](6-) clusters nucleates at low Mo contents resulting in a alpha-MoO3 layer on increasing its content. In presence of H-2, Mobronzes are formed from similar to 200 degrees C enhancing water concentration at the surfaces and boosting the catalytic activity in the WGS reaction. These results pave the way for developing lower volume WGS reactors.
Enero, 2022 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2020.06.003
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
The Response of Tomato Fruit Cuticle Membranes Against Heat and Light
Benitez, JJ; Moreno, AG; Guzman-Puyol, S; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Heredia, A; Dominguez, EFrontiers in Plant Science, 12 (2022) 807723 DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.807723
Abstract
Two important biophysical properties, the thermal and UV-Vis screening capacity, of isolated tomato fruit cuticle membranes (CM) have been studied by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and UV-Vis spectrometry, respectively. A first order melting, corresponding to waxes, and a second order glass transition (T-g) thermal events have been observed. The glass transition was less defined and displaced toward higher temperatures along the fruit ripening. In immature and mature green fruits, the CM was always in the viscous and more fluid state but, in ripe fruits, daily and seasonal temperature fluctuations may cause the transition between the glassy and viscous states altering the mass transfer between the epidermal plant cells and the environment. CM dewaxing reduced the T-g value, as derived from the role of waxes as fillers. T-g reduction was more intense after polysaccharide removal due to their highly interwoven distribution within the cutin matrix that restricts the chain mobility. Such effect was amplified by the presence of phenolic compounds in ripe cuticle membranes. The structural rigidity induced by phenolics in tomato CMs was directly reflected in their mechanical elastic modulus. The heat capacity (Cp-rev) of cuticle membranes was found to depend on the developmental stage of the fruits and was higher in immature and green stages. The average Cp-rev value was above the one of air, which confers heat regulation capacity to CM. Cuticle membranes screened the UV-B light by 99% irrespectively the developmental stage of the fruit. As intra and epicuticular waxes contributed very little to the UV screening, this protection capacity is attributed to the absorption by cinnamic acid derivatives. However, the blocking capacity toward UV-A is mainly due to the CM thickness increment during growth and to the absorption by flavone chalconaringenin accumulated during ripening. The build-up of phenolic compounds was found to be an efficient mechanism to regulate both the thermal and UV screening properties of cuticle membranes.
Enero, 2022 · DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.807723
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Metal micromonoliths for the cleaning of H-2 by means of methanation reactions
Laguna, OH; Munoz-Murillo, A; Bobadilla, LF; Martinez, LM; Montes, M; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JACatalysis Today, 383 (2022) 216-225 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2021.04.026
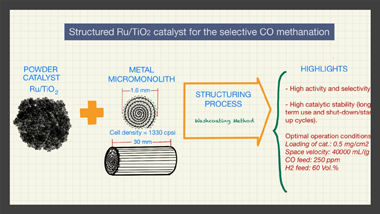
Abstract
The present manuscript presents for the first time the structuring of a Ru/TiO2 catalyst that was achieved by means of the washcoating procedure using homemade metal micromonoliths (Fecralloy (R)) of 1330 cpsi. For this, an optimized formulation of the slurried catalyst as well as a reproducible protocol for the coating of the micromonoliths were successfully achieved. The obtained structured systems were tested in the selective CO methanation reaction and the effect of different variables over the catalytic performance were analyzed such as the amount of loaded catalyst in the micromonoliths, the temperature of reaction, the space velocity, and the amount of CO and H-2 within the feed-stream. The study of all of these parameters allowed to establish optimal conditions to maximize the performance of the structured Ru/TiO2 catalyst and subsequently, this was tested under those cited conditions in long-term tests (similar to 375 h), including shut-down/start-up cycles, aiming to evaluate its catalytic stability. The system presented a considerable stability along the different test without loss of catalytic activity, being specially remarkable its resistance to the inclusion of shut-down/start-up cycles. Therefore, this study lays the foundations for future development of more sophisticated structured systems for the selective CO methanation based on the structuring strategy proposed.
Enero, 2022 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2021.04.026
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Au and Pt Remain Unoxidized on a CeO2-Based Catalyst during the Water-Gas Shift Reaction
Reina, TR; Gonzalez-Castano, M; Lopez-Flores, V; Martinez, LMT; Zitolo, A; Ivanova, S; Xu, WQ; Centeno, MA; Rodriguez, JA; Odriozola, JAJournal of the American Chemical Society, 144 (2022) 446-453 DOI: 10.1021/jacs.1c10481
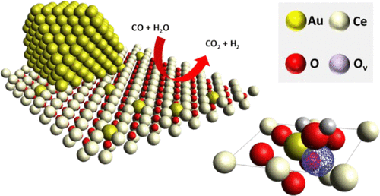
Abstract
The active forms of Au and Pt in CeO2-based catalysts for the water-gas shift (WGS) reaction are an issue that remains unclear, although it has been widely studied. On one hand, ionic species might be responsible for weakening the Ce-O bonds, thus increasing the oxygen mobility and WGS activity. On the other hand, the close contact of Au or Pt atoms with CeO2 oxygen vacancies at the metal-CeO2 interface might provide the active sites for an efficient reaction. In this work, using in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy, we demonstrate that both Au and Pt remain unoxidized during the reaction. Remarkable differences involving the dynamics established by both species under WGS atmospheres were recognized. For the prereduced Pt catalyst, the increase of the conversion coincided with a restructuration of the Pt atoms into cuboctahedrical metallic particles without significant variations on the overall particle size. Contrary to the relatively static behavior of Pt-0, Au-0 nanoparticles exhibited a sequence of particle splitting and agglomeration while maintaining a zero oxidation state despite not being located in a metallic environment during the process. High WGS activity was obtained when Au atoms were surrounded by oxygen. The fact that Au preserves its unoxidized state indicates that the chemical interaction between Au and oxygen must be necessarily electrostatic and that such an electrostatic interaction is fundamental for a top performance in the WGS process.
Enero, 2022 · DOI: 10.1021/jacs.1c10481
Materiales Avanzados
Study of a Waste Kaolin as Raw Material for Mullite Ceramics and Mullite Refractories by Reaction Sintering
Sanchez-Soto, PJ; Eliche-Quesada, D; Martinez-Martinez, S; Perez-Villarejo, L; Garzon, EMaterials, 15 (2022) 583 DOI: 10.3390/ma15020583
Abstract
A deposit of raw kaolin, located in West Andalusia (Spain), was studied in this work using a representative sample. The methods of characterization were X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray fluorescence (XRF), particle size analysis by sieving and sedimentation, and thermal analysis. The ceramic properties were determined. A sample of commercial kaolin from Burela (Lugo, Spain), with applications in the ceramic industry, was used in some determinations for comparison purposes. The kaolin deposit has been produced by alteration of feldspar-rich rocks. This raw kaolin was applied as an additive in local manufactures of ceramics and refractories. However, there is not previous studies concerning its characteristics and firing properties. Thus, the meaning of this investigation was to conduct a scientific study on this subject and to evaluate the possibilities of application. The raw kaolin was washed for the beneficiation of the rock using water to increase the kaolinite content of the resultant material. The results indicated that the kaolinite content of the raw material was 20 wt % as determined by XRD, showing ~23 wt % of particles lower than 63 mu m. The kaolinite content of the fraction lower than 63 mu m was 50 wt %. Thus, an improvement of the kaolinite content of this raw kaolin was produced by wet separation. However, the kaolin was considered as a waste kaolin, with microcline, muscovite and quartz identified by XRD. Thermal analyses by Thermo-Dilatometry (TD), Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA) and Thermo-Gravimetry (TG) allowed observe kaolinite thermal decomposition, quartz phase transition and sintering effects. Pressed samples of this raw kaolin, the fraction lower than 63 mu m obtained by water washing and the raw kaolin ground using a hammer mill were fired at several temperatures in the range 1000-1500 & DEG;C for 2 h. The ceramic properties of all these samples were determined and compared. The results showed the progressive linear firing shrinkage by sintering in these samples, with a maximum value of ~9% in the fraction lower than 63 mu m. In general, water absorption capacity of the fired samples showed a decrease from ~18-20% at 1050 & DEG;C up to almost zero after firing at 1300 & DEG;C, followed by an increase of the experimental values. The open porosity was almost zero after firing at 1350 & DEG;C for 2 h and the bulk density reached a maximum value of 2.40 g/cm(3) as observed in the ground raw kaolin sample. The XRD examination of fired samples indicated that they are composed by mullite, from kaolinite thermal decomposition, and quartz, present in the raw sample, as main crystalline phases besides a vitreous phase. Fully-densified or vitrified materials were obtained by firing at 1300-1350 & DEG;C for 2 h. In a second step of this research, it was examined the promising application of the previous study to increase the amount of mullite by incorporation of alumina (alpha-alumina) to this kaolin sample. Firing of mixtures, prepared using this kaolin and alpha-alumina under wet processing conditions, produced the increase of mullite in relative proportion by reaction sintering at temperatures higher than 1500 & DEG;C for 2 h. Consequently, a mullite refractory can be prepared using this kaolin. This processing of high-alumina refractories is favoured by a previous size separation, which increases the kaolinite content, or better a grinding treatment of the raw kaolin.
Enero, 2022 · DOI: 10.3390/ma15020583
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Plasma engineering of microstructured piezo-Triboelectric hybrid nanogenerators for wide bandwidth vibration energy harvesting
Garcia-Casas, X; Ghaffarinehad, A; Aparicio, FJ; Castillo-Seoane, J; Lopez-Santos, C; Espinos, JP; Cotrino, J; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Barranco, A; Borras, ANano Energy, 91 (2022) 106673 DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.106673
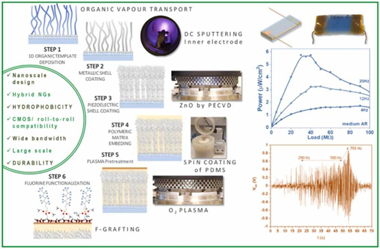
Abstract
We introduce herein the advanced application of low-pressure plasma procedures for the development of piezo and triboelectric mode I hybrid nanogenerators. Thus, plasma assisted deposition and functionalization methods are presented as key enabling technologies for the nanoscale design of ZnO polycrystalline shells, the formation of conducting metallic cores in core@shell nanowires, and for the solventless surface modification of polymeric coatings and matrixes. We show how the perfluorinated chains grafting of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) provides a reliable approach to increase the hydrophobicity and surface charges at the same time that keeping the PDMS mechanical properties. In this way, we produce efficient Ag/ZnO convoluted piezoelectric nanogenerators supported on flexible substrates and embedded in PDMS compatible with a contact-separation triboelectric architecture. Factors like crystalline texture, ZnO thickness, nanowires aspect ratio, and surface chemical modification of the PDMS are explored to optimize the power output of the nanogenerators aimed for harvesting from low-frequency vibrations. Just by manual triggering, the hybrid device can charge a capacitor to switch on an array of color LEDs. Outstandingly, this simple three-layer architecture allows for harvesting vibration energy in a wide bandwidth, thus, we show the performance characteristics for frequencies between 1 Hz and 50 Hz and demonstrate the successful activation of the system up to ca. 800 Hz.
Enero, 2022 · DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.106673
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Visible light photodegradation of blue basic 41 using cobalt doped ZnO: Box–Behnken optimization and DFT calculation
K. Tanji; M. Zouheir; Y. Naciri; H. Ahmoum; A. Hsini; O. Mertah; A. El Gaidoumi; J.A. Navio; M.C. Hidalgo; A KherbecheJournal of the Iranian Chemical Society, 19 (2022) 2779-2794 DOI: 10.1007/s13738-022-02496-w
Abstract
CoxZn1−xO system (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.2) was synthesized using the solution combustion method with urea as a fuel source. Photocatalytic tests were performed under visible light to assess the Basic Blue 41 (BB41) conversion. Various characterization techniques, including XRD, FT-IR analysis, SEM, EDS, XRF, BET-surface area, and DRS were used to investigate the composition, structure, and morphology of the synthesized catalysts. In addition, the density functional theory calculation was used in order to study the electronic properties of the ZnO structure. The Box–Behnken model was valid for describing the degradation of BB41 dye according to the analysis of variances results. A maximum conversion of 100% for BB41 dye has been reached with high mineralization and important removal of chemical oxygen demand. The optimum conditions for BB41 conversion are reported. On the other hand, the reuse tests of the best catalyst showed high-performance stability after five cycles. Furthermore, the activity of superoxide ions (O2·−) and hydroxyl radicals (OH.) as the spices responsible for BB41 dye conversion was well confirmed by the free radicals scavenging tests. The use of Box–Behnken optimization and DFT calculation applied to the synthesized catalysts proves to be a very suitable procedure to establish the operating conditions under which the synthesis strategy of the CoxZn1−xO catalyst in its activity in the visible region performs an excellent efficiency for the degradation of organic dyes and makes contributions to the current literature related to the field of environmental technology.
Enero, 2022 · DOI: 10.1007/s13738-022-02496-w
2021
2021
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
In Situ DRIFTS-MS Methanol Adsorption Study onto Supported NiSn Nanoparticles: Mechanistic Implications in Methanol Steam Reforming
Bobadilla, LF; Azancot, L; Ivanova, S; Delgado, JJ; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Roger, ACNanomaterials, 11 (2021) 3234 DOI: 10.3390/nano11123234
Abstract
Methanol adsorption over both supported NiSn Nps and analogous NiSn catalyst prepared by impregnation was studied by in situ diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS) to gain insights into the basis of hydrogen production from methanol steam reforming. Different intermediate species such as methoxides with different geometry (bridge and monodentate) and formate species were identified after methanol adsorption and thermal desorption. It is proposed that these species are the most involved in the methanol steam reforming reaction and the major presence of metal-support interface sites in supported NiSn Nps leads to higher production of hydrogen. On the basis of these results, a plausible reaction mechanism was elucidated through the correlation between the thermal stability of these species and the evolution of the effluent gas released. In addition, it was demonstrated that DME is a secondary product generated by condensation of methoxides over the acid sites of alumina support in an acid-catalyzed reaction.
Diciembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.3390/nano11123234
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Mechanical Performances of Isolated Cuticles Along Tomato Fruit Growth and Ripening
Benitez, JJ; Guzman-Puyol, S; Vilaplana, F; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Dominguez, E; Heredia, AFrontiers in Chemistry, 12 (2021) 787839 DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.787839
Abstract
The cuticle is the most external layer that protects fruits from the environment and constitutes the first shield against physical impacts. The preservation of its mechanical integrity is essential to avoid the access to epidermal cell walls and to prevent mass loss and damage that affect the commercial quality of fruits. The rheology of the cuticle is also very important to respond to the size modification along fruit growth and to regulate the diffusion of molecules from and toward the atmosphere. The mechanical performance of cuticles is regulated by the amount and assembly of its components (mainly cutin, polysaccharides, and waxes). In tomato fruit cuticles, phenolics, a minor cuticle component, have been found to have a strong influence on their mechanical behavior. To fully characterize the biomechanics of tomato fruit cuticle, transient creep, uniaxial tests, and multi strain dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) measurements have been carried out. Two well-differentiated stages have been identified. At early stages of growth, characterized by a low phenolic content, the cuticle displays a soft elastic behavior. Upon increased phenolic accumulation during ripening, a progressive stiffening is observed. The increment of viscoelasticity in ripe fruit cuticles has also been associated with the presence of these compounds. The transition from the soft elastic to the more rigid viscoelastic regime can be explained by the cooperative association of phenolics with both the cutin and the polysaccharide fractions.
Diciembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.787839
Reactividad de Sólidos
Unravelling the optimization of few-layer graphene crystallinity and electrical conductivity in ceramic composites by Raman spectroscopy
Muñoz-Ferreiro, C; Lopez-Pernia, C; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Poyato, RJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 41 (2021) 290-298 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2021.09.025
Abstract
Zirconia composites with few-layer graphene (FLG) were prepared by two powder processing routines-ultrasonic agitation or planetary ball milling-and spark plasma sintered at 1250 and 1300 degrees C. An in-depth study of the crystallinity of FLG, in terms of presence and nature of defects, was performed by Raman spectroscopy, revealing enhanced FLG crystallinity after sintering. This enhancement was more noticeable in the composites sintered at the highest temperature, with lower amount of structural defects and amorphous carbon. However, remaining amorphous carbon was detected in the composites prepared by planetary ball milling even after sintering at the highest temperature, resulting in lower electrical conductivities. Optimum results in terms of electrical conductivity were achieved for the composites prepared by ultrasonic agitation and sintered at 1300 degrees C, with electrical percolation limit below 2.5 vol% FLG and high electrical conductivity (678 S/m for 5 vol% FLG), as result of the enhanced FLG crystallinity after sintering.
Diciembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2021.09.025
Reactividad de Sólidos
Advanced parametrisation of phase change materials through kinetic approach
Lizana, J; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Energy Storage, 44 (2021) 103441 DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2021.103441
Abstract
Phase change materials (PCM) have been widely investigated for heat storage and transfer applications. Numerous numerical simulation approaches have been proposed for modelling their behaviour and predicting their performance in thermal applications. However, simulation approaches do not consider the kinetics of the phase transition processes, compromising the accuracy of their predictions. The phase change is a kinetically driven process in which both the reaction rate and the reaction progress depend on the heating schedule. This work evaluates and parametrises the influence of kinetics in the melting and crystallisation behaviour of a well-known PCM, PEG1500, and compares potential discrepancies with common phase change parametrisation alternatives. The kinetic dependence was experimentally evaluated through differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The kinetic parameters required for modelling the kinetics of the processes were determined by both model-free and model-fitting procedures following ICTAC (International Confederation for Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry) recommendations. Then, the phase transition was parametrised through a kinetic model and compared with three conventional phase transition models: linear without hysteresis, non-linear without hysteresis, and non-linear with hysteresis. The statistical comparison between models demonstrates the higher accuracy of the kinetic approach to correctly represent the partial enthalpy distribution of latent heat storage materials during alternative phase change rates, obtaining a coefficient of determination (R-2) of 0.80. On the other hand, the accuracy of kinetic-independent models is limited to the range from 0.40 to 0.61. The results highlight the high discrepancies of conventional models compared to the kinetic approach and provide criteria and guidelines for efficient kinetic modelling of phase change in heat transfer evaluations.
Diciembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2021.103441
Reactividad de Sólidos
Fabrication and characterization of FeCoNiCrMn,(Al) high entropy alloy based (Ti,Ta,Nb)(C,N) cermet
Real, C; Alcala, MD; Trigo, I; Fombella, I; Cordoba, JMInternational Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 101 (2021) 105694 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2021.105694
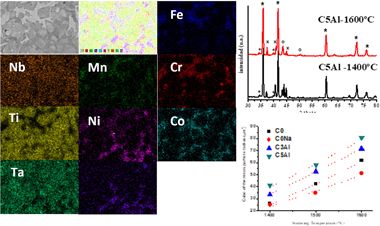
Abstract
From nanostructured mechanically synthesized powder a set of FeCoNiCrMn,(Al) based (Ti,Ta,Nb)(C,N) cermets were fabricated and sintered by a pressureless procedure. Highly dense cermets were obtained, and the nature of chemical change, microstructure, mechanical properties and coarsening kinetic of ceramic phase were characterized by image analysis, microindentation, scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. The design of the material was performed using a set of three different chemical cermet composition and three different sintering temperatures, or comparative purposes.
Diciembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2021.105694
Materiales Coloidales
White, blue, violet, and other colors from Tm3+/Tb3+/Eu3+ co-doped polymorph SrAl2O4 films, deposited by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis technique
Calderon-Olvera, RM; Garcia-Hipolito, M; Alvarez-Fregoso, O; Alvarez-Perez, MA; Baez-Rodriguez, A; Ramos-Brito, F; Garcia-Velasco, AC; Falcony, COpticalls Materials DOI: 10.1016/j.optmat.2021.111737
Abstract
SrAl2O4: Tm3+, SrAl2O4: (Tb3+; Eu3+) and SrAl2O4: (Tb3+; Eu3+; Tm3+) films were deposited by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis (USP) method at 550. C and subsequently heat-treated at 800 degrees C. XRD characterization showed a monoclinic/hexagonal polymorph phase of these films with orthorhombic Sr4Al14O25 as secondary phase. The incorporation of Tm3+ ions in strontium aluminate host lattice generated emissions of blue color for photoluminescence and violet color for cathodoluminescence. The violet emission was associated to the electronic transition from I-1(6) energy level of Tm3+. Photoluminescence of the SrAl2O4: (Tb3+; Eu3+) films resulted in two different colors, white emission was observed when excited with 210 nm and bluish-white emission was achieved by exciting with 275, and 286 nm. When three dopant ions (Tm3+; Tb3+; Eu3+) were incorporated inside strontium aluminate host lattice, it was observed (exciting under 252 nm) white photoluminescence emission (x = 0.3377, y = 0.3294); for excitation wavelengths (lambda(exc)) = 262, 315 and 375 nm, emissions in different shades of blue-green were achieved. Quantum efficiencies between 48 and 57% were obtained.
Diciembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.optmat.2021.111737
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Designed organomicaceous materials for efficient adsorption of iodine
Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Pazos, MC; Alba, MDJournal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9 (2021) 106577 DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.106577
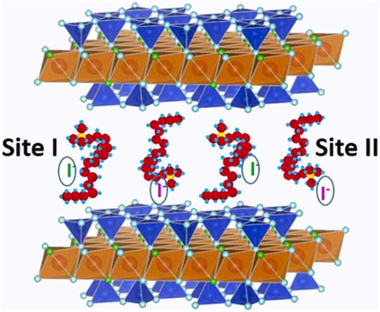
Abstract
The anionic iodine I-129 has a significant contribution to overall long-term dose resulting from the nuclear waste storage and its immobilization by clay barrier is crucial. Organoclays have been tested as ideal adsorption materials, being the clay layer charge and the length and type of organic molecules the most relevant parameters affecting the adsorption. In this work, a family of designed organomicas are explored in term of iodine adsorption capacity. Their adsorption capacities were always higher than that of the traditional clays and organoclays. C-18-M4 shows a maximum monolayer adsorption capacity one order of magnitude higher than natural organoclays, with a free energy typical of physical adsorption and adsorption sites of high affinity. However, its surface is not homogeneous in terms of stability constant according to the Scatchard adsorption parameters. Hence, this study can provide a guidance for the design and construction of ultrahigh-capacity iodine adsorbents.
Diciembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.106577
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
LaFeO3 Modified with Ni for Hydrogen Evolution Via Photocatalytic Glucose Reforming in Liquid Phase
G. Iervolino; V. Vaiano; D. Sannino; F. Puga; J.A. Navío; M.C. HidalgoCatalysts, 11 (2021) 1558 DOI: 10.3390/catal11121558
Abstract
In this work, the optimization of Ni amount on LaFeO3 photocatalyst was studied in the photocatalytic molecular hydrogen production from glucose aqueous solution under UV light irradiation. LaFeO3 was synthesized via solution combustion synthesis and different amount of Ni were dispersed on LaFeO3 surface through deposition method in aqueous solution and using NaBH4 as reducing agent. The prepared samples were characterized with different techniques: Raman spectroscopy, UltraViolet-Visible Diffuse Reflectance Spettroscopy (UV–Vis-DRS), X-ray Diffraction (XRD), X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray Fluorescence (XRF), Transmission Electron microscopy (TEM), and Scanning Electron microscopy (SEM) analyses. For all the investigated photocatalysts, the presence of Ni on perovskite surface resulted in a better activity compared to pure LaFeO3. In particular, it is possible to identify an optimal amount of Ni for which it is possible to obtain the best hydrogen production. Specifically, the results showed that the optimal Ni amount was equal to nominal 0.12 wt% (0.12Ni/LaFeO3), for which the photocatalytic H2 production was equal to 2574 μmol/L after 4 h of UV irradiation. The influence of different of photocatalyst dosage and initial glucose concentration was also evaluated. The results of the optimization of operating parameters indicated that the highest molecular hydrogen production was achieved on 0.12Ni/LaFeO3 sample with 1.5 g/L of catalyst dosage and 1000 ppm initial glucose concentration. To determine the reactive species that play the most significant role in the photocatalytic hydrogen production, photocatalytic tests in the presence of different radical scavengers were performed. The results showed that •OH radical plays a significant role in the photocatalytic conversion of glucose in H2. Moreover, photocatalytic tests carried out with D2O instead of H2O evidenced the role of water molecules in the photocatalytic production of molecular hydrogen in glucose aqueous solution.
Diciembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.3390/catal11121558
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Zinc Polyaleuritate Ionomer Coatings as a Sustainable, Alternative Technology for Bisphenol A-Free Metal Packaging
Morselli, D; Cataldi, P; Paul, UC; Ceseracciu, L; Benitez, JJ; Scarpellini, A; Guzman-Puyol, S; Heredia, A; Valentini, P; Pompa, PP; Marrero-López, D; Athanassiou, A; Heredia-Guerrero, AACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 9 (2021) 15484-15495 DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c04815
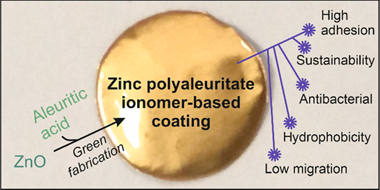
Abstract
Sustainable coatings for metal food packaging were prepared from ZnO nanoparticles (obtained by the thermal decomposition of zinc acetate) and a naturally occurring polyhydroxylated fatty acid named aleuritic (or 9,10,16-trihydroxy-hexadecanoic) acid. Both components reacted, originating under specific conditions zinc polyaleuritate ionomers. The polymerization of aleuritic acid into polyaleuritate by a solvent-free, melt polycondensation reaction was investigated at different times (15, 30, 45, and 60 min), temperatures (140, 160, 180, and 200 degrees C), and proportions of zinc oxide and aleuritic acid (0:100, 5:95, 10:90, and 50:50, w/w). Kinetic rate constants calculated by infrared spectroscopy decreased with the amount of Zn due to the consumption of reactive carboxyl groups, while the activation energy of the polymerization decreased as a consequence of the catalyst effect of the metal. The adhesion and hardness of coatings were determined from scratch tests, obtaining values similar to robust polymers with high adherence. Water contact angles were typical of hydrophobic materials with values >= 94 degrees. Both mechanical properties and wettability were better than those of bisphenol A (BPA)-based resins and most likely are related to the low migration values determined using a hydrophilic food simulant. The presence of zinc provided a certain degree of antibacterial properties. The performance of the coatings against corrosion was studied by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy at different immersion times in an aqueous solution of NaCl. Considering the features of these biobased lacquers, they can be potential materials for bisphenol A-free metal packaging.
Noviembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c04815
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Recent Advances in Alkaline Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis and Electrode Manufacturing
Lopez-Fernandez, E; Sacedon, CG; Gil-Rostra, J; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; De Lucas-Consuegra, AMolecules, 26 (2021) 6326 DOI: 10.3390/molecules26216326
Abstract
Water electrolysis to obtain hydrogen in combination with intermittent renewable energy resources is an emerging sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Among the available electrolyzer technologies, anion exchange membrane water electrolysis (AEMWE) has been paid much attention because of its advantageous behavior compared to other more traditional approaches such as solid oxide electrolyzer cells, and alkaline or proton exchange membrane water electrolyzers. Recently, very promising results have been obtained in the AEMWE technology. This review paper is focused on recent advances in membrane electrode assembly components, paying particular attention to the preparation methods for catalyst coated on gas diffusion layers, which has not been previously reported in the literature for this type of electrolyzers. The most successful methodologies utilized for the preparation of catalysts, including co-precipitation, electrodeposition, sol-gel, hydrothermal, chemical vapor deposition, atomic layer deposition, ion beam sputtering, and magnetron sputtering deposition techniques, have been detailed. Besides a description of these procedures, in this review, we also present a critical appraisal of the efficiency of the water electrolysis carried out with cells fitted with electrodes prepared with these procedures. Based on this analysis, a critical comparison of cell performance is carried out, and future prospects and expected developments of the AEMWE are discussed.
Noviembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.3390/molecules26216326
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Recent Advances in the Bronsted/Lewis Acid Catalyzed Conversion of Glucose to HMF and Lactic Acid: Pathways toward Bio-Based Plastics
Megias-Sayago, C; Navarro-Jaen, S; Drault, F; Ivanova, SCatalysts, 11 (2021) 1395 DOI: 10.3390/catal11111395

Abstract
One of the most trending topics in catalysis recently is the use of renewable sources and/or non-waste technologies to generate products with high added value. That is why, the present review resumes the advances in catalyst design for biomass chemical valorization. The variety of involved reactions and functionality of obtained molecules requires the use of multifunctional catalyst able to increase the efficiency and selectivity of the selected process. The use of glucose as platform molecule is proposed here and its use as starting point for biobased plastics production is revised with special attention paid to the proposed tandem Bronsted/Lewis acid catalysts.
Noviembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.3390/catal11111395
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Polyaniline coated tungsten trioxide as an effective adsorbent for the removal of orange G dye from aqueous media
Hsini, A.; Naciri, Y.; Bouziani, A.; Aarab, N.; Essekri, A; Imgharn, A.; Laabd. M.; Navío, J.A.;Puga, F.; Lakhmirid, R.; Albourine, A.RSC Advances, 11 (2021) 31272-31283 DOI: 10.1039/D1RA04135E

Abstract
In this work, the core–shell PANI@WO3 composite was obtained from the reaction of aniline monomer polymerization with WO3 particles; sodium persulfate was used as an oxidant. Various analytical techniques such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM-EDS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) were used to characterize the as-prepared PANI@WO3 adsorbent, which well confirmed that the WO3 particles were coated by polyaniline polymer. The PANI@WO3 composite was tested as an adsorbent to remove reactive orange G (OG) for the first time. pH, adsorbent dose, contact time, initial dye concentration, and temperature were systematically investigated in order to study their effect on the adsorption process. The experimental findings showed that the PANI@WO3 composite has considerable potential to remove an aqueous OG dye. Langmuir and Freundlich's models were used to analyze the equilibrium isotherms of OG dye adsorption on the PANI@WO3 composite. As a result, the best correlation of the experimental data was provided by the Langmuir model, and the maximum capacity of adsorption was 226.50 mg g−1. From a thermodynamic point of view, the OG dye adsorption process occurred spontaneously and endothermically. Importantly, PANI@WO3 still exhibited an excellent adsorption capability after four regeneration cycles, indicating the potential reusability of the PANI@WO3 composite. These results indicate that the as prepared PANI@WO3 composite could be employed as an efficient adsorbent and was much better than the parent material adsorption of OG dye.
Noviembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1039/D1RA04135E
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Ultrastrong Exciton-Photon Coupling in Broadband Solar Absorbers
Bujalance, C; Esteso, V; Calio, L; Lavarda, G; Torres, T; Feist, J; Garcia-Vidal, FJ; Bottari, G; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 12 (2021) 10706-10712 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c02898
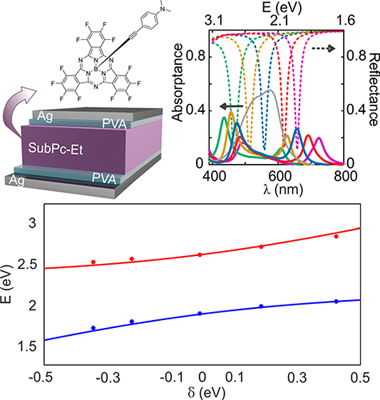
Abstract
The recent development of organic polaritonic solar cells, in which sunlight absorbers and photon modes of a resonator are hybridized as a result of their strong coupling, has revealed the potential this interaction offers to control and enhance the performance of these devices. In this approach, the photovoltaic cell is built in such a way that it also behaves as an optical cavity supporting spectrally well-defined resonances, which match the broad absorption bands of the dyes employed. Herein we focus on the experimental and theoretical analysis of the specific spectral and angular optical absorption characteristics of a broadband light harvester, namely a subphthalocyanine, when operating in the ultrastrong coupling regime. We discuss the implications of having a broad distribution of oscillator strengths and demonstrate that rational design of the layered structure is needed to optimize both the spectral and the angular response of the sunlight harvester dye.
Noviembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c02898
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
K-Promoted Ni-Based Catalysts for Gas-Phase CO2 Conversion: Catalysts Design and Process Modelling Validation
Gandara-Loe, J; Portillo, E; Odriozola, JA; Reina, TR; Pastor-Perez, LFrontiers in Chemistry, 9 (2021) 785571 DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2021.785571
Abstract
The exponential growth of greenhouse gas emissions and their associated climate change problems have motivated the development of strategies to reduce CO2 levels via CO2 capture and conversion. Reverse water gas shift (RWGS) reaction has been targeted as a promising pathway to convert CO2 into syngas which is the primary reactive in several reactions to obtain high-value chemicals. Among the different catalysts reported for RWGS, the nickel-based catalyst has been proposed as an alternative to the expensive noble metal catalyst. However, Ni-based catalysts tend to be less active in RWGS reaction conditions due to preference to CO2 methanation reaction and to the sintering and coke formation. Due to this, the aim of this work is to study the effect of the potassium (K) in Ni/CeO2 catalyst seeking the optimal catalyst for low-temperature RWGS reaction. We synthesised Ni-based catalyst with different amounts of K:Ni ratio (0.5:10, 1:10, and 2:10) and fully characterised using different physicochemical techniques where was observed the modification on the surface characteristics as a function of the amount of K. Furthermore, it was observed an improvement in the CO selectivity at a lower temperature as a result of the K-Ni-support interactions but also a decrease on the CO2 conversion. The 1K catalyst presented the best compromise between CO2 conversion, suppression of CO2 methanation and enhancing CO selectivity. Finally, the experimental results were contrasted with the trends obtained from the thermodynamics process modelling observing that the result follows in good agreement with the modelling trends giving evidence of the promising behaviour of the designed catalysts in CO2 high-scale units.
Noviembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2021.785571
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Influence of helium incorporation on growth process and properties of aluminum thin films deposited by DC magnetron sputtering
Ibrahim, S; Lahboub, FZ; Brault, P; Petit, A; Caillard, A; Millon, E; Sauvage, T; Fernandez, A; Thomann, AlSurface & Coatings Technology, 426 (2021) 127808 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127808
Abstract
The effect of helium content on the morphology, crystallinity, and composition of aluminum films was investigated by depositing He-loaded Al films onto Si substrates via direct current (DC) magnetron sputtering in different Ar/He plasma mixtures. Three different plasma regimes were identified depending on the percentage of He in the gas phase. For a low He to total gas ratio (ΓHe ≤ 70%), the plasma is dominated by argon, where Ar+ ions contribute to sputter out the target atoms. The films deposited in this regime exhibited the classical dense columnar structure and contain very low amount of He (below 2%). Then, as ΓHe increases, helium ions begin to be formed and more fast He neutrals reach the substrate, affecting the film growth. As He amount increased in the gas phase up to 95%, the proportion of He inserted in the films rised up to ⁓15 at. %. Moreover, bubbles/porosity were formed inside the films; those obtained in pure He plasma presented a highly porous fiberform nanostructure. All results confirmed that the modification of the film characteristics was related to the change of the deposition conditions when Ar was replaced by He and to the insertion/release mechanisms of He during the growth.
Noviembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127808
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
By-products revaluation in the production of design micaceous materials
Mouchet, A; Raffin, F; Cota, A; Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDAplied Clay Science, 214 (2021) 106292 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2021.106292
Abstract
One of the main objectives of a sustainable development and circular economy is the recycling of by-products generated in industrial and agricultural production processes. One of the possible solution is the use of such by-product materials in the synthesis of environmental adsorbents. In the current research, we present the synthesis of a high charge swelling mica with enhance adsorbent properties from blast furnace slag and rice husk ash. Moreover, to ensure the sustainable synthesis a natural bentoniteis used as Si and Al source. Thus, the current study investigated the fabrication of swelling high charged micas, Na-Mn (n (layer charge) = 2 or 4), from FEBEX bentonite, blast furnace slag and rice husk ash thorough the NaCl melt method. The reaction yield, cation framework distribution and structural characteristic of micas have been studied thorough X-ray Diffraction and Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. The yields of Na-Mn synthesis and degree of purity of the mica depends on the nature of these precursors. Thus, a sustainable, non-expensive and environmental friendly process has been evaluated.
Noviembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2021.106292
Materiales Coloidales
NaY(MoO4)(2)-based nanoparticles: synthesis, luminescence and photocatalytic properties
Nunez, NO; Gomez-Gonzalez, E; Calderon-Olvera, RM; Becerro, AI; Colon, G; Ocana, MDalton Transactions, 50 (2021) 16539-16547 DOI: 10.1039/d1dt02365a
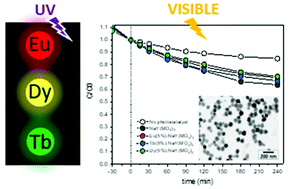
Abstract
Abstract
We report on a novel synthesis method, which produces NaY(MoO4)(2) nanoparticles having an almost spherical shape and hydrophilic character. The procedure is also suitable for the preparation of NaY(MoO4)(2)-based nanophosphors by doping this host with lanthanide cations (Eu3+, Tb3+ and Dy3+), which, under UV illumination, exhibit intense luminescence whose color is determined by the selected doping cation (red for Eu3+, green for Tb3+ and yellow for Dy3+). The effects of the cations doping level on the luminescent properties are analyzed in terms of emission intensities and luminescent lifetime, to find the optimum phosphors. Finally, the performance of these nanophosphors and that of the undoped system for the photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B, used as a model compound, is also analyzed.
Noviembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1039/d1dt02365a
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Extraction of microstructural parameters from sculptured thin films nanoindentation
Gaillard, Y; Jimenez-Pique, E; Oliva-Ramirez, M; Rico, VJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARSurface & Coatings Technology, 425 (2021) 127696 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127696
Abstract
This work deals with the indentation analysis of nanocolumnar thin films and the difficulties encountered to deduce relevant mechanical parameters by this methodology. SiO2 thin films prepared by physical vapour oblique angle deposition with different nanocolumnar microstructures have been subjected to indentation analysis. Despite the fact that the films had been made of the same material, deposited on the same substrate and had similar thickness, their indentation responses were different and depended on their particular microstructure. It has been also realised that the measured hardness and elastic modulus variation with the indentation depth were length scale dependent and that there is not a unique analytical thin-film nanoindentation model to extract the mechanical properties from the experimental nanoindentation curves. To overcome these limitations a numerical finite element model (FEM) of the nanocolumnar coatings has been built to figure out the contributions of the different physical phenomena intervening in the indentation process. This FEM simulation relies on a description of the elasto-plastic microstructural units of the coatings and the contact friction interactions between them. Based on this simulation a parametrical representation, incorporating two length scales and the contributions of densification and/or the buckling of nanocolumnar units, has been developed to account for the evolution of the apparent elastic modulus deduced from numerical indentation tests. A Hall-Petch modification of this description considering two length scales instead of the common approximation considering a single length scale has rendered the best agreement with the elastic values determined experimentally. Although, at the present stage, the particular microstructure of the films can not be deduced from the evolution of their elastic moduli with the indentation depth, the obtained results and their interpretation constitute a first though essential step for the elaboration of an inverse analysis methodology capable of correlating microstructure and elastic response of nanocolumnar coatings.
Noviembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127696
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Impact of flame confinement with inert ceramic foams on the particulate emissions of domestic heating systems
Ciria, D; Orihuela, MP; Becerra, JA; Chacartegui, R.; Ramirez-Rico, J.Fuel, 304 (2021) 121264 DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.121264
Abstract
Small solid biomass combustion systems are among the main contributors to the global particulate emissions share, and cheap, efficient abatement systems are not yet available for them. The placement of inert porous material to confine the combustion region is being recently explored as a possible mitigation system for this kind of pollution. However, given the complexity of biomass thermochemical decomposition processes, it is challenging to justify the performance of these systems on the basis of a physicochemical understanding. A foundational experiment-based study is carried out in this work to understand how combustion confinement affects the particulate emissions production mechanisms. A combustion unit was designed and built to systematically test ceramic foams with different porosities: keeping constant airflow and fuel feed rates. A comprehensive characterisation study was carried out on the solid biomass fuel, the temperature profile, the particulate emissions, and the remaining solid residue. The results evidenced that the use of foams has a substantial impact on the temperature distribution in the combustion chamber. The higher the cell density of the foam, the higher and more homogeneous are the temperatures reached in the combustion bed. This fact improved the thermal decomposition process of the pellets due to a better air-fuel mixture, leading to a reduction of the solid particulate matter emissions by more than 70%. These findings suggest that the use of an inert porous material above the combustion region might be a feasible solution for particulate emission control in small-size biomass combustion technology.
Noviembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.121264
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Assessing the impact of textural properties in Ni-Fe catalysts for CO2 methanation performance
Gonzalez-Castano, M; de Miguel, JCN; Boelte, JH; Centeno, MA; Klepel, O; Arellano-Garcia, HMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 327 (2021) 111405 DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2021.111405
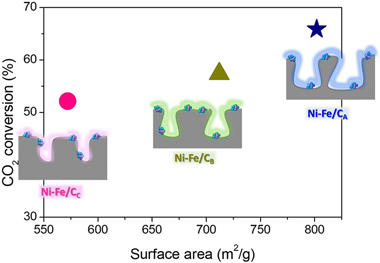
Abstract
In heterogeneous catalysis, the benefits of employing adequate textural properties on the catalytic performances are usually stated. Nevertheless, the quantification of the extent of improvement is not an easy task since variations on the catalysts' specific areas and pore structures might involve modifications on a number of other surface catalytic features. This study establishes the impact of the catalyst textural properties on the CO2 methanation performance by investigating bimetallic Ni–Fe catalysts supported over carbon supports with different textural properties regarding surface area and pore structure. The comparable metal loading and dispersions attained for all systems enabled establishing forthright relationships between the catalyst textural properties and CO2 methanation rate. Once the influence of the external mass diffusions on the catalysts’ performance was experimentally discarded, the estimated Thiele modulus and internal effectiveness (φ and ηEff) values showed that the catalyst performance was majorly governed by the surface reaction rate whilst the pore size affected in no significant manner within the examined range (Dpore = 10.2 to 5.8 nm). Therefore, the rapport between the catalyst performance and surface area was quantified for the CO2 methanation reaction over Ni–Fe catalysts: increasing the surface area from 572 to 802 m2/g permit obtaining ca. 10% higher CO2 conversions.
Noviembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2021.111405
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Waterproof-breathable films from multi-branched fluorinated cellulose esters
Tedeschi, G; Guzman-Puyol, S; Ceseracciu, L; Benitez, JJ; Goldoni, L; Koschella, A; Heinze, T; Cavallo, G; Dichiarante, V; Terraneo, G; Athanassiou, A; Metrangolo, P; Heredia-Guerrero, JACarbohydrate Polymers, 271 (2021) 118031 DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118031
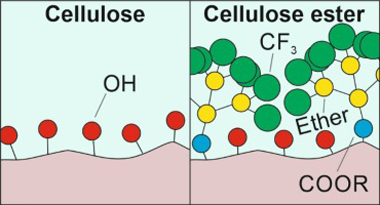
Abstract
Cellulose ester films were prepared by esterification of cellulose with a multibranched fluorinated carboxylic acid, "BRFA" (BRanched Fluorinated Acid), at different anhydroglucose unit:BRFA molar ratios (i.e., 1:0, 10:1, 5:1, and 1:1). Morphological and optical analyses showed that cellulose-BRFA materials at molar ratios 10:1 and 5:1 formed flat and transparent films, while the one at 1:1 M ratio formed rough and translucent films. Degrees of substitution (DS) of 0.06, 0.09, and 0.23 were calculated by NMR for the samples at molar ratios 10:1, 5:1, and 1:1, respectively. ATR-FTIR spectroscopy confirmed the esterification. DSC thermograms showed a single glass transition, typical of amorphous polymers, at -11 degrees C. The presence of BRFA groups shifted the mechanical behavior from rigid to ductile and soft with increasing DS. Wettability was similar to standard fluoropolymers such as PTFE and PVDF. Finally, breathability and water uptake were characterized and found comparable to materials typically used in textiles.
Noviembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118031
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Nanophotonics for current and future white light-emitting devices
Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Lozano, GJournal of Applied Physics, 130 (2021) 200901 DOI: 10.1063/5.0065825
Abstract
Photonic nanostructures have proven useful to enhance the performance of a wide variety of materials and devices for sensing, catalysis, light harvesting, or light conversion. Herein, we discuss the role of nanophotonics in current and next-generation designs of white light-emitting diodes (LEDs). We discuss recent developments on luminescent materials designed as alternatives to rare earth-doped inorganic microcrystals, i.e., phosphors, for color conversion in LEDs, which has opened the door to the integration of resonant photonic architectures. Nanophotonics enables the devised light-matter interaction with luminescent materials in the nanoscale, which allows providing emitting devices with both enhanced performance and novel functionalities to tackle technological challenges
Noviembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1063/5.0065825
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
HfB2 ceramic polycrystals: A low-temperature metal-like ceramic at high temperatures?
Zapata-Solvas, E; Moshtaghioun, BM; Gomez-Garcia, D; Dominguez-Rodriguez, A; Lee, WEScripta Materialia, 203 (2021) 114037 DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114037
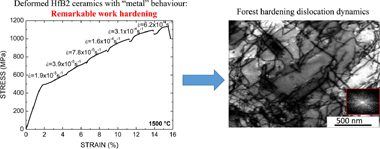
Abstract
Hafnium diboride (HfB2) is a highly refractory (melting above 3000 degrees C) ceramic with many potential applications at high temperatures. To enable its use at temperature for extended periods its high-temperature plasticity must be known. This paper examines the mechanical response at temperatures between 900 degrees C and 2000 degrees C in air and in a reducing atmosphere, interpreting the data in the frame of classical models for the plasticity of compact-packed metals at low temperatures. In particular, the Friedel law and the principle of similitude for dislocation patterning are assessed. This reveals that HfB2 is a singular example of a ceramic material with "metal" mechanical behaviour.
Octubre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114037
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Effect of potassium loading on basic properties of Ni/MgAl2O4 catalyst for CO2 reforming of methane
Azancot, L; Bobadilla, LF; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAJournal of CO2 Utilization, 52 (2021) 101681 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2021.101681
Abstract
Coke deposition is one of the key issues in the dry reforming of methane on Ni catalysts. In the present work, we investigate the effect of potassium addition for suppressing carbon deposition in the Dry Reforming of Methane. The results obtained demonstrated that potassium contents above 3 wt% promote carbon gasification, favouring both Reverse Water Gas Shift and Boudouard reaction. Strong basic Mg-O-K sites are responsible for these reactions allowing the suppression of carbon deposits and allowing the stability of the catalyst.
Octubre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2021.101681
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photocatalytic Treatment of Stained Wastewater Coming from Handicraft Factories. A Case Study at the Pilot Plant Level
Murcia Mesa, JJ; Hernández Niño, JS; González, W; Rojas, H; Hidalgo, MC; Navío, JAWater, 13 (2021) 2705 DOI: 10.3390/w13192705
Abstract
UV/H2O2 process and TiO2-based photocatalysis were studied in the present work. The effectiveness of these methods was tested in the treatment of effluents taken from handicraft factories. Microorganisms, dyes, and different organic pollutants were detected in the industrial effluents. The experimental procedure for the wastewater treatment was carried out in a patented sunlight reactor on a pilot plant scale. From this study, UV/H2O2 was found to be the best treatment for dye elimination. The optimal peroxide dosage for the degradation of dyes and the elimination of bacteria was 0.07 M. In this case, 70.80% of discoloration was achieved after 7 h of sunlight exposure, under an average sunlight intensity of 3.42 W/m2. The photocatalytic treatment based on TiO2 achieved the highest elimination of coliform bacteria and the lowest TOC value; however, the presence of this material in the reactor had a detrimental effect on the overall elimination of dyes. A combination of both UV/H2O2 and TiO2 treatments significantly improves the dyes discoloration, the elimination of bacteria, and the organic compounds degradation. Some of the results of this study were presented at the 4th Congreso Colombiano de Procesos Avanzados de Oxidación, 4CCPAOx.
Octubre, 2021 · DOI: 10.3390/w13192705
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Development of a novel PANI@WO3 hybrid composite and its application as a promising adsorbent for Cr(VI) ions removal
Abdelghani Hsinia, Yassine Naciri, Mohamed Laabd, Asmae Bouziani, J.A.Navío, F.Puga, Rabah Boukherroub, Rajae Lakhmiri, Abdallah AlbourineJournal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9 (2021) 105885 DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.105885

Abstract
In the current study, an in-situ oxidative polymerization method was used to synthesize polyaniline-coated tungsten trioxide biphasic composite (PANI@WO3). The as-developed composite material properties were elucidated using different characterization tools such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), N2 sorption-desorption isotherm, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The PANI@WO3 was further applied to remove hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) from aqueous solutions. The results demonstrated that the optimal removal efficacy was achieved at pH 2. Meanwhile, the pseudo-second-order kinetic and isotherm of the Langmuir model were fitted for Cr(VI) adsorption. Cr(VI) amount of 549.37 mg·g−1 was the maximum capacity of adsorption attained for PANI@WO3, which is significantly higher than that of existing adsorbents. From a thermodynamic point of view, the Cr(VI) adsorption process occurred spontaneously and endothermically. Importantly, PANI@WO3 still exhibited an excellent adsorption capability after five regeneration cycles, indicating the potential reusability of the PANI@WO3 composite. XPS analysis of PANI@WO3 surface after adsorption of Cr(VI) confirmed its adsorption and concomitant reduction into Cr(III) ions. The transfer of mass phenomenon, electrostatic attraction, and reduction reaction were the primary processes for Cr(VI) ions elimination. These findings revealed that the synthesized PANI@WO3 exhibited a high potential for wastewater treatment containing Cr(VI).
Octubre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.105885
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Mechanically Switchable Wetting Petal Effect in Self-Patterned Nanocolumnar Films on Poly(dimethylsiloxane)
Parra-Barranco, J; Lopez-Santos, C; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Barranco, ANanomaterials, 11 (2021) 2566 DOI: 10.3390/nano11102566
Abstract
Switchable mechanically induced changes in the wetting behavior of surfaces are of paramount importance for advanced microfluidic, self-cleaning and biomedical applications. In this work we show that the well-known polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) elastomer develops self-patterning when it is coated with nanostructured TiO2 films prepared by physical vapor deposition at glancing angles and subsequently subjected to a mechanical deformation. Thus, unlike the disordered wrinkled surfaces typically created by deformation of the bare elastomer, well-ordered and aligned micro-scaled grooves form on TiO2/PDMS after the first post-deposition bending or stretching event. These regularly patterned surfaces can be reversibly modified by mechanical deformation, thereby inducing a switchable and reversible wetting petal effect and the sliding of liquid droplets. When performed in a dynamic way, this mechanical actuation produces a unique capacity of liquid droplets (water and diiodomethane) transport and tweezing, this latter through their selective capture and release depending on their volume and chemical characteristics. Scanning electron and atomic force microscopy studies of the strained samples showed that a dual-scale roughness, a parallel alignment of patterned grooves and their reversible widening upon deformation, are critical factors controlling this singular sliding behavior and the possibility to tailor their response by the appropriate manufacturing of surface structures.
Octubre, 2021 · DOI: 10.3390/nano11102566
Reactividad de Sólidos
Relevance of Particle Size Distribution to Kinetic Analysis: The Case of Thermal Dehydroxylation of Kaolinite
Arcenegui-Troya, J;Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LAProcesses, 9 (2021) 1852 DOI: 10.3390/pr9101852
Abstract
Kinetic models used for the kinetic analysis of solid-state reactions assume ideal conditions that are very rarely fulfilled by real processes. One of the assumptions of these ideal models is that all sample particles have an identical size, while most real samples have an inherent particle size distribution (PSD). In this study, the influence of particle size distribution, including bimodal PSD, in kinetic analysis is investigated. Thus, it is observed that PSD can mislead the identification of the kinetic model followed by the reaction and even induce complex thermoanalytical curves that could be misinterpreted in terms of complex kinetics or intermediate species. For instance, in the case of a bimodal PSD, kinetics is affected up to the point that the process resembles a reaction driven by a multi-step mechanism. A procedure for considering the PSD in the kinetic analysis is presented and evaluated experimentally by studying the thermal dehydroxylation of kaolinite. This process, which does not fit any of the common ideal kinetic models proposed in the literature, was analyzed considering PSD influence. However, when PSD is taken into account, the process can be successfully described by a 3-D diffusion model (Jander's equation). Therefore, it is concluded that the deviations from ideal models for this dehydroxylation process could be explained in terms of PSD.
Octubre, 2021 · DOI: 10.3390/pr9101852
Reactividad de Sólidos
Scaling-up the Calcium-Looping Process for CO2 Capture and Energy Storage
Ortiz, C; Valverde, JM; Chacartegui, R; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Gimenez-Gavarrell, PKona Powder and Particle Journal, 38 (2021) 189-209 DOI: 10.14356/kona.2021005
Abstract
The Calcium-Looping (CaL) process has emerged in the last years as a promising technology to face two key challenges within the future energy scenario: energy storage in renewable energy-based plants and CO2 capture from fossil fuel combustion. Based on the multicycle calcination-carbonation reaction of CaCO3 for both thermochemical energy storage and post-combustion CO2 capture applications, the operating conditions for each application may involve remarkably different characteristics regarding kinetics, heat transfer and material multicycle activity performance. The novelty and urgency of developing these applications demand an important effort to overcome serious issues, most of them related to gas-solids reactions and material handling. This work reviews the latest results from international research projects including a critical assessment of the technology needed to scale up the process. A set of equipment and methods already proved as well as those requiring further demonstration are discussed. An emphasis is put on critical equipment such as gas-solids reactors for both calcination and carbonation, power block integration, gas and solids conveying systems and auxiliary equipment for both energy storage and CO2 capture CaL applications.
Octubre, 2021 · DOI: 10.14356/kona.2021005
Reactividad de Sólidos
Pure perovskite BiFeO3-BaTiO3 ceramics prepared by reaction flash sintering of Bi2O3-Fe2O3-BaTiO3 mixed powders
Taibi, A; Chaguetmi, S; Sánchez-Jiménez, PE; Perejón, A; García, JE; Satha, H; Pérez-Maqueda, LACeramics International, 47 (2021) 26947-26954 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.06.108
Abstract
In this work, the 0.67BiFeO(3)-0.33BaTiO(3) ferroelectric ceramic was prepared by Reaction Flash Sintering (RFS). This preparation technique combines synthesis and sintering in a single Flash experiment. The starting oxides reacted during the flash to produce a stoichiometric well-sintered solid solution at a temperature of 858 degrees C by applying a modest field of 35 V cm(-1). The process takes place in a matter of seconds, which allows obtaining a pure perovskite structure without secondary phases. X-ray diffraction (XRD) results show the mixture of rhombohedral and pseudocubic phases expected for a composition that lies within a morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) region, since a significant splitting is observed in the reflections at 2 theta values of 39 degrees and 56.5 degrees. The microstructure exhibit a peculiar bimodal grain size distribution that determines the electrical properties. As compared with previous results, flash-prepared 0.67BiFeO(3)-0.33BaTiO(3) evidences smaller grain size, as well as slightly lower remanent polarization (P-r) and smaller coercive field (E-c) under similar electric fields. It is also demonstrated that the preparation by RFS provides benefits regarding electrical energy consumption.
Octubre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.06.108
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Photonic sensor systems for the identification of hydrocarbons and crude oils in static and flow conditions
Gil-Rostra, J; Quintero-Moreno, S; Rico, VJ; Yubero, F; Sanza, FJ; Casquel, R; Gallo-Valverde, E; Jara-Galan, ME; Sanz-Sanz, P; Holgado, M; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARSensors and Actuators B-Chemical, 344 (2021) 130265 DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2021.130265
Abstract
Identification of hydrocarbons and crude oils is typically carried out with samples that, taken from natural sources or refineries, must be brought to the laboratory for their analysis with rather sophisticated instruments. Alternatively, "in situ" procedures have been also developed for this purpose. In this work, we propose the use of a series of several sensor systems based on photonic transducers in the form of chips for the identification and classification of crude oils and hydrocarbons through the determination of their refractive index in the visible and absorption in the near infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Two of the photonic transducers rely on modifications of a Bragg microcavity and they monitor the changes in visible light interference phenomena that occur in response to the variation of the refractive index of oils. The third one, in the form of a dielectric mirror, monitors the near infrared absorption of crude oils and hydrocarbons through the recording of a transflectance spectrum. The capacity of these transducers for crude oil identification is proved by the analysis of a series of oils and distilled fractions that have been properly identified and classified as a function of their density and partition of long hydrocarbon chains. The three photonic transducers are operated with optical fibers and can be used in static and dynamic modes, this latter under conditions that are especially well-suited for "insitu" analysis of oil streams in real facilities. The proved resistance of the chips to high pressure and temperature conditions supports their suitability to withstand harsh working environments as those existing in extraction wells.
Octubre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2021.130265
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Plasma-Assisted Deposition of TiO2 3D Nanomembranes: Selective Wetting, Superomniphobicity, and Self-Cleaning
Montes, L; Roman, JM; Garcia-Casas, X; Castillo-Seoane, J; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Barranco, A; Lopez-Santos, C; Borras, AAdvanced Materials Interfaces (2021) 2100767 DOI: 10.1002/admi.202100767
Abstract
Fabrication of tunable wetting surfaces is sought for the last years given its importance on energy, biomaterials and antimicrobials, water purification, microfluidics, and smart surfaces. Liquid management on surfaces mainly depends on the control at the micro- and nanoscale of both roughness and chemical composition. Herein, the combination of a soft-template method and plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition is presented for the synthesis of TiO2 nanofibers on porous substrates such as cellulose and stainless-steel membranes. The protocol, carried out under mild conditions, produces 3D nanomembranes with superhydrophobicity and oleophilicity that are tested as microliter water/oil filters. Photoactivation of TiO2 by UV illumination provides a straightforward approach for wetting tunability that converts the surface into amphiphilic. A final chemical modification of the TiO2 nanofibers by embedding them in an elastomeric polymeric shell and by fluorine-based grafting opens the path toward the formation of superomniphobic and self-cleaning surfaces with long-lasting lifetimes. Thus, a reliable procedure is demonstrated for the fabrication of TiO2 nanofibers, which allows the modification of porous supports and provides an innovative route for the development of 3D nanomembranes with under design wetting. This protocol is extendable to alternative metal oxides, metals, and core@shell nanoarchitectures with potential multifunctionalities.
Octubre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1002/admi.202100767
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Effect of Al content on the hardness and thermal stability study of AlTiN and AlTiBN coatings deposited by HiPIMS
Mendez, A; Monclus, MA; Santiago, JA; Fernandez-Martinez, I; Rojas, TC; Garcia-Molleja, J; Avella, M; Dams, N; Panizo-Laiz, M; Molina-Aldareguia, JMSurface & Coatings Technology, 422 (2021) 127513 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127513
Abstract
The microstructure, mechanical properties and thermal stability of AT(x)Ti(1-x)N and Al1Ti1-xBN coatings grown by reactive high-power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS) have been analyzed as a function of Al/(Al + Ti) ratio (x) between 0.5 and 0.8. The coatings were predominantly formed by a face-centered cubic Ti(Al)N crystalline phase, both with and without B, even for x ratios as high as 0.6, which is higher than the ratio typically encountered for AlxTi1-xN coatings deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering. B doping, in combination with the highly energetic deposition conditions offered by HiPIMS, results in the suppression of the columnar grain morphology typically encountered in AlxTi1-xN coatings. On the contrary, the AlxTi1-xN coatings grown by HiPIMS present a dense nanocomposite type microstructure, formed by nanocrystalline Ti(Al) N domains and amorphous regions composed of Ti(Al)B 2 and BN. As a result, high-Al content (x approximate to 0.6) AlxTi1-xN coatings grown by HiPIMS offer higher hardness, elasticity and fracture toughness than AlxTi1-xN coatings. Moreover, the thermal stability and the hot hardness are substantially enhanced, delaying the onset of formation of the detrimental hexagonal AlN phase from 850 degrees C in the case of Al0.6Ti0.4N, to 1000 degrees C in the case of Al0.6Ti0.4N.
Septiembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127513
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photocatalytic production of hydrogen and methane from glycerol reforming over Pt/TiO2–Nb2O5
Iervolino, G; Vaiano, V; Murcia, JJ; Lara, AE; Hernández, JS; Rojas, H; Navío, JA; Hidalgo, MCInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.09.111
Abstract
In this study, platinized mixed oxides (TiO2–Nb2O5) were tested on photocatalytic hydrogen production from a glycerol solution under UV light. Different samples with different Ti:Nb ratios were prepared by using a simple method that simultaneously combined a physical mixture and a platinum photochemical reduction. This method led to improved physicochemical properties such as low band gap, better Pt nanoparticle distribution on the surface, and the formation of different Pt species. Niobia content was also found to be an important factor in determining the overall efficiency of the Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 photocatalyst in the glycerol reforming reaction. The photocatalytic results showed that Pt on TiO2–Nb2O5 enhanced hydrogen production from the aqueous glycerol solution at a 5 wt% initial glycerol concentration. The influence of different operating conditions such as the catalyst dosage and initial glycerol concentration was also evaluated. The results indicated that the best hydrogen and methane production was equal to 6657 μmol/L and 194 μmol/L, respectively after 4 h of UV radiation using Pt/Ti:Nb (1:2) sample and with 3 g/L of catalyst dosage. Moreover, the role of water in photocatalytic hydrogen production was studied through photocatalytic activity tests in the presence of D2O. The obtained results confirmed the role of water molecules on the photocatalytic production of hydrogen in an aqueous glycerol solution.
Septiembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.09.111
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Nb-C thin films prepared by DC-MS and HiPIMS: Synthesis, structure, and tribomechanical properties
Sala, N; Abad, MD; Sánchez-López, JC; Caro, J; Colominas, CSurface & Coatings Technology, 422 (2021) 127569 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127569

Abstract
Nanostructured Nb-C thin films were prepared by direct current magnetron sputtering (DC-MS) and high-power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS). The films were characterized in depth by X-ray diffraction (XRD), grazing incidence X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy, electron probe microanalysis, and Raman spectroscopy. The mechanical properties were measured by nanoindentation, and the tribological properties were measured by pin-on-disk tests in ambient air. The wear tracks and ball scars were analyzed by Raman spectroscopy to elucidate the tribochemical reactions that occurred at the contact area and to determine the wear mechanism for each specimen type. The thermal stability of the coatings was studied up to 1000 degrees C using Raman spectroscopy and XRD. The samples prepared by DC-MS were very dense, and the phase composition changed from purely nanocrystalline (Nb2C and NbC) to a mixture of NbC crystals embedded in an amorphous carbon-based matrix (NbC/a-C(:H)). However, the samples prepared by HiPIMS developed a marked columnar morphology with a NbC/a-C(:H) nanocomposite structure. The hardness values ranged from 11 to 20 GPa depending on the deposition technique and the amount of the soft a-C(:H) phase present in the sample. The tribological properties of all the coatings were remarkably good when the carbon content was approximately 50 at.%. The formation of a lubricating sp(2)-rich C tribofilm between the ball and coating during the pin-on-disk tests was observed by Raman spectroscopy. The tribofilm formed preferentially on the samples prepared by HiPIMS, which had higher C contents. At 750 degrees C, the degradation of the NbC phases resulted in the formation of an additional a-C phase and niobium oxides.
Septiembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127569
Materiales Coloidales
Si sputtering yield amplification: a study of the collisions cascade and species in the sputtering plasma
Cruz, J; Sangines, S; Soto-Valle; Muhl; Sierra, I; De Lucio-Morales, O; Mitrani, A; Calderon-Olvera, RM; Mendoza-Perez, R; Machorro-Mejia, RJournal of Physics D-Applied Physics, 54 (2021) 375201 DOI: 10.1088/1361-6463/ac0c4e
Abstract
The sputtering yield amplification (SYA) is a phenomenon based on doping a sputtering target with atoms of higher atomic mass. This doping changes the depth and the direction of the collision cascade in the target surface promoting a higher ejection of target atoms. In this work, we present a new way of generating the SYA phenomenon without the need of expensive and complex deposition systems. This was accomplished by increasing the working pressure and adding small pieces of W, as dopant element, on the racetrack of a Si target. The physical phenomena necessary to promote the SYA, for our experimental parameters, were analysed in two different deposition chambers and two sizes of sputtering targets. Based on the collisions in the gas phase, a calculation on the number of W atoms returning to the racetrack area was made, considering the number of atoms deposited on the thin films, to determine their effect on the cascade of collisions. In addition, calculations with the simulation of metal transport code were developed to determine the location on the racetrack zone the returning atoms were redeposited. By using reference samples placed on the racetrack of the Si target, we found that the percentage of SYA depends on the number of dopant atoms redeposited as well as the depth distribution these atoms had in the racetrack surface.
Septiembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1088/1361-6463/ac0c4e
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Pd-C Catalytic Thin Films Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering for the Decomposition of Formic Acid
Arzac, GM; Fernandez, A; Godinho, V; Hufschmidt, D; de Haro, MCJ; Medran, B; Montes, ONanomaterials, 11 (2021) 2326 DOI: 10.3390/nano11092326
Abstract
Formic acid is an advantageous liquid organic hydrogen carrier. It is relatively nontoxic and can be synthesized by the reaction of CO2 with sustainable hydrogen or by biomass decomposition. As an alternative to more widely studied powdery catalysts, supported Pd-C catalytic thin films with controlled nanostructure and compositions were newly prepared in this work by magnetron sputtering on structured supports and tested for the formic acid decomposition reaction. A two-magnetron configuration (carbon and tailored Pd-C targets) was used to achieve a reduction in Pd consumption and high catalyst surface roughness and dispersion by increasing the carbon content. Activity and durability tests were carried out for the gas phase formic acid decomposition reaction on SiC foam monoliths coated with the Pd-C films and the effects of column width, surface roughness and thermal pre-reduction time were investigated. Activity of 5.04 mol(H2)center dot g(Pd)(-1)center dot h(-1) and 92% selectivity to the dehydrogenation reaction were achieved at 300 degrees C for the catalyst with a lower column width and higher carbon content and surface roughness. It was also found that deactivation occurs when Pd is sintered due to the elimination of carbon and/or the segregation and agglomeration of Pd upon cycling. Magnetron sputtering deposition appears as a promising and scalable route for the one-step preparation of Pd-C catalytic films by overcoming the different deposition characteristics of Pd and C with an appropriate experimental design.
Septiembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.3390/nano11092326
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Examination of the Deactivation Cycle of NiAl- and NiMgAl-Hydrotalcite Derived Catalysts in the Dry Reforming of Methane
Abdelsadek, Z.; Holgado, J.P.; Halliche, D.; Caballero, A.; Cherifi, O.; Gonzalez-Cortes, S.; Masset, P.J.Catalysis Letters, 151 (2021) 2696-2715 DOI: 10.1007/s10562-020-03513-4

Abstract
The importance of the dry reforming of methane (DRM) lies in its capability to upgrade two greenhouse gases (CH4 and CO2) into synthesis gas (CO and H-2), which is one of the main building block for synthesizing hydrocarbons. However, the Ni-based catalysts for DRM reaction usually have a major catalytic stability drawback. This works aims to assess the catalytic activity and stability of two Ni-based catalysts obtained from hydrotalcite (HT) precursors (i.e., NiAl-HT and NiMgAl-HT). The precursors, calcined (-c), reduced (-R) and spent samples were characterized by a series of techniques to gain insight into the influence of MgO over Ni-based catalyst in the drying reforming of methane. An in-situ ageing cycle process to speed up the deactivation of hydrotalcite-derived catalysts showed that the NiMgAl-HTc-R catalyst displayed a higher activity and resistance to coke formation (stability) than NiAl-HTc-R because of the introduction of Mg into hydrotalcite structure in the catalyst precursor. The presence of this element enhances several factors involved in the stability of Ni-based catalysts for the DRM process such as the reducibility and textural features of the catalysts, size and dispersion of Ni-0 nanoparticles and also maintains a good compromise between the acid and base properties of the solid catalysts.
Septiembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1007/s10562-020-03513-4
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Structure-sensitivity of formic acid dehydrogenation reaction over additive-free Pd NPs supported on activated carbon
Santos, J.L.; Megías-Sayago, C.; Ivanova, S.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A.Chemical Engineering Journal, 420 (2021) 127641 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127641
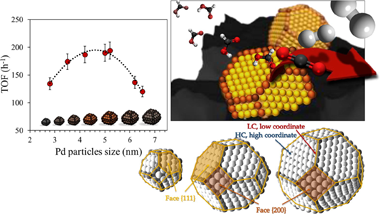
Abstract
In this study the size-activity dependence of palladium based catalysts in formic acid dehydrogenation reaction was investigated and evaluated. A wide range of particle sizes was considered and the catalyst series were prepared upon variation of some synthetic parameters, precursor and solvent nature in particular. Synthesis method variations affect significantly Pd particle size and results in diverse activity toward hydrogen production. An optimal size was observed and explained by the diverse proportion of low and high coordinated Pd states available for different samples within the series. The evaluation of particles much bigger than 6 nm changes importantly the fraction of high and low coordination atoms and allows the clear confirmation of the importance of the presence of low coordination atoms on the surface of catalyst.
Septiembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127641
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Mesoporous Carbon Production by Nanocasting Technique Using Boehmite as a Template
Ortega-Franqueza, M; Ivanova, S; Dominguez, MI; Centeno, MACatalysts, 11 (2021) 1132 DOI: 10.3390/catal11091132

Abstract
A series of mesoporous carbonaceous materials were synthesized by the nanocasting technique using boehmite as a template and glucose as a carbon precursor. After pyrolysis and template removal, the resulting material is a mesoporous carbon that can be additionally doped with N, B and K during prepyrolysis impregnation. In addition, the influence of doping on the morphology, crystallinity and stability of the synthesized carbons was studied using X-ray diffraction, nitrogen physisorption, thermogravimetry, Raman and IR spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy. While the nanocasting process is effective for the formation of mesopores, KOH and urea do not modify the textural properties of carbon. The use of H3PO4 as a dopant, however, led to the formation of an AlPO4 compound and resulted in a solid with a lower specific surface area and higher microporosity. All doped solids present higher thermal stability as a positive effect of the introduction of heteroatoms to the carbon skeleton. The phosphorus-doped sample has better oxidation resistance, with a combustion temperature 120-150 degrees C higher than those observed for the other materials.
Septiembre, 2021 · DOI: 10.3390/catal11091132
- ‹ anterior
- 8 of 37
- siguiente ›














