Artículos SCI
2024
2024
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Nucleation and growth of plasma sputtered silver nanoparticles under acoustic wave activation
Reichel, H; García-Valenzuela, A; Espino-Román, JA; Gil-Rostra, J; Regodón, GF; Rico-Gavira, V; Borrás, A; Gómez-Ramírez, A; Palmero, A; González-Elipe, AR; Oliva-Ramírez, MApplied Surface Science, 669 (2024) 160566
Show abstract ▽
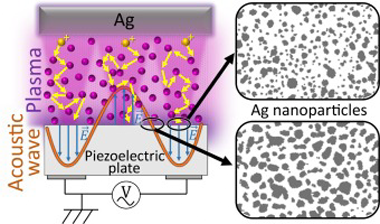
Early results on the plasma deposition of dielectric thin films on acoustic wave (AW) activated substrates revealed a densification pattern arisen from the focusing of plasma ions and their impact on specific areas of the piezoelectric substrate. Herein, we extend this methodology to tailor the plasma deposition of metals onto AW-activated LiNbO3 piezoelectric substrates. Our investigation reveals the tracking of the initial stages of nanoparticle (NP) formation and growth during the submonolayer deposition of silver. We elucidate the specific role of AW activation in reducing particle size, enhancing particle circularity, and retarding NP agglomeration and account for the physical phenomena making these processes differ from those occurring on non-activated substrates. We provide a comparative analysis of the results obtained under two representative plasma conditions: diode DC sputtering and magnetron sputtering. In the latter case, the AW activation gives rise to a 2D pattern of domains with different amounts of silver and a distinct size and circularity for the silver NPs. This difference was attributed to the specific characteristics of the plasma sheath formed onto the substrate in each case. The possibilities of tuning the plasmon resonance absorption of silver NPs by AW activation of the sputtering deposition process are discussed.
Octubre, 2024 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2024.160566
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
In situ XRD and operando XRD-XANES study of the regeneration of LaCo0.8Cu0.2O3 perovskite for preferential oxidation of CO
Pereñiguez, RP; Ferri, DMaterials Today Sustainability, 27 (2024) 100867
Show abstract ▽
Combinations of perovskite-type oxides with transition and precious metals exhibit remarkable regenerating properties that can be exploited for catalytic applications. The objective of the present work was to study the structural changes experienced by LaCo0.8Cu0.2O3 under reducing/oxidizing atmosphere (redox) and Preferential Oxidation of CO (PrOx, with high H2 concentration) conditions and their reversibility. LaCo0.8Cu0.2O3 was prepared by ultrasonic spray combustion and was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS). Structural changes were followed by operando XRD and XAS. Metallic Co and Cu were segregated under both sets of reducing conditions and re-dissolved into the perovskite upon oxidation at 500 °C. Simultaneously, the perovskite-type oxide disappeared under reducing conditions and formed again upon high-temperature oxidation. The effects of this reversible reduction/dissolution of B-site metals on catalyst structure and activity were studied concerning the catalytic process of PrOx. The active phases of cobalt and copper oxides suffer a reduction during the PrOx reaction due to the high H2 concentration; thus, the application of an intermediate oxidation treatment can regenerate the catalytic system and the perovskite can be used for several cycles of reaction and regeneration. In contrast, when this intermediate oxidation treatment is not applied, the catalytic performance decreases in successive activity cycles.
Septiembre, 2024 | DOI: 10.1016/j.mtsust.2024.100867
Reactividad de Sólidos - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
BN nanosheets reinforced zirconia composites: An in-depth microstructural and mechanical study
Muñoz-Ferreiro, C; Reveron, H; Rojas, TC; Reyes, DF; Cottrino, S; Moreno, P; Prada-Rodrigo, J; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Chevalier, J; Gallardo-López, A; Poyacto, RJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 44(10) (2024) 5846-5860
Show abstract ▽
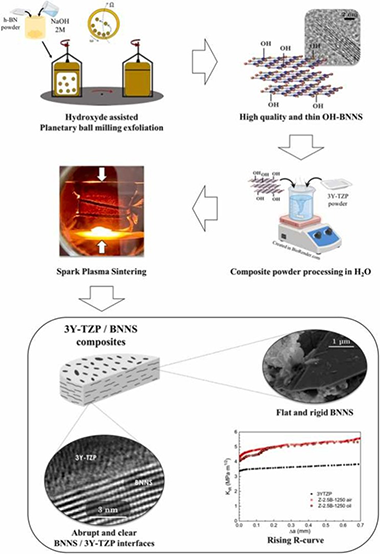
This paper deals with the effect of hydroxylated boron nitride nanosheets (BNNS) incorporation on the microstructural and mechanical features of zirconia ceramics. Few-layered BNNS were synthesized via a simple hydroxide-assisted planetary ball milling exfoliation technique. 3 mol% yttria tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (3Y-TZP) with 2.5 vol% BNNS powders were prepared by an environmentally friendly process in water, and spark-plasma sintered at three temperatures to explore the in-situ reduction of the functionalized BNNS. An exhaustive study by (S)TEM techniques was performed to elucidate the influence of the sintering temperature on the matrix and the 3Y-TZP/BNNS interfaces, revealing that BNNS were homogeneously distributed throughout the matrix with an abrupt transition at 3Y-TZP/BNNS interfaces. BNNS effectively hindered slow crack growth, thus increasing the composite's crack growth resistance by about 30 %. A 1 MPa·m1/2 rising R-curve was also induced by crack bridging.
Agosto, 2024 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2024.02.002
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Titania modifications with fluoride, sulfate, and platinum for photochemical reduction of chromium (VI)
Murcia, JJ; Hernández-Laverde, MS; Correa-Camargo, IA; Rojas-Sarmiento, HA; Navío, JA;Revista Facultad de Ingenieria, Universidad de Antiquia, 112 (2024) 86-97
Show abstract ▽
En este trabajo, la Titania se modificó por sulfatación o fluorización y platino en superficie, con el objetivo de mejorar la eficiencia en la reducción de Cr (VI) en comparación con el material TiO2 base sintetizado por el método sol-gel. Los materiales fueron caracterizados por DRX, SBET, UV-Vis DRS, FRX, TEM, FTIR y XPS. Las modificaciones permitieron obtener una mayor estabilidad en la fase Anatasa y en el área superficial del semiconductor. La adición de F y Pt en el TiO2 provocaron aumentos de absorción en la región visible del espectro electromagnético. Se observó una correlación entre las nuevas propiedades fisicoquímicas obtenidas tras la modificación del TiO2 y el rendimiento fotocatalítico del material. El mejor resultado en la reducción de cromo se obtuvo utilizando Pt-S-TiO2 como fotocatalizador, este material mostró una combinación adecuada de área superficial, alta absorción UV-Vis, alta hidroxilación y la existencia de nanopartículas de Pt en la superficie que favorecen un aumento de la vida media del par electrón-hueco. También se evaluaron parámetros de reacción que demostraron que el mejor desempeño fotocatalítico se obtuvo bajo atmósfera de N2, intensidad de luz de 120 W/m2 y 2 horas de tiempo total de reacción. Así mismo, se observó que aumentar el tiempo de reacción de 2 a 5 horas tuvo un efecto perjudicial sobre la eficiencia en la reducción de Cr (VI).
Julio, 2024 | DOI: 10.17533/udea.redin.20240304
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
New insights for valorization of polyolefins/light alkanes: catalytic dehydrogenation of n-alkanes by immobilized pincer-iridium complexes
Centeno-Vega, I; Megías-Sayago, C; Ivanova, SDalton Transactions, 53 (2024) 11216-11227
Show abstract ▽
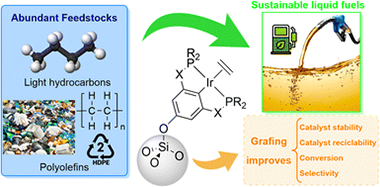
This scientific review delves into the innovative realm of polyolefins/light alkanes valorization through their catalytic dehydrogenation employing pincer-ligated iridium organometallic complexes. These widely studied catalysts exhibit outstanding properties, although the intrinsic characteristics of homogeneous catalysis (such as challenging product–catalyst separation, poor applicability to continuous-flow processes and low recyclability) limit their activity and industrial application, as well as their thermal stability. Through the immobilization of complexes on inorganic supports, these downsides have been bypassed, harnessing the true potential of these catalysts, affording more selective and stable catalysts in addition to facilitating their implementation in industrial processes. The findings described herein contribute to the advancement in the understanding of catalytic processes in hydrocarbon transformations, offering promising avenues for sustainable and selective production of valuable chemical intermediates from readily available feedstocks.
Julio, 2024 | DOI: 10.1039/D4DT00847B
- 1 of 419
- siguiente ›














