Artículos SCI
2020
2020
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Novel procedure for laboratory scale production of composite functional filaments for additive manufacturing
Diaz-Garcia, A; Law, JY; Cota, A; Bellido-Correa, A; Ramirez-Rico, J; Schafer, R; Franco, VMaterials Today Communications, 24 (2020) 101049 DOI: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101049
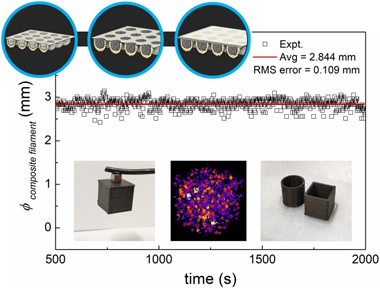
Abstract
Successful 3D printing by material extrusion of functional parts for new devices requires high quality filaments. Uniform homogeneity and good dispersion of particles embedded in filaments typically takes several cycles of extrusion or well-prepared feedstock by injection molding, industrial kneaders or twin-screw compounding. These methods need specific production devices that are not available in many laboratories non-specialized in polymer research, such as those working on different material science and technology topics that try to connect with additive manufacturing. Therefore, laboratory studies are usually limited to compositions and filler concentrations provided by commercial companies. Here, we present an original laboratory scale methodology to custom-prepare the feedstock for extruding magnetic composite filaments for fused filament fabrication (FFF), which is attainable by a desktop single-screw extruder. It consists in encapsulating the fillers in custom made capsules that are used as feedstock and reach the melting area of the extruder maintaining the same concentration of fillers. Results have shown that our approach can create smooth and continuous composite filaments with good homogeneity and printability with fine level of dimensional control. We further show the good dispersion of the particles in the composite filament using X-Ray Tomography, which enabled a 3D reconstruction of the spacial distribution of the embedded magnetic particles. The major advantage of this new way of preparing the composite feedstock is that it avoids the hassle of multiple extrusion runs and industrial machinery, yet providing uniform filaments of well controlled filler concentration, which is predictable and reproducible. The proposed methodology is suitable for different polymer matrices and applicable to other functional particle types, not just limited to magnetic ones. This opens an avenue for further laboratory scale development of novel functional composite filaments, useful for any community. This democratization of complex filament preparation, including consumers preparing their own desired uniform novel filaments, will facilitate to unify efforts nearing 3D printing of new functional devices.
Septiembre, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101049
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Experimental evidence of HCO species as intermediate in the fischer tropsch reaction using operando techniques
Diaz-Sanchez, RM; de-Paz-Carrion, A; Serrera-Figallo, MA; Torres-Lagares, D; Barranco, A; Leon-Ramos, JR; Gutierrez-Perez, JLApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 272 (2020) 119032 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119032
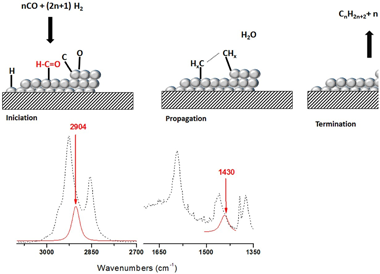
Abstract
Fischer Tropsch's reaction, known from 1925, receives special attention nowadays due to its key role in the CO2 or biomass valorization to liquid fuels and chemicals. Several aspects on the exact mechanism or the role of water in this reaction are not yet completely clear. Formyl species, HCO, have been proposed as the most probable reaction intermediate, but they have never been observed under operation conditions closed to the real ones. In this work, using DRIFTS-MS operando techniques, HCO intermediates are detected under a H2/CO flow and 200 °C. IR bands at 2900 cm−1 and 1440 cm−1 attributed to ν(C–H) and δ(HCO) vibrations modes characterize these species. Evolution of these bands with the reaction time evidences its high reactivity with OH groups, which explains the positive effect of water on the CO conversion previously observed.
Septiembre, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119032
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Tailoring materials by high-energy ball milling: TiO2 mixtures for catalyst support application
Rinaudo, MG; Beltran, AM; Fernandez, MA; Cadus, LE; Morales, MRMaterials Today Chemistry, 17 (2020) 100340 DOI: 10.1016/j.mtchem.2020.100340
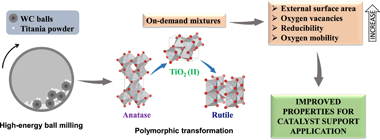
Abstract
We carried out a rational design of catalyst supports by high-energy ball milling. Tailored mixtures of TiO2 crystalline phases were obtained using rotational speed and milling time as variable parameters. Polymorphic transformation from anatase to rutile through high-pressure TiO2 (II) as intermediate was confirmed by X-ray Diffraction (XRD), Raman Spectroscopy and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM). Also, starting material doubled its specific surface area due to particle fragmentation, as confirmed by surface area of Brunauer-Emmet-Teller (S-BET) and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). Defects introduced during milling process generated oxygen vacancies in the surface and bulk of supports, as evidenced by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) and Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR). Furthermore, longer milling time increased reducibility and oxygen mobility of supports, as observed by H-2 Temperature Programmed Reduction (H-2-TPR) and O-2 Temperature Programmed Desorption (O-2-TPD). Phase composition remained unchanged even under extreme conditions, highlighting the stability of unusual TiO2 (II) phase. Properties achieved in present materials could benefit metal-support interactions and play a major role in supported catalysts.
Septiembre, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mtchem.2020.100340
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Elucidating esterification reaction during deposition of cutin monomers from classical molecular dynamics simulations
Bueno, OVM; Benitez, JJ; San-Miguel, MAJournal of Molecular Modeling, 26 (2020) 280 DOI: 10.1007/s00894-020-04544-9
Abstract
The structural behavior of some cutin monomers, when deposited on mica support, was extensively investigated by our research group. However, other events, such as esterification reaction (ER), are still a way to explore. In this paper, we explore possible ER that could occur when these monomers adsorb on support. Although classical molecular dynamics simulations are not able to capture reactive effects, here, we show that they become valuable strategies to analyze the initial structural configurations to predict the most favorable reaction routes. Thus, when depositing aleuritic acid (ALE), it is observed that the loss of capacity to form self-assembled (SA) systems favors different routes to occur ER. In pure ALE bilayers systems, an ER is given exclusively through the -COOH and primary -OH groups. In pure ALE monolayers systems, the ER does not happen when the system is self-assembled. However, for disorganized systems, it is able to occur by two possible routes: -COOH and primary -OH (route 1) and -COOH and secondary -OH (route 2). When palmitic acid (PAL) is added in small quantities, ALE SAMs can now form an ER. In this case, ER occurs mostly through the -COOH and secondary -OH groups. However, when the presence of PAL is dominant, ER can occur with either of both possibilities, that is, routes 1 and 2.
Septiembre, 2020 · DOI: 10.1007/s00894-020-04544-9
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Bimetallic PdAu catalysts for formic acid dehydrogenation
Santos, JL; Leon, C; Monnier, G; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 45 (2020) 23056-23068 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.06.076
Abstract
A series of monometallic and bimetallic palladium gold catalyst were prepared and studied for the formic acid dehydrogenation reaction. Different Pd/Au compositions were employed (PdxAu100-x, where x = 25; 50 and 75) and their impact on alloy structure, particle size and dispersion was evaluated. Active phase composition and reaction parameters such as temperature, formic acid concentration or formate/formic acid ratio were adjusted to obtain active and selective catalyst for hydrogen production. An important particle size effect was observed and related to Pd/Au composition for all bimetallic catalysts.
Septiembre, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.06.076
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Free-Carbon Surface for PtCu Nanoparticles: An In Situ Near Ambient Pressure X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Study
Castillo, R; Navarro-Jaen, S; Romero-Sarria, F; Perez-Dieste, V; Escudero, C; Centeno, MA; Daturi, M; Odriozola, JAJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 124 (2020) 19046-19056 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c04713

Abstract
Usually, nanoparticle synthesis methodologies require the use of organic molecules (capping agent, solvent molecules, etc.), which results in carbon deposits on the nanoparticle surface. These residues modify the surface properties mainly affecting the catalytic behavior. In this work, unsupported poly(vinylpyrrolidone) (PVP)-stabilized PtCu (1:3 molar ratio) bimetallic alloy nanoparticles were synthetized and characterized. An alternative surface cleaning method has been designed, which successfully removes the presence of organic fragments. To address this key issue, we have combined a first nanoparticle washing step with a near ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (NAPXPS) study in order to obtain a clean active site and the total understanding of the carbon elimination mechanism. The dynamic evolution of the surface organic species composition under different gas mixtures at 750 mTorr and 350 degrees C has been studied, and only under CO2 exposure, NAPXPS analysis revealed a total availability of the active site by the removal of the organic nanoparticle coating.
Septiembre, 2020 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c04713
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
The wrinkling concept applied to plasma-deposited polymer-like thin films: A promising method for the fabrication of flexible electrodes
Thiry, Damien; Vinx, Nathan; Damman, Pascal; Aparicio, Francisco F.J.; Tessier, Pierre-Yves; Moerman, David; Leclere, Philippe; Godfroid, Thomas; Deprez, Sylvain; Snyders, RonyPlasma Processes and Polymers, 17 (2020) e2000119 DOI: 10.1002/ppap.202000119
Abstract
In this communication, we report on an innovative solvent-free method that allows for the design of nano-/micropatterns with tuneable dimensions. Our approach is based on the spontaneous wrinkling phenomenon taking place in a bilayer system formed by a mechanically responsive bottom plasma polymer layer and a top aluminum thin film. The dimensions of the wrinkles can be adjusted in a wide range (i.e., from nanometer to micrometer range) by modulating the cross-linking density as well as the thickness of the plasma polymer layer. Finally, it is demonstrated that these wrinkled surfaces could efficiently be used as flexible electrodes. The whole set of our data unambiguously reveals the attractiveness of our method for the fabrication of the micro-/nanopattern with dimensions on demand.
Septiembre, 2020 · DOI: 10.1002/ppap.202000119
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Mg2SiO4-MgAl2O4 directionally solidified eutectics: Hardness dependence modelled through an array of screw dislocations
Moshtaghioun, BM; Gomez-Garcia, D; Pena, JIJournal of The European Ceramic Society, 40 (2020) 4171-4176 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2020.05.015
Abstract
Mg2SiO4-MgAl2O4 eutectic ceramics have been fabricated by means of the laser floating zone (LFZ) technique. The microstructure has revealed as an unusual one at lower growth rate, composed of broken lamellae of MgAl2O4 distributed randomly along one matrix, composed of Mg2SiO4. At higher growth rates, a cell structure with intra-cell lamella structure is dominant. Contrary to most eutectic systems, hardness is not dependent upon the inter-spacing, but it does depend on one characteristic length of lamellae: their perimeter. One simple model based upon the dislocation is proposed, which successfully accounts for such extraordinary hardness law. Accordingly, Mg2SiO4-MgAl2O4 eutectic ceramics fabricated at 50 mm/h growth rate with the smallest MgAl2O4 lamella perimeter favorably showed more elevated hardness (13.4 GPa from Vickers indentation and 15.3 GPa from nanoindentation) and strength (430 MPa) than those found in the monolithic Mg2SiO4 matrix.
Septiembre, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2020.05.015
Materiales Coloidales
Design of a nanoprobe for high field magnetic resonance imaging, dual energy X-ray computed tomography and luminescent imaging
Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Becerro, AI; Corral, A; Garcia-Embid, S; Balcerzyk, M; Garcia-Martin, ML; de la Fuente, JM; Ocana, MJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 573 (2020) 278-286 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.03.101
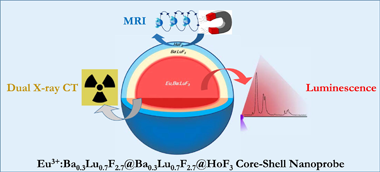
Abstract
The combination of different bioimaging techniques, mainly in the field of oncology, allows circumventing the defects associated with the individual imaging modalities, thus providing a more reliable diagnosis. The development of multimodal endogenous probes that are simultaneously suitable for various imaging modalities, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), X-ray computed tomography (CT) and luminescent imaging (LI) is, therefore, highly recommended. Such probes should operate in the conditions imposed by the newest imaging equipment, such as MRI operating at high magnetic fields and dual-energy CT. They should show, as well, high photoluminescence emission intensity for their use in optical imaging and present good biocompatibility. In this context, we have designed a single nanoprobe, based on a core-shell architecture, composed of a luminescent Eu3+:Ba0.3Lu0.7F2.7 core surrounded by an external HoF3 shell that confers the probe with very high magnetic transverse relaxivity at high field. An intermediate, optically inert Ba0.3Lu0.7F2.7 layer was interposed between the core and the shell to hinder Eu3+-Ho3+ cross-relaxation and avoid luminescence quenching. The presence of Ba and Lu, with different K-edges, allows for good X-ray attenuation at high and low voltages. The core-shell nanoparticles synthesized are good potential candidates as trimodal bioprobes for MRI at high field, dual-energy CT and luminescent imaging.
Agosto, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.03.101
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
An electrochemical evaluation of nitrogen-doped carbons as anodes for lithium ion batteries
Gomez-Martin, A; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Ruttert, M; Winter, M; Placke, T; Ramirez-Rico, JCarbon, 164 (2020) 261-271 DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.04.003
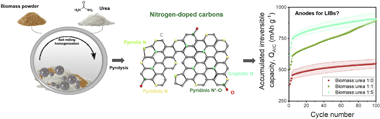
Abstract
New anode materials beyond graphite are needed to improve the performance of lithium ion batteries (LIBs). Chemical doping with nitrogen has emerged as a simple strategy for enhancing lithium storage in carbon-based anodes. While specific capacity and rate capability are improved by doping, little is known about other key electrochemical properties relevant to practical applications. This work presents a systematic evaluation of electrochemical characteristics of nitrogen-doped carbons derived from a biomass source and urea powder as anodes in LIB half- and full-cells. Results show that doped carbons suffer from a continuous loss in capacity upon cycling that is more severe for higher nitrogen contents. Nitrogen negatively impacts the voltage and energy efficiencies at low charge/discharge current densities. However, as the charge/discharge rate increases, the voltage and energy efficiencies of the doped carbons outperform the non-doped ones. We provide insights towards a fundamental understanding of the requirements needed for practical applications and reveal drawbacks to be overcome by novel doped carbon-based anode materials in LIB applications. With this work, we also want to encourage other researchers to evaluate electrochemical characteristics besides capacity and cycling stability which are mandatory to assess the practicality of novel materials.
Agosto, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.04.003
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Disclination dipoles are the Holy Grail for high temperature superplasticity in ceramics
Moshtaghioun, BM; Bejarano-Palma, JA; Garcia, DGScripta Materialia, 185 (2020) 21-24 DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.03.049
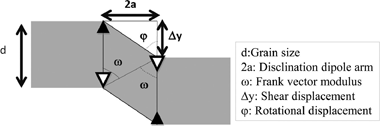
Abstract
A model for high-temperature plasticity of polycrystals controlled by disclination dipoles is proposed that predict a parabolic dependence of the strain rate versus the applied stress. The presence of a precise stationary disclination density explains the origin of plasticity without microstructural invariance, commonly known as superplasticity. The disclination mechanism is universal, although other processes, such as dislocation glide, are superposed to this one in many systems such as metals or metallic alloys. While, in ceramics it is likely to be the only operative mechanism. Activation of disclination dipoles is a necessary condition for plasticity and sufficient one for superplastic yielding.
Agosto, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.03.049
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Thermo-Photocatalytic Methanol Reforming for Hydrogen Production over a CuPd-TiO2 Catalyst
Lopez-Martin, A; Platero, F; Caballero, A; Colon, GChemPhotoChem, 4 (2020) 630-637 DOI: 10.1002/cptc.202000010

Abstract
A bimetallic CuPd/TiO2 system has been prepared by a two-step synthesis and was used for a methanol steam photoreforming reaction. By sequential deposition, palladium is deposited over copper nanoclusters through a galvanic replacement process. Hydrogen production by steam reforming from methanol was achieved by both thermo-photocatalytic and photocatalytic processes. It appears that H-2 production on the bimetallic system is notably higher than the Pd monometallic reference. Moreover this difference in the catalytic performance could be related to the higher CO evolution observed for the monometallic Pd-1.0 TiO2 system which is partially inhibited in the bimetallic catalyst. In addition, an important thermal effect can be envisaged in all cases. Nevertheless, this improved effect in the thermo-photocatalytic process is accompanied by a remarkable CO evolution and SMSI effect (important strong metal-support interactions) that hindered the efficiency as temperature increases. On this basis, optimal operational conditions for H-2 production are obtained for thermo-photocatalytic reforming at 100 degrees C, for which the synergetic effect is higher with lower CO production (H-2/CO=4)
Agosto, 2020 · DOI: 10.1002/cptc.202000010
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Elucidation of Water Promoter Effect of Proton Conductor in WGS Reaction over Pt-Based Catalyst: An Operando DRIFTS Study
Jurado, L; Garcia-Moncada, N; Bobadilla, LF; Romero-Sarria, F; Odriozola, JACatalysts, 10 (2020) 841 DOI: 10.3390/catal10080841

Abstract
A conventional Pt/CeO2/Al(2)O(3)catalyst physically mixed with an ionic conductor (Mo- or Eu-doped ZrO2) was tested at high space velocity (20,000 h(-1)and 80 L h(-1)g(cat)(-1)) under model conditions (only with CO and H2O) and industrial conditions, with a realistic feed. The promoted system with the ionic conductor physically mixed showed better catalytic activity associated with better water dissociation and mobility, considered as a rate-determining step. The water activation was assessed by operando diffuse reflectance infrared fourier transformed spectroscopy (DRIFTS) studies under reaction conditions and the Mo-containing ionic conductor exhibited the presence of both dissociated (3724 cm(-1)) and physisorbed (5239 cm(-1)) water on the Eu-doped ZrO(2)solid solution, which supports the appearance of proton conductivity by Grotthuss mechanism. Moreover, the band at 3633 cm(-1)ascribed to hydrated Mo oxide, which increases with the temperature, explains the increase of catalytic activity when the physical mixture was used in a water gas shift (WGS) reaction.
Agosto, 2020 · DOI: 10.3390/catal10080841
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Influence of Sr-doping on structural, optical and photocatalytic properties of synthesized Ca3(PO4)2
Y.Naciri; A.Hsini; Z.Ajmal; A.Bouddouch; B.Bakiz; J.A.Navío; A.Albourine; J-C.Valmalette; M.Ezahri; A.BenlhachemiJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 572 (2020) 269-280 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.03.105
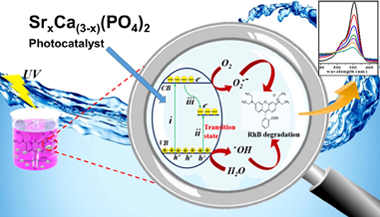
Abstract
Well-crystallized Ca3(PO4)2 doped and un-doped nano-particles with the maximum strontium content (40 wt% Sr) followed by calcination at 800 °C for 3 h were synthesized via facile co-precipitation method. DTA/TGA, X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy dispersive scanning electron microscopy (SEM/EDX), UV–vis diffuse reflectance spectrum (UV–vis DRS), Raman spectroscopy and photoluminescence (PL) techniques were used for material characterization. The (XRD) patterns of as-synthesized Sr-doped Ca3(PO4)2 solid solution samples exhibited a systematic shift toward lower angles by possessing a single rhombohedral crystal structure without any secondary phases. The UV light driven photocatalytic activity was assessed for rhodamine B (RhB) degradation. As a result, ultrafast photodegradation activity was observed after Sr doping. Moreover, the 30 wt% Sr-Ca3(PO4)2 sample showed the highest photocatalytic degradation among the Sr-doped Ca3(PO4)2 samples toward RhB. It was further suggested that as-synthesized 30 wt% Sr-Ca3(PO4)2 superior photocatalytic performance is ascribed to the more proficient partition of photogenerated electron-hole pairs. Furthermore, the involved mechanism of superior photocatalytic performance of the 30 wt% Sr-Ca3(PO4)2 solid solution was also investigated. In addition, regeneration cycles indicated the higher stability of the photocatalyst to be effectively recycled up to four times without any considerable reduction in photocatalytic performance. Thus, these informations further provides us a scalable pathway to fabricate Sr doped Ca3(PO4)2 and its consequent use as an efficient photocatalyst for rhodamine B (RhB) contaminated wastewater treatment.
Julio, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.03.105
Reactividad de Sólidos
ICTAC Kinetics Committee recommendations for analysis of multi-step kinetics
Vyazovkin, S; Burnham, AK; Favergeon, L; Koga, N; Moukhina, E; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Sbirrazzuoli, NThermochimica Acta, 689 (2020) 178597 DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2020.178597
Abstract
The present recommendations have been developed by the Kinetics Committee of the International Confederation for Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry (ICTAC). The recommendations provide guidance on kinetic analysis of multi-step processes as measured by thermal analysis methods such as thermogravimetry (TGA) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Ways of detecting the multi-step kinetics are discussed first. Then, four different approaches to evaluation of kinetic parameters (the activation energy, the pre-exponential factor, and the reaction model) for individual steps are considered. The approaches considered include multi-step model-fitting as well as distributed reactivity, isoconversional, and deconvolution analyses. For each approach practical advice is offered on its effective usage. Due attention is also paid to the typical problems encountered and to the ways of resolving them. The objective of these recommendations is to help a non-expert with efficiently performing multi-step kinetic analysis and interpreting its results.
Julio, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2020.178597
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Sustainable, High-Barrier Polyaleuritate/Nanocellulose Biocomposites
Tedeschi, G; Guzman-Puyol, S; Ceseracciu, L; Benitez, JJ; Cataldi, P; Bissett, M; Heredia, A; Athanassiou, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JAACS Sistainable Chemistry & Engineering, 8 (2020) 10682-10690 DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c00909
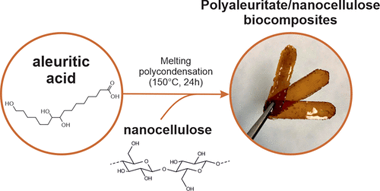
Abstract
Free-standing and flexible biocomposite films formed by a polyaleuritate matrix and nanocellulose fillers (i.e., cellulose nanofibrils) have been fabricated by a sustainable process. For this, 9,10,16-trihydroxyhexadecanoic (aleuritic) acid from shellac and nanocellulose were blended at different ratios in water through a sonication process. Polymerization of the polyhydroxylated fatty acid into polyaleuritate was induced by a solvent-free, melting polycondensation reaction in the oven. These biocomposites were characterized to evaluate their chemical (by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy) and physical (e.g., density, thermal stability, rigidity, gas permeability, surface energy, etc.) properties. The compatibility between the polyester matrix and the polysaccharide fillers was excellent due to the interaction by H bonds of the polar groups of both components. The addition of nanocellulose increased all determined mechanical parameters as well as the wettability and the barrier properties, while the thermal stability and the water uptake were determined by the polyaleuritate matrix. The physical properties of these biocomposites were compared to those of petroleum-based plastics and bio-based polymers, indicating that the developed materials can represent a sustainable alternative for different applications such as packaging.
Julio, 2020 · DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c00909
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Evaluation of the Oxygen Mobility in CePO4-Supported Catalysts: Mechanistic Implications on the Water-Gas Shift Reaction
Navarro-Jaen, S; Bobadilla, LF; Romero-Sarria, F; Laguna, OH; Bion, N; Odriozola, JAJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 124 (2020) 16391-16401 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c03649

Abstract
The hexagonal and monoclinic phases of CePO4 have been demonstrated to be excellent catalytic supports for Pt-based water-gas shift (WGS) catalysts. Consequently, the elucidation of the WGS reaction mechanism in these materials constitutes a fundamental aspect in order to explain their catalytic behavior. Because the observed WGS reaction path is closely related to the absence or presence of oxygen vacancies in the support, the study of the oxygen mobility in these solids constitutes a key factor for the understanding of the structure of the materials and its influence on the reaction mechanism. In this study, the oxygen mobility in CePO4 supports and the corresponding Pt catalysts has been evaluated by means of isotopic exchange experiments using O-18(2) and (CO2)-O-18 as probe molecules. Results demonstrate that the evaluated solids present a low exchange activity when O-18(2) is used, indicating the absence of oxygen vacancies in these solids, thus suggesting a poor influence of the WGS redox mechanism. On the contrary, a high oxygen exchange activity is observed using (CO2)-O-18, demonstrating that the exchange in these materials takes place through the formation of carbonate-like intermediates, thus suggesting the associative mechanism of the WGS reaction as the preferred path in these solids. Operando diffuse reflectance infrared spectroscopy experiments under WGS reaction conditions confirm these results, proving that the WGS reaction in the studied materials takes place through a formate-mediated associative mechanism.
Julio, 2020 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c03649
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Metal catalysts supported on biochars: Part I synthesis and characterization
Santos, JL; Maki-Arvela, P; Monzon, A; Murzin, DY; Centeno, MAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 268 (2020) 118423 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118423
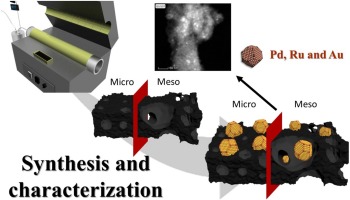
Abstract
In the current study, synthesis and detailed characterization of cellulose biochars as a waste biomass model component and vine shoot biochars as a real waste biomass catalyst was performed. Although initially biochars exhibit poor textural properties, a simple activation process can make them much more suitable as a catalyst supports. A combination of physical (CO2) and chemical activation (ZnCl2) was evaluated. The characterization results indicated that the surface area and pore volume of the biochars have increased significantly by chemical activation treatment with ZnCl2. A series of metal catalysts (Pd, Au and Ru) supported on biochars was prepared and characterized. The prepared materials represent a set of noble metal catalysts supported on biochars with different textural and surface properties, which can be used to evaluate the catalytic role of the active phase and carbon support nature in catalytic reactions of interest, such as hydrodeoxygenation, described in the part II.
Julio, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118423
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Hydrodeoxygenation of vanillin over noble metal catalyst supported on biochars: Part II: Catalytic behaviour
Santos, JL; Maki-Arvela, P; Warna, J; Monzon, A; Centeno, MA; Murzin, DYApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 268 (2020) 118425 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118425
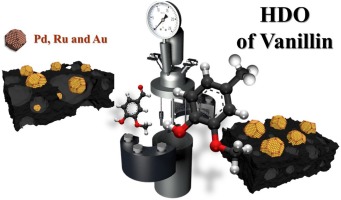
Abstract
Vanillin hydrodeoxygenation was investigated using noble metal (Pd, Au, Ru) supported on active carbon prepared from waste derived biochars, which were produced via pyrolysis in CO2 atmosphere. Chemical activation with ZnCl2 and HNO3 was also used in the preparation of active carbon to enhance the specific surface area and demineralize material, respectively. Both fresh and spent catalysts were characterized with X-ray diffraction, DRIFTS, zeta potential measurement and HR-TEM. The highest selectivity to p-creosol, 92 % selectivity at complete vanillin conversion after 3 h was obtained in vanillin hydrodeoxygenation at 100 degrees C under 30 bar in hydrogen in water with Pd/C catalyst prepared via pyrolysis under CO2 from wine waste and using ZnCl2 as a chemical activation agent. Hydrodeoxygenation activity increased with increasing metal dispersion. A kinetic model including adsorption of vanillin described well the experimental data.
Julio, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118425
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Performance trends in wall-flow diesel particulate filters: Comparative analysis of their filtration efficiency and pressure drop
Orihuela, MP; Chacartegui, R; Gomez-Martin, A; Ramirez-Rico, J; Villanueva, JABJournal of Cleaner Production, 60 (2020) 12063 DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120863
Abstract
Soot and particulate emissions from the transport sector are a major concern worldwide, given their harmful effects on public health and the environment. On-road vehicles are the main contributing source to this kind of pollution. They are strictly regulated in many countries, with limitations on the number and concentration of released particles, and they must be equipped with particle abatement systems. Wall-flow particulate filters are the most popular and effective devices to reduce particulate emissions from diesel and gasoline vehicles. Diesel Particulate Filters (DPFs) have been a recurrent research topic since the last century. There are different research studies analysing different aspects of these systems, at different levels, using different methodologies and different approaches. Their results are not always comparable. This work analyses the latest advances and trends in this technology by comparing two relevant performance parameters: their filtration efficiency and pressure drop. The findings of this study suggest that, in order to be competitive, upcoming DPFs should have filtration efficiencies above 80%, and pressure drops below 10 kPa, for space velocities of 1.5.10(5) h(-1) or more at the clean state. They should reach similar to 100% efficiency after a short operation period, before the soot load reaches 0.2 g/L. Later, they should keep a low pressure drop for a longer time, with a reference of no more than 13 kPa for 6 g/L of soot load. Based on this analysis, this work proposes some test criteria and suggestions for the main parameters.
Julio, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120863
Reactividad de Sólidos
Calcium-Looping Performance of Biomineralized CaCO3 for CO2 Capture and Thermochemical Energy Storage
Arcenegui-Troya, J; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Valverde, JM; Chacartegui, R; Perez-Maqueda, LAIndustrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 59 (2020) 12924-12933 DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.9b05997
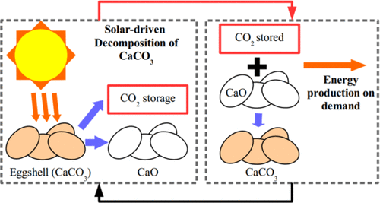
Abstract
The commercial deployment of calcium-looping (CaL)-based technologies relies on the availability of nontoxic, widely available and cheap CaCO3 rich materials. Biomineralized CaCO3 from waste amply fulfills the aforementioned requirements. In the present work, we study the performance of eggshell and snail shell from food waste as CaO precursors for CaL applications. The results obtained suggest the feasible use of these waste materials. The multicyclic conversion exhibited by biomineralized CaCO3 was comparable to that demonstrated by limestone, which is a commonly proposed material for CaL applications. In addition, the temperature needed to completely calcine biomineralized CaCO3 in short residence times is lower than that required to fully calcine limestone. This would mitigate the energy cost of the technology.
Julio, 2020 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.9b05997
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Cost-effective routes for catalytic biomass upgrading
Jin, W; Pastor-Perez, L; Yu, J; Odriozola, JA; Gu, S; Reina, TRCurrent Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 23 (2020) 1-9 DOI: 10.1016/j.cogsc.2019.12.008
Abstract
Catalytic hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) is a fundamental and promising route for bio-oil upgrading to produce petroleum-like hydrocarbon fuels or chemical building blocks. One of the main challenges of this technology is the demand of high-pressure H-2, which poses high costs and safety concerns. Accordingly, developing cost-effective routes for biomass or bio-oil upgrading without the supply of commercial H-2 is essential to implement the HDO at commercial scale. This article critically reviewed the very recent studies relating to the novel strategies for upgrading the biofeedstocks with 'green' H-2 generated from renewable sources. More precisely, catalytic transfer hydro-genation/hydrogenolysis, combined reforming and HDO, combined metal hydrolysis and HDO, water-assisted in-situ HDO and nonthermal plasma technology and self-supported hydrogenolysis are reviewed herein. Current challenges and research trends of each strategy are also proposed aiming to motivate further improvement of these novel routes to become competitive alternatives to conventional HDO technology.
Junio, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cogsc.2019.12.008
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
New biomorphic filters to face upcoming particulate emissions policies: A review of the FIL-BIO-DIESEL project
Orihuela, MP; Chacartegui, R; Martinez-Fernandez, JEnergy, 201 (2020) 117577 DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2020.117577
Abstract
With a high number of diesel vehicles worldwide, particulate emission control is an urgent issue with a global impact, from the health of citizens to commercial future of this technology in some transport segments. Particulate filters are widely used in automotive engines to comply emissions regulations, but current technologies have room for improvement as they add additional backpressure in the exhaust system, and efficient on-board regeneration process is challenging.
The Fil-Bio-Diesel Project is a R&D initiative to improve current particle filtration systems, based on the development of novel biomorphic substrates. By replicating the biologic tissue of a wood precursor, a biomorphic silicon carbide with hierarchic orthotropic microstructure can be produced. The porosity, the pore size, and pore orientation of this bioceramic material can be tailored through the selection of a suitable precursor, widening the initially narrow relationship between filtration efficiency and pressure drop that characterizes granular ceramic materials. In this paper the methodology and main results of the Fil-Bio-Diesel Project are presented. This work shows the peculiar advantages of biomorphic silicon carbide through several experimental studies. The results show the potential of this novel filter substrate to be used in future particulate abatement systems.
Junio, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2020.117577
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
5-Hydroxymethyl-2-Furfural Oxidation Over Au/Ce(x)Zr(1-x)O(2)Catalysts
Megias-Sayago, C; Bonincontro, D; Lolli, A; Ivanova, S; Albonetti, S; Cavani, F; Odriozola, JAFrontiers in Chemistry, 8 (2020) 461 DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2020.00461
Abstract
A series of gold catalysts supported on pure CeO2, ZrO2, and two different Ce-Zr mixed oxides have been prepared and tested in the 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furfural oxidation reaction. All catalysts show high catalytic activity (100% conversion) and important selectivity (27-41%) to the desired product i.e., 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid at low base concentration. Products selectivity changes with the support nature as expected, however, the observed trend cannot be related neither to gold particle size, nor to catalyst reducibility and oxygen mobility. An important relation between the FDCA selectivity and the support textural properties is observed, conducing to the general requirement for optimal pore size for this reaction.
Junio, 2020 · DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2020.00461
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Supported Porous Nanostructures Developed by Plasma Processing of Metal Phthalocyanines and Porphyrins
Obrero, JM; Filippin, AN; Alcaire, M; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Jacob, M; Matei, C; Aparicio, FJ; Macias-Montero, M; Rojas, TC; Espinos, JP; Saghi, Z; Barranco, A; Borras, AFrontiers in Chemistry, 8 (2020) 520 DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2020.00520
Abstract
The large area scalable fabrication of supported porous metal and metal oxide nanomaterials is acknowledged as one of the greatest challenges for their eventual implementation in on-device applications. In this work, we will present a comprehensive revision and the latest results regarding the pioneering use of commercially available metal phthalocyanines and porphyrins as solid precursors for the plasma-assisted deposition of porous metal and metal oxide films and three-dimensional nanostructures (hierarchical nanowires and nanotubes). The most advanced features of this method relay on its ample general character from the point of view of the porous material composition and microstructure, mild deposition and processing temperature and energy constrictions and, finally, its straightforward compatibility with the direct deposition of the porous nanomaterials on processable substrates and device-architectures. Thus, taking advantage of the variety in the composition of commercially available metal porphyrins and phthalocyanines, we present the development of metal and metal oxides layers including Pt, CuO, Fe2O3, TiO2, and ZnO with morphologies ranging from nanoparticles to nanocolumnar films. In addition, we combine this method with the fabrication by low-pressure vapor transport of single-crystalline organic nanowires for the formation of hierarchical hybrid organic@metal/metal-oxide and @metal/metal-oxide nanotubes. We carry out a thorough characterization of the films and nanowires using SEM, TEM, FIB 3D, and electron tomography. The latest two techniques are revealed as critical for the elucidation of the inner porosity of the layers.
Junio, 2020 · DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2020.00520
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Surface Modification of Rutile TiO2 with Alkaline-Earth Oxide Nanoclusters for Enhanced Oxygen Evolution
Rhatigan, S; Sukola, E; Nolan, M; Colon, GACS Applied Nano Materials, 3 (2020) 6017-6033 DOI: 10.1021/acsanm.0c01237
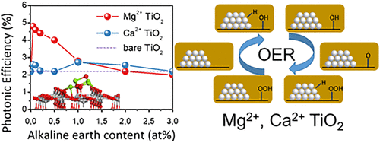
Abstract
The oxygen (O-2) evolution reaction (OER) is accepted as the bottleneck in the overall water splitting and has seen intense interest. In this work, we prepared rutile TiO2 modified with nanoclusters of alkaline-earth metal oxides for the OER. Photocatalytic OER was performed over rutile TiO2 surface-modified with alkaline-earth oxide nanoclusters, namely, CaO and MgO. The O-2 evolution activity is notably enhanced for MgO-modified systems at low loadings and a combination of characterization and first-principles simulations allows interpretation of the role of the nanocluster modification in improving the photocatalytic performance of alkaline-earth-modified rutile TiO2. At such low loadings, the nanocluster modifiers would be small, and this facilitates a close correlation with theoretical models. Structural and surface characterizations of the modified systems indicate that the integrity of the rutile phase is maintained after modification. However, charge-carrier separation is strongly affected by the presence of surface nanoclusters. This improved performance is related to surface features such as higher ion dispersion and surface hydroxylation, which are also discussed with first-principles simulations. The modified systems are reducible so that Ti3+ ions will be present. Water dissociation is favorable at cluster and interfacial sites of the stoichiometric and reduced modified surfaces. Pathways to water oxidation at interfacial sites of reduced MgO-modified rutile TiO2 are identified, requiring an overpotential of 0.68 V. In contrast, CaO-modified systems required overpotentials in excess of 0.85 V for the reaction to proceed.
Junio, 2020 · DOI: 10.1021/acsanm.0c01237
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Recent progress on the enhancement of photocatalytic properties of BiPO4 using π–conjugated materials
Naciri, Y., Hsini, A., Ajmal, Z., Navio, J.A., Bakiz, B., Albourine, A., Ezahri, M., Benlhachemi, A.Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 280 (2020) 102160 DOI: 10.1016/j.cis.2020.102160
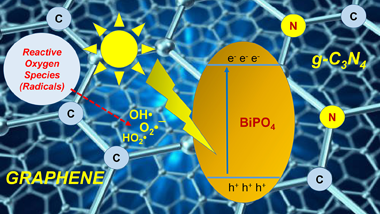
Abstract
Semiconductor photocatalysis is regarded as most privileged solution for energy conversion and environmental application. Recently, photocatalysis methods using bismuth-based photocatalysts, such as BiPO4, have been extensively investigated owing to their superior efficacy regarding organic pollutant degradation and their further mineralization into CO2 and H2O. It is well known that BiPO4 monoclinic phase exhibited better photocatalytic performance compared to Degussa (Evonik) P25 TiO2 in term of ultraviolet light driven organic pollutants degradation. However, its wide band gap, poor adsorptive performance and large size make BiPO4 less active under visible light irradiation. However, extensive research works have been conducted in the past with the aim of improving visible light driven BiPO4 activity by constructing a series of heterostructures, mainly coupled with π-conjugated architecture (e.g., conductive polymer, dye sensitization and carbonaceous materials). However, a critical review of modified BiPO4 systems using π-conjugated materials has not been published to date. Therefore, this current review article was designed with the aim of presenting a brief current state-of-the-art towards synthesis methods of BiPO4 in the first section, with an especial focuses onto its crystal-microstructure, optical and photocatalytic properties. Moreover, the most relevant strategies that have been employed to improve its photocatalytic activities are then addressed as the main part of this review. Finally, the last section presents ongoing challenges and perspectives for modified BiPO4 systems using π–conjugated materials
Junio, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cis.2020.102160
Reactividad de Sólidos
Electrochemically Exfoliated Graphene-Like Nanosheets for Use in Ceramic Nanocomposites
Poyato, R; Verdugo, R; Munoz-Ferreiro, C; Gallardo-Lopez, AMaterials, 13 (2020) 11 DOI: 10.3390/ma13112656
Abstract
In this work, the synthesis of graphene-like nanosheets (GNS) by an electrochemical exfoliation method, their microstructural characterization and their performance as fillers in a ceramic matrix composite have been assessed. To fabricate the composites, 3 mol % yttria tetragonal zirconia (3YTZP) powders with 1 vol % GNS were processed by planetary ball milling in tert-butanol to enhance the GNS distribution throughout the matrix, and densified by spark plasma sintering (SPS). According to a thorough Raman analysis and SEM observations, the electrochemically exfoliated GNS possessed less than 10 graphene layers and a lateral size lower than 1 mu m. However, they contained amorphous carbon and vacancy-like defects. In contrast the GNS in the sintered composite exhibited enhanced quality with a lower number of defects, and they were wavy, semi-transparent and with very low thickness. The obtained nanocomposite was fully dense with a homogeneous distribution of GNS into the matrix. The Vickers hardness of the nanocomposite showed similar values to those of a monolithic 3YTZP ceramic sintered in the same conditions, and to the reported ones for a 3YTZP composite with the same content of commercial graphene nanosheets.
Junio, 2020 · DOI: 10.3390/ma13112656
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
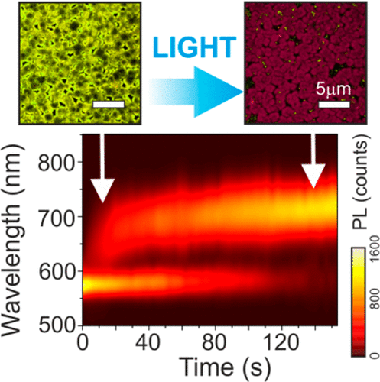
Local Rearrangement of the Iodide Defect Structure Determines the Phase Segregation Effect in Mixed-Halide Perovskites
Tiede, DO; Calvo, ME; Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 11 (2020) 4911-4916 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c01127
Abstract
Mixed-halide perovskites represent a particularly relevant case within the family of lead-halide perovskites. Beyond their technological relevance for a variety of optoelectronic devices, photoinduced structural changes characteristic of this type of material lead to extreme photophysical changes that are currently the subject of intense debate. Herein we show that the conspicuous photoinduced phase segregation characteristic of these materials is primarily the result of the local and metastable rearrangement of the iodide sublattice. A local photophysical study comprising spectrally resolved laser scanning confocal microscopy is employed to find a correlation between the defect density and the dynamics of photoinduced changes, which extend far from the illuminated region. We observe that iodide-rich regions evolve much faster from highly defective regions. Also, by altering the material composition, we find evidence for the interplay between the iodide-related defect distribution and the intra- and interdomain migration dynamics giving rise to the complexity of this process.
Junio, 2020 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c01127
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
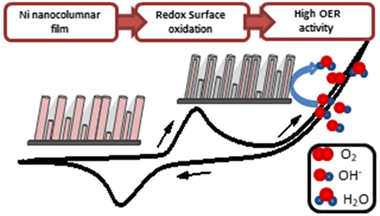
Chemistry and Electrocatalytic Activity of Nanostructured Nickel Electrodes for Water Electrolysis
Lopez-Fernandez, E; Gil-Rostra, J; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Consuegra, AD; Yubero, FACS Catalysis, 10 (2020) 6159-6170 DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.0c00856
Abstract
Herein we have developed nanostructured nickel-based electrode films for anion exchange membrane water electrolysis (AEMWE). The electrodes were prepared by magnetron sputtering (MS) in an oblique angle configuration and under various conditions aimed at preparing metallic, oxide, or oxyhydroxide films. Their electrochemical analysis has been complemented with a thorough physicochemical characterization to determine the effect of microstructure, chemical state, bilayer structure, and film thickness on the oxygen evolution reaction (OER). The maximum electrocatalytic activity was found for the metallic electrode, where analysis by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) demonstrated that the active catalytic phase at the surface after its electrochemical conditioning is a kind of oxidized nickel oxide/hydroxide layer with the thickness of a few nanometers. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy analysis of these steady-state working electrodes supports that the enhanced performance of the metallic nickel anode vs other chemical states resides in the easier electron transfer through the electrode films and the various interlayers built up during their fabrication and activation. The long-term steady-state operation of the anodes and their efficiency for water splitting was proved in a full-cell AEMWE setup incorporating magnetron-sputtered metallic nickel as the cathode. This work proves that MS is a suitable technique to prepare active, stable, and low-cost electrodes for AEMWE and the capacity of this technique to control the chemical state of the electrocatalytically active layers involved in the OER.
Junio, 2020 · DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.0c00856
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
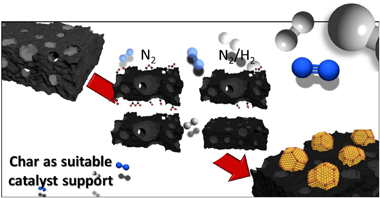
Reductant atmospheres during slow pyrolysis of cellulose: First approach to obtaining efficient char -based catalysts in one pot
Santos, JL; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAJournal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 148 (2020) 104821 DOI: 10.1016/j.jaap.2020.104821
Abstract
Char based metallic (Pd-Au-Ru-Pt/C) catalysts have drawn increasing research interest due to their versatility in biomass related industrial reactions. Recent studies dealing with the synthesis of char-based catalysts in one single step (one-pot) use reductant atmospheres for biomass pyrolysis. In this work, the influence of the use of a reductant N2/H2 atmosphere on the physicochemical properties of the resulting chars was evaluated in comparison with the use of an inert N2 atmosphere. Specifically, the fundamental parameter of the pyrolysis process, the temperature, was evaluated in the 500−900 °C range. Produced chars were fully characterized by N2 isotherms, ultimate CHNS analysis, X-ray Diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, Diffuse Reflectance Infrared spectroscopy, X-ray Photoelectron spectroscopy, helium Temperature Programmed Decomposition and Isoelectric Point analysis. Slow pyrolysis under reductant atmosphere favours deoxygenation reaction against dehydrogenation ones, reduces the carbon yield and results in chars with a more hydrophobic and graphitic character, higher thermal stability and weak surface functionalization. The use of intermediates temperatures (700 °C) favours the obtaining of chars with suitable physicochemical properties and good surface functionalization, which will facilitate the anchoring of the active phase on the surface, improving the metallic dispersion of the resulting one pot catalyst. This leads us to affirm that the use of reducing atmospheres at intermediate temperatures, is superior to the use of inert atmospheres for this purpose. This analysis on the impact of the use of a reductant atmosphere during slow pyrolysis of microcrystalline cellulose opens a new working path for the optimization of char-based catalysts obtained in a single stage.
Junio, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jaap.2020.104821
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Time-resolved operando DRIFTS-MS study of the moisture tolerance of small-pore SAPO-34 molecular sieves during CH4/CO2 separation
Romero, M; Navarro, JC; Bobadilla, LF; Dominguez, MI; Ivanova, S; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 298 (2020) 110071 DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110071
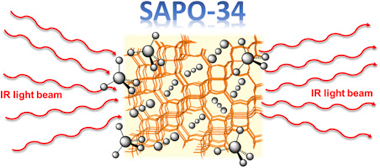
Abstract
This study pretends to evaluate and understand the effect of moisture presence during CO2/CH4 separation on small-pore SAPO-34 molecular sieves. Two SAPO-34 samples with different physicochemical properties (composition, crystal size and texture) were prepared by hydrothermal synthesis using either one or a mixture of two templates. Transient operando DRIFTS-MS measurements revealed that the sample's hydrophobic character is associated to the presence of Si islands, which enhanced sample's moisture tolerance during repetitive adsorption/desorption cycles. This knowledge is fundamental to achieve the rational design of efficient SAPO-34 membranes under realistic conditions.
Mayo, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110071
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Structural and surface considerations on Mo/ZSM-5 systems for methane dehydroaromatization reaction
Lopez-Martin, A; Caballero, A; Colon, GMolecular Catalysis, 486 (2020) 110787 DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2020.110787
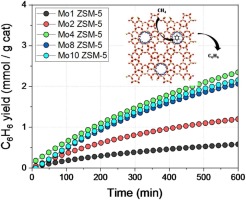
Abstract
We have prepared a series of Mo/ZSM-5 systems by impregnation method with different metal loading. The optimum performance has been attained for 4% metal loading, yielding to ca. 2 mmol(benzene)/g(ca)(t) at the end of the reaction. The obtained catalysts were widely structural and surface characterized. As Mo content increases, the surface feature of the support is affected specially its mesoporosity. It has been stated the enormous complexity of Mo species present in the studied system. In situ characterization by XPS reveals different reduction and carburization behaviour depending on the Mo content.
Mayo, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2020.110787
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Microwave-assisted sol-gel synthesis of TiO2 in the presence of halogenhydric acids. Characterization and photocatalytic activity
Puga,F.;Navío,J.A.;Jaramillo-Páez,C.;Sánchez-Cid,P.;Hidalgo,M.C.Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 394 (2020) 112457 DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2020.112457

Abstract
The synthesis of mesoporous TiO2 nanosheets is reported using Ti(IV) Isopropoxide as Ti(IV) precursor. A sol-gel process combined with microwave activation is used. Three different halogenhydric acids (HX), were used to peptise the sol: HF(ac), HCl (ac) and HBr (ac). The three obtained TiO2-I(HX) samples were characterized by XRD, XRF, N2-adsorption, SEM, TEM, DRS and XPS. The three synthesized samples have high values of specific surfaces (between 100 m2/g and 200 m2/g) and similar band gap values (3.2–3.3 eV). The analysis of the surface composition by XPS confirms the presence of the halogenated species (F, Cl or Br) on the surface of each ones of the samples. The nanometric size (ca 5 nm) of the particles for each of the three samples was confirmed by XRD and by TEM. On the other hand, the nature of the halogenated acid used plays a role in the composition of the phases. While the TiO2-I (HF) sample was 100 % anatase, the other samples turned out to be biphasic, showing anatase/rutile in the TiO2-I(HCl) sample and anatase/brookite in the TiO2-I(HBr) sample. The samples were tested under two illumination conditions (UV and visible light) using rhodamine B and caffeine. The indirect role of the halide agent on the photocatalytic activities thereof is discussed.
Mayo, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2020.112457
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Dibenzo-tetraphenyl diindeno perylene as hole transport layer for high-bandgap perovskite solar cells
Pegu, M; Caliò, L; Ahmadpour, M; Rubahn, HG; Kazim, S; Madsen, M; Ahmad, SEmergent Materials, 3 (2020) 109-116 DOI: 10.1007/s42247-020-00098-x
Abstract
Semi-transparent perovskite solar cells have the competitive edge of being employed for building integrated photovoltaics due to their esthetic benefits as light harvesting windows/facades. Perovskites have received considerable attention in recent years as a thin film photovoltaic alternative, that can also be tweaked for its transparency, evolving from potentially high bandgaps that are suited for semi-transparent solar cell fabrication. Due to the existing trade of between the efficiency and transparency of a perovskite solar cell, tuning the band gap can address this by making a bridge between the aforementioned parameters. We report our findings on the use of a wide-bandgap perovskite MAPbBr3, with a rational energetic level hole transport materials based on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon molecules that can be a promising alternative class of p-type material. In the present work, DBP (Dibenzo{[f,f′]-4,4′,7,7′-tetraphenyl}diindeno[1,2,3-cd :1′,2′,3′-lm]perylene was evaluated with high bandgap as well as with mixed (FAPbI3)0.85(MAPbBr3)0.15 perovskites for the fabrication of solar cell. DBP-based solar cells yielded competitive power conversion efficiencies as compared with classical HTMs.
Mayo, 2020 · DOI: 10.1007/s42247-020-00098-x
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Optical properties of molybdenum in the ultraviolet and extreme ultraviolet by reflection electron energy loss spectroscopy
Pauly, N; Yubero, F; Tougaard, SApplied Optics, 59 (2020) 4527-4532 DOI: 10.1364/AO.391014
Abstract
Optical properties of polycrystalline molybdenum are determined from ultraviolet up to extreme ultraviolet by reflection electron energy loss spectroscopy (REELS). Calculations are performed within the dielectric response theory by means of the quantitative analysis of electron energy losses at surfaces QUEELS-epsilon (k, omega)-REELS software [Surf. Interface Anal. 36, 824 (2004)] that allows the simulation of inelastic scattering cross sections, using a parametric energy loss function describing the optical response of the material. From this energy loss function, the real and imaginary parts of the dielectric function, the refractive index, and the extinction coefficient are deduced and compared with previously published results.
Mayo, 2020 · DOI: 10.1364/AO.391014
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Premelting of ice adsorbed on a rock surface
Esteso, V; Palacios, SC; MacDowell, LG; Fiedler, J; Parsons, DF; Spallek, F; Miguez, H; Persson, C; Buhmann, SY; Brevik, I; Bostrom, MPhysical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 22 (2020) 11362-11373 DOI: 10.1039/c9cp06836h
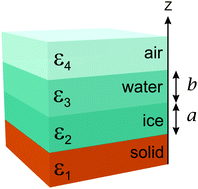
Abstract
Considering ice-premelting on a quartz rock surface (i.e. silica) we calculate the Lifshitz excess pressures in a four layer system with rock-ice-water-air. Our calculations give excess pressures across (1) ice layer, (2) water layer, and (3) ice-water interface for different ice and water layer thicknesses. We analyse equilibrium conditions where the different excess pressures take zero value, stabilized in part by repulsive Lifshitz interactions. In contrast to previous investigations which considered varying thickness of only one layer (ice or water), here we present theory allowing for simultaneous variation of both layer thicknesses. For a given total thickness of ice and water, this allows multiple alternative equilibrium solutions. Consequently the final state of a system will depend on initial conditions and may explain variation in experimental measurements of the thicknesses of water and ice layers.
Mayo, 2020 · DOI: 10.1039/c9cp06836h
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
A 4-view imaging to reveal microstructural differences in obliquely sputter-deposited tungsten films
El Beainou, R; Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Raschetti, M; Cote, JM; Alvarez, R; Palmero, A; Potin, V; Martin, NMaterials Letters, 264 (2020) 127381 DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.127381

Abstract
We report on the morphological disparity of the columnar growth in W thin films sputter-deposited by oblique angle deposition. Oriented tungsten thin films (400 +/- 50 nm thick) are prepared using a tilt angle alpha of 80 degrees and a sputtering pressure of 0.25 Pa. Inclined columns (beta = 38 +/- 2 degrees) are produced and the microstructure is observed by scanning electron microscopy. A 4-view imaging is performed in order to show inhomogeneous growing evolutions in the columns. Morphological features vs. viewing direction are also investigated from a growth simulation of these tilted W columns. Experimental and theoretical approaches are successfully compared and allow understanding how the direction of the W particle flux leads to dense or fibrous morphologies, as the column apexes are in front of the flux or in the shadowing zone.
Abril, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.127381
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Monitoring, Modeling, and Optimization of Lead Halide Perovskite Nanocrystal Growth within Porous Matrices
Tiede, DO; Rubino, A; Calvo, ME; Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 124 (2020) 8041-8046 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c01750
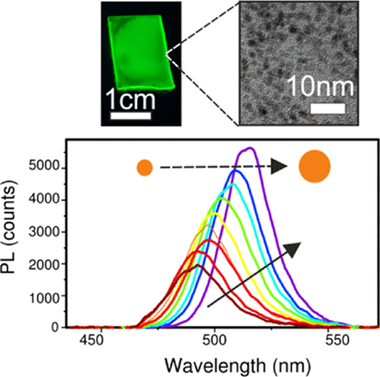
Abstract
The growth of lead halide perovskites within metal-oxide nanoporous films has been recently considered as a means to obtain chemically and photostable ligand-free high-quality nanocrystals (NCs). The growth process, governed by the reactions taking place in nanoreactors dictated by the matrix pore size, has not been explored so far. In this work, we use photoluminescence as a tool to monitor the growth of perovskite NCs within the void network of an optically transparent matrix. We consider the effect of different external factors, such as temperature, light illumination, or precursor concentration, on the growth dynamics, and discuss a possible formation mechanism of the confined perovskite NCs. Based on this analysis, guidelines that could serve to improve the fabrication and optoelectronic quality of this type of NCs are also proposed.
Abril, 2020 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c01750
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Advanced Strategies in Thin Films Engineering by Magnetron Sputtering
Palmero, A; Martin, NCoatings, 10 (2020) 419 DOI: 10.3390/coatings10040419
Abstract
This Special Issue contains a series of reviews and papers representing some recent results and some exciting perspectives focused on advanced strategies in thin films growth, thin films engineering by magnetron sputtering and related techniques. Innovative fundamental and applied research studies are then reported, emphasizing correlations between structuration process parameters, new ideas and approaches for thin films engineering and resulting properties of as-deposited coatings.
Abril, 2020 · DOI: 10.3390/coatings10040419
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Bio-Based Coatings for Food Metal Packaging Inspired in Biopolyester Plant Cutin
Benitez, JJ; Osbild, S; Guzman-Puyol, S; Heredia, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JAPolymers, 12 (2020) 942 DOI: 10.3390/polym12040942
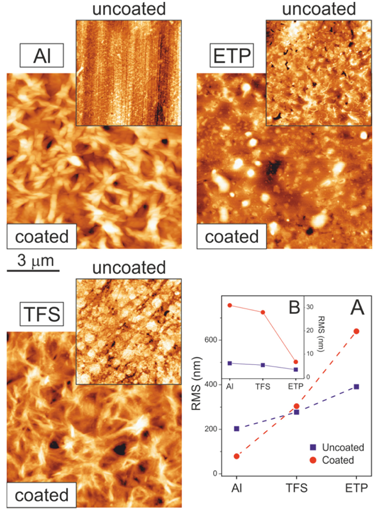
Abstract
Metals used for food canning such as aluminum (Al), chromium-coated tin-free steel (TFS) and electrochemically tin-plated steel (ETP) were coated with a 2-3-mu m-thick layer of polyaleuritate, the polyester resulting from the self-esterification of naturally-occurring 9,10,16-trihydroxyhexadecanoic (aleuritic) acid. The kinetic of the esterification was studied by FTIR spectroscopy; additionally, the catalytic activity of the surface layer of chromium oxide on TFS and, in particular, of tin oxide on ETP, was established. The texture, gloss and wettability of coatings were characterized by AFM, UV-Vis total reflectance and static water contact angle (WCA) measurements. The resistance of the coatings to solvents was also determined and related to the fraction of unreacted polyhydroxyacid. The occurrence of an oxidative diol cleavage reaction upon preparation in air induced a structural modification of the polyaleuritate layer and conferred upon it thermal stability and resistance to solvents. The promoting effect of the tin oxide layer in such an oxidative cleavage process fosters the potential of this methodology for the design of effective long-chain polyhydroxyester coatings on ETP.
Abril, 2020 · DOI: 10.3390/polym12040942
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Study of the influence of the precursors on the sensing properties of ZnO:Cu system
Ramos, A; Urbieta, A; Escalante, G; Hidalgo, P; Espinos, JP; Fernandez, PCeramics International, 46 (2020) 8358-8367 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.12.068
Abstract
The properties of ZnO based materials for ethanol detection have been studied. Cu doped samples obtained from different precursors have been investigated. ZnO and ZnS have been used as host and Cu and CuO as dopant sources.
The sensing measurements have been mostly performed at room temperature. To monitor the effect of the presence of gas, resistivity and photoluminescence experiments with and without sensing gas have been carried out. The sensing behaviour is affected by the nature of the precursors used. For ZnO:Cu and ZnO:CuO series, a higher sensitivity is obtained at the lower gas concentrations, the better response is obtained for the sample ZnO:Cu with wt.1% of metallic copper. Strong segregation effects observed in these samples could be deleterious for the sensing properties. In the series ZnS:CuO, no segregation is observed, however the sensing behaviour is erratic and attributed to the reduction of Cu ions to the metallic state.
Abril, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.12.068
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Vegetable hierarchical structures as template for bone regeneration: New bio‐ceramization process for the development of a bone scaffold applied to an experimental sheep model
Filardo, G; Roffi, A; Fey, T; Fini, M; Giavaresi, G; Marcacci, M; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Martini, L; Ramirez-Rico, J; Salamanna, F; Sandri, M; Sprio, S; Tampieri, A; Kon, EJournal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B-Applied Materials, 108 (2020) 600-611 DOI: 10.1002/jbm.b.34414
Abstract
Long bone defects still represent a major clinical challenge in orthopedics, with the inherent loss of function considerably impairing the quality of life of the affected patients. Thus, the purpose of this study was to assess the safety and potential of bone regeneration offered by a load‐bearing scaffold characterized by unique hierarchical architecture and high strength, with active surface facilitating new bone penetration and osseointegration in critical size bone defects. The results of this study showed the potential of bio‐ceramization processes applied to vegetable hierarchical structures for the production of new wood‐derived bone scaffolds, further improved by surface functionalization, with good biological and mechanical properties leading to successful treatment of critical size bone defects in the sheep model. Future studies are needed to evaluate if these scaffolds prototypes, as either biomaterial alone or in combination with augmentation strategies, may represent an optimal solution to enhance bone regeneration in humans.
Abril, 2020 · DOI: 10.1002/jbm.b.34414
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
A Microstructure Insight of MTA Repair HP of Rapid Setting Capacity and Bioactive Response
Jimenez-Sanchez, MC; Segura-Egea, JJ; Diaz-Cuenca, AMaterials, 13 (2020) 1641 DOI: 10.3390/ma13071641

Abstract
Mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) is considered a bioactive endodontic material, which promotes natural mineralization at the material-tooth tissue interface. MTA Repair HP stands out because of the short setting time and the quick and effective bioactive response in vitro. The bioactivity, depens on material composition and microstructure. This work is devoted to analyze MTA Repair HP microstructural features, of both the powder precursor and set material, to get insights into the material physicochemical parameters-functionality performance relationships. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and field emission gun scanning electron microscopy (FEG-SEM) coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) analyses were performed. X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements were carried out at different times to investigate setting process. Bioactivity evaluation in vitro was carried out by soaking the processed cement disk in simulated body fluid (SBF). The presented results point out those MTA Repair HP precursor material characteristics of tricalcium silicate particles of nanometric size and high aspect ratio, which provide an elevated surface area and maximized components dispersion of calcium silicate and very reactive calcium aluminate. The MTA Repair HP precursor powder nanostructure and formulation, allows a hydration process comprising silicate hydrate structures, which are very effective to achieve both fast setting and efficient bioactive response.
Abril, 2020 · DOI: 10.3390/ma13071641
Reactividad de Sólidos
Development of a high-pressure thermobalance working under constant rate thermal analysis
Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Criado, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Thermal Analysis ande Calorimetry, 142 (2020) 1329-1334 DOI: 10.1007/s10973-020-09644-5
Abstract
A thermogravimetric instrument that works at high pressure of different gases has been designed and assembled. The instrument has been devised to work in a temperature range from room temperature to 1000 degrees C in various controlled pressures of selected gas up to 15 bar, and under conventional rising temperature and constant rate thermal analysis (CRTA) modes. CRTA method allows an intelligent control of the reaction temperature using a feedback system that monitors the mass gain or mass loss of the sample in such a way that the reaction rate is maintained constant all over the process at a preselected value. CRTA method provides a significant advantage for studying processes under high pressure as it reduces heat and mass transfer phenomena that are very relevant under these high-pressure experimental conditions. The thermal oxidation of Ni at 8 bar of pure oxygen has been used for testing the performance of the instrument under both linear heating rate and CRTA conditions.
Abril, 2020 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-020-09644-5
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
In Vitro and In Vivo Study of Titanium Grade IV and Titanium Grade V Implants with Different Surface Treatments
Diaz-Sanchez, RM; de-Paz-Carrion, A; Serrera-Figallo, MA; Torres-Lagares, D; Barranco, A; Leon-Ramos, JR; Gutierrez-Perez, JLMetals, 10 (2020) 449 DOI: 10.3390/met10040449
Abstract
The aim of our study is to evaluate different implant surface treatments using TiIV and TiV in in vitro and in vivo studies. An in vitro study was established comprising four study groups with treated and untreated TiIV titanium discs (TiIVT and TiIVNT) and treated and untreated TiV titanium discs (TiVT and TiVNT). The surface treatment consisted in a grit blasting treatment with alumina and double acid passivation to modify surface roughness. The surface chemical composition and the surface microstructure of the samples were analyzed. The titanium discs were subjected to cell cultures to determine cell adhesion and proliferation of osteoblasts on them. The in vivo study was carried out on the tibia of three New Zealand rabbits in which 18 implants divided into three experimental groups were placed (TiIVT, TiIVNT, and TiVT). Micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) was performed to determine bone density around the implants. The results showed that cell culture had minor adhesion and cell proliferation in TiIVT and TiVT within the first 6 and 24 h. However, no differences were found after 48 h. No statistically significant differences were found in the in vivo micro-CT and histological study; however, there was a positive trend in bone formation in the groups with a treated surface. Conclusions: All groups showed a similar response to in vitro cell proliferation cultures after 48 h. No statistically significant differences were found in the in vivo micro-CT and histological study
Abril, 2020 · DOI: 10.3390/met10040449
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Potentialization of bentonite properties as support in acid catalysts
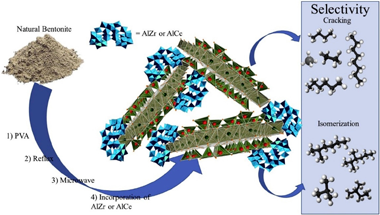
Amaya, J; Bobadilla, L; Azancot, L; Centeno, M; Moreno, S; Molina, RMaterials Research Bulletin, 123 (2020) 110728 DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2019.110728
Abstract
Enhancement of the main physicochemical properties of a natural bentonite was carried out by means of modifications using surfactant, reflux, microwave treatment and, subsequently, the incorporation of AlZr and AlCe species. The evolution of the main changes in each modification stage was evaluated by means of X-ray diffraction, N-2 sortometry, scanning microscopy (SEM), NH3-TPD, NH3-DRIFTS and CO adsorption at low temperature. For the evaluation of the catalytic behavior, the dehydration-dehydrogenation reactions of 2-propanol and hydro-conversion of decane were used; both of which generate, in addition, information regarding the acidic properties of the materials. The correlation of the number, type and acid strength with the catalytic behavior, allowed establishing the effect produced by both the delamination method and the nature of the incorporated cation. This generated tools that allow controlling the physicochemical properties, and more specifically, the enhancement of the acidity of new supports based on this type of natural clay mineral.
Marzo, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2019.110728
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of the Test Configuration and Temperature on the Mechanical Behaviour of WC-Co
Gonzalez, LM; Chicardi, E; Gotor, FJ; Bermejo, R; Llanes, L; Torres, YMetals, 10 (2020) 322 DOI: 10.3390/met10030322

Abstract
In this work, the effect of the test configuration and temperature on the mechanical behaviour of cemented carbides (WC-Co) with different carbide grain sizes (d(WC)) and cobalt volume fractions (V-Co), implying different binder mean free paths (lambda (Co)), was studied. The mechanical strength was measured at 600 degrees C with bar-shaped specimens subjected to uniaxial four-point bending (4PB) tests and with disc specimens subjected to biaxial ball-on-three-balls (B3B) tests. The results were analysed within the frame of the Weibull theory and compared with strength measurements performed at room temperature under the same loading conditions. A mechanical degradation greater than 30% was observed when the samples were tested at 600 degrees C due to oxidation phenomena, but higher Weibull moduli were obtained as a result of narrower defect size distributions. A fractographic analysis was conducted with broken specimens from each test configuration. The number of fragments (N-f) and the macroscopic fracture surface were related to the flexural strength and fracture toughness of WC-Co. For a given number of fragments, higher mechanical strength values were always obtained for WC-Co grades with higher K-Ic. The observed differences were discussed based on a linear elastic fracture mechanics (LEFM) model, taking into account the effect of the temperature and microstructure of the cemented carbides on the mechanical strength.
Marzo, 2020 · DOI: 10.3390/met10030322
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction as effective photocatalyst for the degradation of diclofenac and ketoprofen
Sacco, O.l; Murcia, J.J.; Lara, A.E.; Hernández-Laverde, M.; Rojas, H.; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Vaiano, V.Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 107 (2020) 104839 DOI: 10.1016/j.mssp.2019.104839

Abstract
Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction was synthetized and studied for the photocatalytic removal of diclofenac (DCF) and ketoprofen (KTF) under UV light irradiation. The physical-chemical properties of the prepared catalysts were analysed by different characterization techniques revealing that the lowest platinum nanoparticle size and the better metal distribution was observed in Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 sample. The Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction possessed the best photocatalytic activity toward both the photodegradation and mineralization of the two selected pollutants. The optimal photocatalyst showed a DCF and KTF mineralization rate of 0.0555 and 0.0746 min−1, respectively, which were higher than those of Pt–TiO2 (0.0321 min−1 for DCF and 0.0597 min−1 for KTF). The experiments driven to analyse the effects of free radical capture showed that ·OH, ·O2− and h+ have a primary role in reactive during the photocatalytic reaction. The improved photocatalytic performances of the Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction could be argue by a direct Z-scheme mechanism in which the Pt0 nanoparticles could act as a bridge between TiO2 and Nb2O5, improving the electron-hole separation and, ultimately, enhancing the photocatalytic removal rate of both DCF and KTF.
Marzo, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mssp.2019.104839
Reactividad de Sólidos
Role of particle size on the multicycle calcium looping activity of limestone for thermochemical energy storage
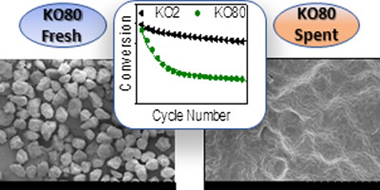
Duran-Martin, JD; Jimenez, PES; Valverde, JM; Perejon, A; Arcenegui-Troya, J; Trinanes, PG; Maqueda, LAPJournal of Advanced Research, 22 (2020) 67-76 DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2019.10.008
Abstract
The calcium looping process, based on the reversible reaction between CaCO3 and CaO, is recently attracting a great deal of interest as a promising thermochemical energy storage system to be integrated in Concentrated Solar Power plants (CaL-CSP). The main drawbacks of the system are the incomplete conversion of CaO and its sintering-induced deactivation. In this work, the influence of particle size in these deactivation mechanisms has been assessed by performing experimental multicycle tests using standard limestone particles of well-defined and narrow particle size distributions. The results indicate that CaO multicycle conversion benefits from the use of small particles mainly when the calcination is carried out in helium at low temperature. Yet, the enhancement is only significant for particles below 15 μm. On the other hand, the strong sintering induced by calcining in CO2 at high temperatures makes particle size much less relevant for the multicycle performance. Finally, SEM imaging reveals that the mechanism responsible for the loss of activity is mainly pore-plugging when calcination is performed in helium, whereas extensive loss of surface area due to sintering is responsible for the deactivation when calcination is carried out in CO2 at high temperature.
Marzo, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2019.10.008
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
An insight on the design of mercapto functionalized swelling brittle micas
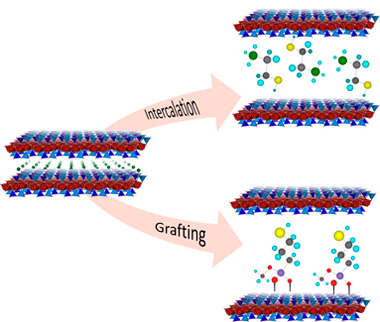
Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 561 (2020) 533-541 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.11.028
Abstract
Surface modification of natural clay minerals with reagents containing metal chelating groups has great environmental value. The functionalization by adsorption or grafting guarantees a durable immobilization of the reactive organic groups, preventing their leaching when they are used in liquid media. The aim of this research was the designed mercapto functionalization of swelling brittle micas, Na-Mn, thorough both chemical and physical mechanisms. Na-Mn were functionalized with 2-mercaptoethylammonium (MEA), 2,3-dimercapto-1-propanol (BAL) and (3-mercaptopropyl)trimethoxysilane (MPTMS). The thiol concentration on swelling brittle micas is higher than the observed value for others adsorbents. The cation exchange reaction with MEA and one-step grafting with MPTMS in acid medium are the most efficient mercapto functionalization mechanism.
Marzo, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.11.028
Reactividad de Sólidos
Development by Mechanochemistry of La0.8Sr0.2Ga0.8Mg0.2O2.8 Electrolyte for SOFCs
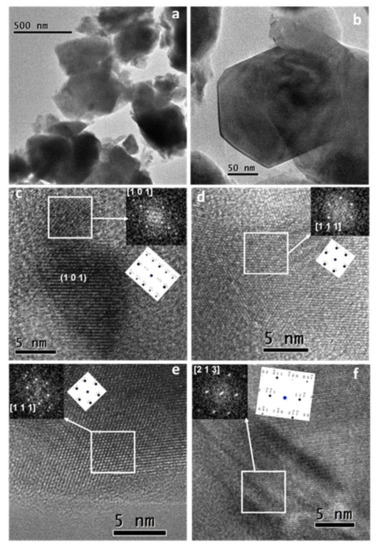
Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Tang, YQ; Gotor, FJ; Sayagues, MJMaterials, 13 (2020) DOI: 10.3390/ma13061366
Abstract
In this work, a mechanochemical process using high-energy milling conditions was employed to synthesize La0.8Sr0.2Ga0.8Mg0.2O3-δ (LSGM) powders from the corresponding stoichiometric amounts of La2O3, SrO, Ga2O3, and MgO in a short time. After 60 min of milling, the desired final product was obtained without the need for any subsequent annealing treatment. A half solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) was then developed using LSGM as an electrolyte and La0.8Sr0.2MnO3 (LSM) as an electrode, both obtained by mechanochemistry. The characterization by X-ray diffraction of as-prepared powders showed that LSGM and LSM present a perovskite structure and pseudo-cubic symmetry. The thermal and chemical stability between the electrolyte (LSGM) and the electrode (LSM) were analyzed by dynamic X-ray diffraction as a function of temperature. The electrolyte (LSGM) is thermally stable up to 800 and from 900 °C, where the secondary phases of LaSrGa3O7 and LaSrGaO4 appear. The best sintering temperature for the electrolyte is 1400 °C, since at this temperature, LaSrGaO4 disappears and the percentage of LaSrGa3O7 is minimized. The electrolyte is chemically compatible with the electrode up to 800 °C. The powder sample of the electrolyte (LSGM) at 1400 °C observed by HRTEM indicates that the cubic symmetry Pm-3m is preserved. The SOFC was constructed using the brush-painting technique; the electrode–electrolyte interface characterized by SEM presented good adhesion at 800 °C. The electrical properties of the electrolyte and the half-cell were analyzed by complex impedance spectroscopy. It was found that LSGM is a good candidate to be used as an electrolyte in SOFC, with an Ea value of 0.9 eV, and the LSM sample is a good candidate to be used as cathode
Marzo, 2020 · DOI: 10.3390/ma13061366
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Platinum nanoparticles stabilized by N-heterocyclic thiones. Synthesis and catalytic activity in mono- and di-hydroboration of alkynes
Moraes, LCC; Figueiredo, RCC; Espinos, JPP; Vattier, F; Franconetti, A; Jaime, C; Lacroix, B; Rojo, J; Lara, P; Conejero, SNanoscale, 12 (2020) 6821-6831 DOI: 10.1039/d0nr00251h
Abstract
N-Heterocyclic Thiones (NHT) proved to be efficient ligands for the stabilization of small platinum nanoparticles (1.3-1.7 nm), synthesized by decomposition of [Pt(dba)(2)], under a H-2 atmosphere, in the presence of variable sub-stoichiometric amounts of the NHT. Full characterization by means of TEM, HR-TEM, NMR, ICP, TGA and XPS have been carried out, providing information about the nature of the metal nanoparticles and the interaction of the NHT ligands to the metal surface. Importantly, DFT calculations indicate that some NHT ligands interact with the metal through the C & xe001;C double bond of the imidazole fragment in addition to the sulfur atom, thus providing additional stabilization to the nanoparticles. According to XPS, TGA and ICP techniques, the surface coverage by the ligand increases by decreasing the size of the substituents on the nitrogen atom. The platinum nanoparticles have been used as catalyst in the hydroboration of alkynes. The most active system is that with a less covered surface area lacking an interaction of the ligand by means of the C & xe001;C double bond. This catalyst hydroborates alkynes with excellent selectivities towards the monoborylated anti-Markovnikov product (vinyl-boronate) when one equiv. of borane is used. Very interestingly, aliphatic alkynes undergo a second hydroborylation process leading to the corresponding 1,1- and 1,2-diboroylated species with good selectivities towards the former.
Marzo, 2020 · DOI: 10.1039/d0nr00251h
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Localized surface plasmon effects on the photophysics of perovskite thin films embedding metal nanoparticles
Bayles, A; Carretero-Palacios, S; Calio, L; Lozano, G; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 8 (2020) 916-921 DOI: 10.1039/c9tc05785d
Abstract
Herein we provide direct experimental evidence that proves that the photophysical properties of thin methylammonium lead iodide perovskite films are significantly enhanced by localized surface plasmon resonances (SPRs). Observations are well supported by rigorous calculations that prove that improved light harvesting can be unequivocally attributed to plasmonic scattering and near field reinforcement effects around silver nanoparticles embedded within the semiconductor layer. Adequate design of the localized SPR allows raising the absorptance of a 300 nm thick film at well-defined spectral regions while minimizing the parasitic absorption from the metallic inclusions. Measured enhancements can be as large as 80% at specific wavelengths and 20% when integrated over the whole range at which SPR occurs, in agreement with theoretical estimations. Simultaneously, the characteristic quenching effect that the vicinity of metals has on the photoluminescence of semiconductors is largely compensated for by the combined effect of the enhanced photoexcitation and the higher local density of photon states occurring at SPR frequencies, with a two fold increase of the perovskite photoemission efficiency being measured.
Marzo, 2020 · DOI: 10.1039/c9tc05785d
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Optofluidic liquid sensing on electromicrofluidic devices
Oliva-Ramirez, M; Wang, SL; Rico-Gavira, V; Lopez-Santos, C; Fan, SK; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARMaterials Research Express, 7 (2020) 036407 DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab7fdf

Abstract
Electromicrofluidic (EMF) devices are used to handle and move tiny amounts of liquids by electrical actuation, including electrowetting-on-dielectric (EWOD) and dielectrophoresis (DEP). Monitoring the liquid characteristics in one of these devices requires suitable sensing transducers incorporated within the microfluidic structure. In the present work, we describe the incorporation of an optofluidic photonic transducer in an EMF device to monitor the refractive index of a liquid during its manipulation. The incorporated transducer consists of a responsive porous Bragg Microcavity (BM) deposited via physical vapor oblique angle deposition. Besides reporting the manufacturing procedure of the sensing-EMF device combining liquid handling and monitoring, the performance of the BM is verified by infiltrating several liquids dripped on its surface and comparing the responses with those of liquid droplets electrically moved from the delivery part of the chip to the BM location. This study proved that modified EMF devices can incorporate photonic structures to analyze very low liquid volumes (similar to 0.2 mu L) during its handling.
Marzo, 2020 · DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab7fdf
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Preparation of ZnFe2O4/ZnO composite: Effect of operational parameters for photocatalytic degradation of dyes under UV and visible illumination
Zouhier, M.; Tanji, K.; Navio, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Jaramillo-Páez, C.; Kherbeche, A.Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 390 (2020) 112305 DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.112305

Abstract
An ZnFe2O4/ZnO composite catalyst was prepared by solution combustion method. In this study, one nominal molar percentage of iron was used in the synthesis, corresponding to 20 % molar relative to ZnO. The samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray Fluorescence (XRF), Scanning Electronic Microscopy (SEM), Transmission Electronic Microscopy (TEM) and Ultraviolet-visible (UV–vis) diffuse spectroscopy (DRS). The photocatalytic activities of the catalysts were investigated based on the degradation of two dyes, methylene blue (MB) and remazol brilliant blue (RBB), in aqueous solution under both UV and visible light illumination respectively. It was found that the composite had a good photocatalytic activity at basic pH by using 1 g/L of catalyst under UV illumination for both MB and RBB. Under visible illumination, while pristine ZnO showed no activity, the composite exhibited an excellent visible efficiency, reaching up to an 80 % conversion of the initial dye concentrations in 2 h. The enhancement of the visible photocatalytic activity of Fe/ZnO sample with respect to pristine ZnO is attributed to the formation of ZnFe2O4 coupled with ZnO, having a narrow band gap value that contributes to the absorption of visible photons with an improved separation path for the photo-generated carriers.
Marzo, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.112305
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Positron annihilation analysis of nanopores and growth mechanism of oblique angle evaporated TiO2 and SiO2 thin films and multilayers
Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Butterling, M; Liedke, MO; Hirschmann, E; Trinh, TT; Attallah, AG; Wagner, A; Alvarez, R; Gil-Rostra, J; Rico, V; Palmero, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 295 (2020) 109968 DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.109968
Abstract
The nano-porosity embedded into the tilted and separated nanocolumns characteristic of the microstructure of evaporated thin films at oblique angles has been critically assessed by various variants of the positron annihilation spectroscopy. This technique represents a powerful tool for the analysis of porosity, defects and internal interfaces of materials, and has been applied to different as-deposited SiO2 and TiO2 thin films as well as SiO2/TiO2 multilayers prepared by electron beam evaporation at 70 and 85 zenithal angles. It is shown that, under same deposition conditions, the concentration of internal nano-pores in SiO2 is higher than in TiO2 nanocolumns, while the situation is closer to this latter in TiO2/SiO2 multilayers. These features have been compared with the predictions of a Monte Carlo simulation of the film growth and explained by considering the influence of the chemical composition on the growth mechanism and, ultimately, on the structure of the films.
Marzo, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.109968
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Binder-free supercapacitor electrodes: Optimization of monolithic graphitized carbons by reflux acid treatment
Gomez-Martin, A; Gutierrez-Pardo, A; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Ramirez-Rico, JFuel Processing Technology, 199 (2020) 106279 DOI: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2019.106279

Abstract
The rational design of electrodes mimicking the cellular structure of natural bio-resources has been a matter of increasing interest for applications in energy storage. Due to their anisotropic and hierarchical porosity, monolithic carbon materials from natural wood precursors are appealing as electrodes for supercapacitor applications due to their interconnected channels, relatively low cost and environmentally friendly synthesis process. In this work, a liquid-phase oxidative treatment with refluxing nitric acid at 100 degrees C for 8 h was performed to enhance the surface properties of beech-derived graphitized carbons treated with an iron catalyst. Microstructural, textural and surface investigations revealed that this strategy was successful in removing amorphous carbon and in functionalizing their surfaces. The crystallinity, accessible surface area, micropore volume and surface functionality of beech-derived carbons were increased upon the reflux treatment. The resulting porous carbon materials were evaluated as binderless monolithic electrodes for supercapacitors applications in aqueous KOH electrolyte. A maximum specific capacitance of 179 F.g(-1) and a volumetric capacitance of 89 Fcm(-3) in galvanostatic charge/discharge experiments were reached. Monolithic electrodes exhibited good cycling stability, with a capacitance retention over 95% after 10,000 cycles.
Marzo, 2020 · DOI: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2019.106279
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Optical Responses of Localized and Extended Modes in a Mesoporous Layer on Plasmonic Array to Isopropanol Vapor
Murai, S; Cabello-Olmo, E; Kamakura, R; Calvo, ME; Lozano, G; Atsumi, T; Miguez, H; Tanaka, KJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 124 (2020) 5772-5779 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b10999
Abstract
Mesoporous silica features open and accessible pores that can intake substances from the outside. The combination of mesoporous silica with plasmonic nanostructures represents an interesting platform for an optical sensor based on the dependence of plasmonic modes on the refractive index of the medium in which metallic nanoparticles are embedded. However, so far only a limited number of plasmonic nanostructures are combined with mesoporous silica, including random dispersion of metallic nanoparticles and flat metallic thin films. In this study, we make a mesoporous silica layer on an aluminum nanocylinder array. Such plasmonic arrangements support both localized surface plasmon resonances (LSPRs) and extended modes which are the result of the hybridization of LSPRs and photonic modes extending into the mesoporous layer. We investigate in situ optical reflectance of this system under controlled pressure of isopropanol vapor. Upon exposure, the capillary condensation in the mesopores results in a gradual spectral shift of the reflectance. Our analysis demonstrates that such shifts depend largely on the nature of the modes; that is, the extended modes show larger shifts compared to localized ones. Our materials represent a useful platform for the field of environmental sensing.
Marzo, 2020 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b10999
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Optical interference effects on the Casimir-Lifshitz force in multilayer structures
Esteso, V; Carretero-Palacios, S; Miguez, HPhysical Review A, 101 (2020) 033815 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.101.033815
Abstract
The Casimir-Lifshitz force F(C-L) between planar objects when one of them is stratified at the nanoscale is herein investigated. Layering results in optical interference effects that give rise to a modification of the optical losses, which, as stated by the fluctuation-dissipation theorem, should affect the Casimir-Lifshitz interaction. On these grounds, we demonstrate that, by nanostructuring the same volume of dielectric materials in diverse multilayer configurations, it is possible to access F(C-L) of attractive or repulsive nature, even getting canceled, at specific separation distances.
Marzo, 2020 · DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.101.033815
- ‹ anterior
- 11 of 37
- siguiente ›














