Artículos SCI
2015
2015
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales - Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Flexible Distributed Bragg Reflectors from Nanocolumnar Templates
Calvo, ME; Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Parra-Barranco, J; Barranco, A; Jimenez-Solano, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Miguez, HAdvanced Optical Materials, 3 (2015) 171-175
Show abstract ▽
A flexible distributed Bragg reflector is made by the infiltration of a nanocolumnar array with polydimethyl siloxane oligomers. The high optical reflectance displayed by the final material is a direct consequence of the high refractive index contrast of the columnar layers whereas the structural stability is due to the polymer properties.
Febrero, 2015 | DOI: 10.1002/adom.201400338
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Tribocorrosion behavior of TiBxCy/a-C nanocomposite coating in strong oxidant disinfectant solutions
Gracia-Escosa, E; Garcia, I; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Abad, MD; Mariscal, A; Arenas, MA; de Damborenea, J; Conde, ASurface & Coatings Technology, 263 (2015) 78-85
Show abstract ▽
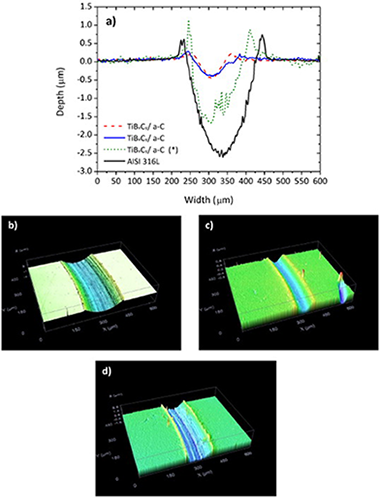
Corrosion and tribocorrosion studies of a TiBxCy/a-C coating deposited on AISI 316L steel have been performed in an aqueous solution of 026 vol.% acetic, 0.16 vol.% peracetic and 0.18 vol.% hydrogen peroxide (commercial product Oxonia I vol.%). The corrosion current density of the TiBxCy/a-C coating ranges on the same order as bare steel but with a significantly decreasing friction (0.1 vs. 0.6) and wear rate (similar to 10 times lower). The compact microstructure of the coating hinders the access of the aggressive electrolyte to the substrate, preventing the onset of the corrosion attack, while maintaining an excellent tribological behavior in strong oxidant solutions.
Febrero, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2014.12.047
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Photocatalytic activity of bismuth vanadates under UV-A and visible light irradiation: Inactivation of Escherichia coli vs oxidation of methanol
Adan, C; Marugan, J; Obregon, S; Colon, GCatalysis Today, 240 (2015) 93-99
Show abstract ▽
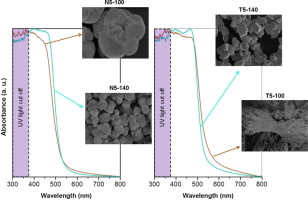
Four bismuth vanadates have been synthesized by using two different precipitating agents (NH3 and triethylamine) following a hydrothermal treatment at 100 °C for 2 h and at 140 °C for 20 h. Then, solids were characterized by X-ray diffraction, BET surface area, UV–vis spectroscopy and scanning microscopy techniques. The characterization of the synthesized materials showed a well crystallized scheelite monoclinic structure with different morphologies. All materials display optimum light absorption properties for visible light photocatalytic applications. The photocatalytic activity of the catalysts was investigated for the inactivation of Escherichia coli bacteria and the oxidation of methanol under UV–vis and visible light irradiation sources. Main results demonstrate that BiVO4 are photocatalytically active in the oxidation of methanol and are able to inactivate bacteria below the detection level. The activity of the catalyst decreases when using visible light, especially for methanol oxidation, pointing out differences in the reaction mechanism. In contrast with bacteria, whose interaction with the catalyst is limited to the external surface, methanol molecules can access the whole material surface.
Febrero, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2014.03.059
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Laser Treatment of Ag@ZnO Nanorods as Long-Life-Span SERS Surfaces
Macias-Montero, M; Pelaez, RJ; Rico, VJ; Saghi, Z; Midgley, P; Afonso, CN; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Borras, AACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 7 (2015) 2331-2339
Show abstract ▽
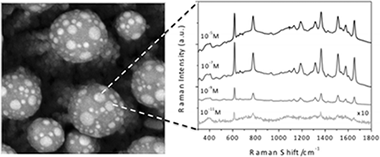
UV nanosecond laser pulses have been used to produce a unique surface nanostructuration of Ag@ZnO supported nanorods (NRs). The NRs were fabricated by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) at low temperature applying a silver layer as promoter. The irradiation of these structures with single nanosecond pulses of an ArF laser produces the melting and reshaping of the end of the NRs that aggregate in the form of bundles terminated by melted ZnO spherical particles. Well-defined silver nanoparticles (NPs), formed by phase separation at the surface of these melted ZnO particles, give rise to a broad plasmonic response consistent with their anisotropic shape. Surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) in the as-prepared Ag@ZnO NRs arrays was proved by using a Rhodamine 6G (Rh6G) chromophore as standard analyte. The surface modifications induced by laser treatment improve the stability of this system as SERS substrate while preserving its activity.
Febrero, 2015 | DOI: 10.1021/am506622x
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Polyester Films Obtained by Noncatalyzed Melt-Condensation Polymerization of Aleuritic (9,10,16-Trihydroxyhexadecanoic) Acid in Air
Benitez, JJ; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Guzman-Puyol, S; Dominguez, E; Heredia, AJournal of Applied Polymer, 132 (2015) Art. 41328
Show abstract ▽
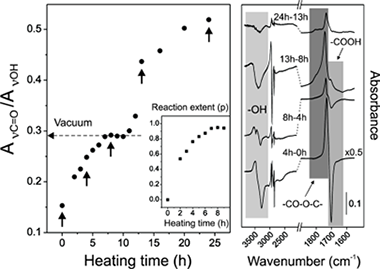
To mimic nontoxic and fully biodegradable biopolymers like the plant cutin, polyester films from a natural occurring fatty polyhydroxyacid like aleuritic (9,10,16-trihydroxyhexadecanoic) acid have been prepared by noncatalyzed melt-polycondensation at moderate temperature (150 degrees C) directly in air. The course of the reaction has been followed by infrared spectroscopy, C-13 magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray diffraction and well differentiated stages are observed. First, a high conversion esterification reaction leads to an amorphous rubbery, infusible, and insoluble material whose structure is made out of ester linkages mostly involving primary hydroxyls and partially branched by minor esterification with secondary ones. Following the esterification stage, the cleavage of vicinal secondary hydroxyls and further oxidation to carboxylic acid is observed at the near surface region of films. New carboxylic groups created also undergo esterification and generate cross-linking points within the polymer structure. Additionally, and despite the harsh preparation conditions used, very little additional side reaction like peroxidation and dehydration are observed. Results demonstrate the feasibility of polyester films fabrication from a reference fatty polyhydroxyacid like aleuritic acid by noncatalyzed melt-polycondensation directly in air. The methodology can potentially be extended to similar natural occurring hydroxyacids to obtain films and coatings to be used, for instance, as nontoxic and biodegradable food packaging material.
Febrero, 2015 | DOI: 10.1002/app.41328
- ‹ anterior
- 256 of 420
- siguiente ›














