Artículos SCI
2014
2014
Reactividad de Sólidos
Enhanced general analytical equation for the kinetics of the thermal degradation of poly(lactic acid)/montmorillonite nanocomposites driven by random scission
Carrasco, F; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Santana, OO; Maspoch, MLPolymer Degradation and Stability, 101 (2014) 52-59
Show abstract ▽
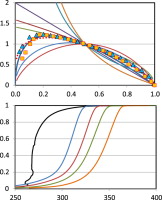
An enhanced general analytical equation has been developed in order to evaluate the kinetic parameters of the thermal degradation of nanocomposites, composed of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and organo-modified montmorillonite (OMMT) nanoparticles. This improvement has consisted of replacing the n-order conversion function by a modified form of the Sestak–Berggren equation f(α) = c (1 − α)nαm that led to a better adjustment of experimental data and also adequately represented the conventional mechanisms for solid-state processes. The kinetic parameters so obtained have been compared to those determined by conventional differential and isoconversional methods. Given that the thermal degradation of PLA has been argued to be caused by random chain scission reactions of ester groups, the conversion function f(α) = L (L − 1)x(1 − x)L−1, corresponding to a random scission mechanism, has been tested. Once optimized the kinetic model, the thermal degradation kinetics of nanocomposites (0.5 and 2.5% of OMMT) was compared to that of the polymer matrix. Moreover, the thermal stability of nanocomposites was tested and compared to that of the polymer matrix.
Marzo, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2014.01.014
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Osteoblasts Interaction with PLGA Membranes Functionalized with Titanium Film Nanolayer by PECVD. In vitro Assessment of Surface Influence on Cell Adhesion during Initial Cell to Material Interaction
Terriza, A; Vilches-Perez, JI; Gonzalez-Caballero, JL; de la Orden, E; Yubero, F; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Vilches, J; Salido, MMaterials, 7(3) (2014) 1687-1708
Show abstract ▽
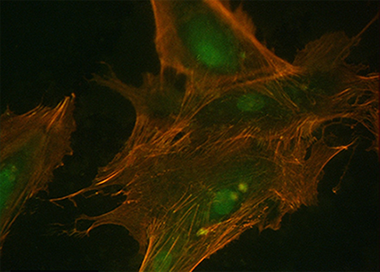
New biomaterials for Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR), both resorbable and non-resorbable, are being developed to stimulate bone tissue formation. Thus, the in vitro study of cell behavior towards material surface properties turns a prerequisite to assess both biocompatibility and bioactivity of any material intended to be used for clinical purposes. For this purpose, we have developed in vitro studies on normal human osteoblasts (HOB®) HOB® osteoblasts grown on a resorbable Poly (lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) membrane foil functionalized by a very thin film (around 15 nm) of TiO2 (i.e., TiO2/PLGA membranes), designed to be used as barrier membrane. To avoid any alteration of the membranes, the titanium films were deposited at room temperature in one step by plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition. Characterization of the functionalized membranes proved that the thin titanium layer completely covers the PLGA foils that remains practically unmodified in their interior after the deposition process and stands the standard sterilization protocols. Both morphological changes and cytoskeletal reorganization, together with the focal adhesion development observed in HOB osteoblasts, significantly related to TiO2 treated PLGA in which the Ti deposition method described has revealed to be a valuable tool to increase bioactivity of PLGA membranes, by combining cell nanotopography cues with the incorporation of bioactive factors.
Marzo, 2014 | DOI: 10.3390/ma7031687
Mineralogical Characterization of the Polychrome in Cultural Heritage Artifacts (Antiquity to Date) from Southern Spain Using Micro-Raman Spectroscopy and Complementary Techniques
Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Duran, ASpectroscopy Letters: An International Journal for Rapid Communication, 47 (2014) 223-237
Show abstract ▽
This work reports on the use of micro-Raman spectroscopy for the characterization of materials used for producing the polychrome in cultural heritage artifacts from southern Spain. The micro-Raman technique was applied for the characterization of several types of artworks or for cross-sections from these works, which were produced along different historical epochs. This technique was demonstrated to be valuable for the characterization of compounds, which were all detected within the artworks studied. The identification of all of these compounds by micro-Raman was confirmed by other complementary techniques, such as micro-X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy.
Marzo, 2014 | DOI: 10.1080/00387010.2013.791857
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
c- C4F8 Plasmas for the Deposition of Fluorinated Carbon Films
Terriza, A; Macias-Montero, M; Lopez-Santos, MC; Yubero, F; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARPlasma Processes and Polymers, 11 (2014) 289-299
Show abstract ▽
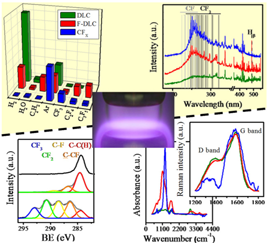
Highly fluorinated polymeric (CFX), fluorine containing diamond-like carbon (F-DLC) and, for comparison, diamond-like carbon (DLC) films have been plasma deposited in a RF parallel plate reactor by using c-C4F8 as fluorine precursor and different mixtures of argon, C2H2, and H2. Plasmas have been characterized by optical emission spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, and Langmuir probe measurements. Differences in the film composition and structure have been related with the type of species formed in the plasma and with the self-bias potential developed at the deposition electrode. Additional experiments using CF4 have confirmed that the formation in the plasmas of neutral or ionized CxFy species with x > 2 is a critical factor for the synthesis of fluorine rich films.
Marzo, 2014 | DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201300129
Reactividad de Sólidos
Analysis on the mechanical strength of WC-Co cemented carbides under uniaxial and biaxial bending
Torres, Y; Bermejo, R; Gotor, FJ; Chicardi, E; Llanes, LMaterials & Design, 55 (2014) 851-856
Show abstract ▽
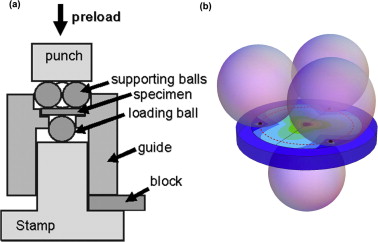
The mechanical strength of three WC-Co grades was determined and compared under uniaxial and biaxial bending. Uniaxial four-point bending was conducted on bar-shaped specimens; biaxial testing was performed on discs using the ball-on-three-balls (B3B) method. Strength results were analysed within the frame of the Weibull theory. Differences in characteristic strength between uniaxial and biaxial bending were explained as an effect of the effective surface tested in each case. A higher Weibull modulus was obtained in one grade, independent of the testing method, which was related to its higher fracture toughness. The use and validity of the B3B biaxial test to determine the strength distribution of cemented carbides is discussed.
Marzo, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2013.10.051
- ‹ anterior
- 282 of 420
- siguiente ›














