Artículos SCI
2012
2012
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Optical interference for the matching of the external and internal quantum efficiencies in organic photovoltaic cells
Betancur, R; Martinez-Otero, A; Elias, X; Romero-Gomez, P; Colodrero, S; Miguez, H; Martorell, JSolar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 104 (2012) 87-91
Show abstract ▽
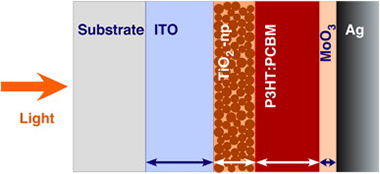
We demonstrate experimentally that an appropriate combination of the layer thicknesses in an inverted P3HT:PCBM cell leads to an optical interference such that the EQE amounts to 91% of IQE. We observe that reflectivity between layers is minimized in a wavelength range of more than 100 nm. In that range the EQE closely matches the IQE. The role played by the optical interference in improving the performance of the fabricated solar cells is confirmed by EQE calculated numerically using a model based on the transfer matrix method. Additionally, we observed that a similar cell with an active material 1.7 times thicker exhibited a lower PCE. The poor photon harvesting in the later cell configuration is attributed to an EQE that amounts only to 72% of the IQE.
Septiembre, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2012.04.047
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Critical thickness and nanoporosity of TiO2 optical thin films
Borras, A; Alvarez, R; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Ferrer, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARMicroscopy and Microanalysis, 18 (2012) 1-9
Show abstract ▽
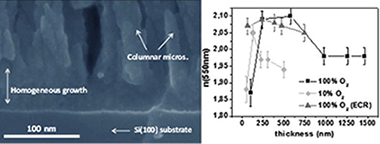
This work reports on the porosity and refraction index of TiO2 thin films as a function of the film thickness. Samples were fabricated by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) in a microwave electron cyclotron resonance (MW-ECR) reactor at room temperature using titanium tetra-isopropoxide (MP) as precursor. Experimental parameters such as plasma gas composition (pure oxygen and argon/oxygen mixtures) and pressure (either ECR conditions or "normal" pressure, i.e. 10(-4) or 10(-3) torrs correspondently) were varied. The evolution of the thin film microstructure, porosity and optical properties is critically studied by AFM, SEM, water adsorption isotherms, ellipsometry and UV-Vis transmittance and the existence of a certain critical thickness (t(c)) demonstrated. The porosity of the films with thicknesses ranging from several tens of nanometers up to half a micrometer is evaluated by QCM-isotherms at room temperature. The dependency of this critical thickness with the plasma conditions is evaluated experimental and theoretically. Thus, the microstructure change at t(c) is attributed to a transition from a surface diffused dominated growth mechanism for t < t(c) to another where shadowing is predominant. Dynamic scaling analysis of the two regimes and their Monte Carlo simulation complete the reported study.
Septiembre, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2012.04.035
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Evidence of upconversion luminescence contribution to the improved photoactivity of erbium doped TiO2 systems
Obregon, S; Colon, GChemical Communications, 48 (2012) 7865-7867
Show abstract ▽
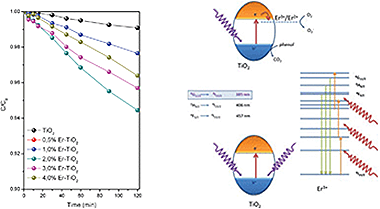
Er3+–TiO2 synthesized by a surfactant free hydrothermal method exhibits good photoactivities under sun-like excitation for the degradation of phenol. The presence of Er3+ does not affect the structural and morphological features of the TiO2 significantly. The best photocatalytic performance was attained for the samples with 2 wt% of Er. Different photocatalytic runs indicated that the incorporation of the Er3+ cation would be responsible for the enhanced photocatalytic activity, which participates in different mechanisms under UV and NIR excitation.
Agosto, 2012 | DOI: 10.1039/C2CC33391K
Reactividad de Sólidos
Microstructural Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications
A. P. Zaderenkoa1, P. M. Castillo, M. de la Mata, M.J. Sayagués and J. A. SánchezMicroscopy and Microanalysis, 18 (2012) 55-56
Show abstract ▽
There is a growing interest in nanoparticles as carriers of chemotherapeutic agents in order to improve their administration and minimize their side effects. Despite the fact that silver nanoparticles can be conjugated to therapeutic agents, offering additionally advantages due their unique and tunable optical properties, few examples have been described yet.
Agosto, 2012 | DOI: 10.1017/S1431927612012937
Reactividad de Sólidos
Microstructural Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles for Bioimaging Applications
Zaderenko, AP; Caro, C; de la Mata, M; Sanchez, JA; Sayagues, MJMicroscopy and Microanalysis, 18 (2012) 53-54
Show abstract ▽
Silver nanoparticles are emerging as a powerful tool in bioimaging applications owing to their unique plasmonic properties i.e., extremely high molar extinction coefficients, resonant Rayleigh scattering and enhanced local electromagnetic fields. Through the optimization of these properties, by controlling composition, size, shape, and interparticle spacing of nanoparticles and their assemblies, highly enhanced local electromagnetic fields in the vicinity of nanoparticles are achievable giving rise to IR, Raman and fluorescence surface enhanced spectroscopies (SEIRS, SERS and MEF, respectively).
Agosto, 2012 | DOI: 10.1017/S1431927612012925
- ‹ anterior
- 324 of 422
- siguiente ›














