Artículos SCI
2012
2012
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Software package to calculate the effects of the core hole and surface excitations on XPS and AES
Tougaard, S; Yubero, FSurface and Interface Analysis, 44 (2012) 1114-1118
Show abstract ▽
We report on a new software package that allows to calculate the energy loss processes in a photo- and Auger electron spectrum. The calculations are performed within our previously published semiclassical dielectric response model. The model takes into account energy loss, which takes place because of the sudden creation of the static core hole and as the photoelectron travels in the bulk, passes the surface region and continues in the vacuum where it interacts with its image charge before it ends up in the electron spectrometer. It is a one-step model, which includes interference effects between these excitations. The only input in the calculations is the dielectric function of the material. We discuss the capabilities of the software and illustrate some examples of its practical application, including comparison with experimental spectra. We hope the software will be useful for the investigations of fundamental excitation mechanisms in XPS and AES. The software is free for noncommercial use.
Agosto, 2012 | DOI: 10.1002/sia.4855
Materiales Coloidales
Structural and kinetic study of phase transitions in LaYSi2O7
Fernandez-Carrion, AJ; Escudero, A; Suchomel, MR; Becerro, AIJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 32 (2012) 2477-2486
Show abstract ▽
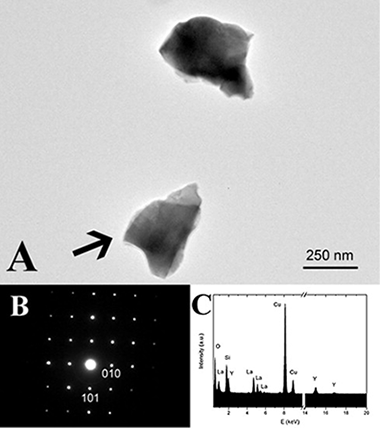
Phase transitions in LaYSi 2O 7 have been investigated as a function of temperature using XRD, NMR and TEM. Previously described empirical crystal structure guidelines based on average cation radius in rare-earth RE 2Si 2O 7-type disilicates predict a stable tetragonal A-LaYSi 2O 7 polymorph at temperatures below 1500°C. This study demonstrates that A-LaYSi 2O 7 is not thermodynamically stable at these temperatures and suggests that guidelines based on average cation size do not accurately describe the equilibrium behaviour of this silicate system. The A to G-type polymorph transition is extremely sluggish; complete transformation requires ~250h at 1200°C, and more than 3 weeks of calcination at 1100°C. This observation is important when this type of material is used as environmental barrier coating (EBC) of advanced ceramics. Analysis of XRD and TEM data reveal complete substitution of Y and La on the rare-earth cation sites in both LaYSi 2O 7 polymorphs, but indicate preferential site occupancies in the G-type polymorph.
Agosto, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2012.03.009
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Introducing structural colour in DSCs by using photonic crystals: interplay between conversion efficiency and optical properties
Colonna, D; Colodrero, S; Lindstrom, H; Di Carlo, A; Miguez, HEnergy & Environmental Science, 5 (2012) 8238-8243
Show abstract ▽
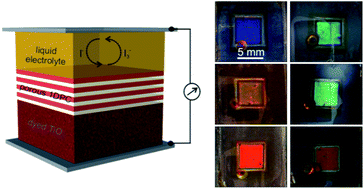
Herein we analyze experimentally the effect that introducing highly reflecting photonic crystals, operating at different spectral ranges, has on the conversion efficiency of dye sensitized solar cells. The interplay between structural colour and cell performance is discussed on the basis of the modified spectral response of the photogenerated current observed and the optical characterization of the cells. We demonstrate that, with the approach herein discussed, it is possible to achieve relatively high efficiencies using thin electrodes while preserving transparency. At the same time, the appearance of the device can be controllably modified, which is of relevance for their potential application in building integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) as window modules.
Agosto, 2012 | DOI: 10.1039/c2ee02658a
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Evidence of upconversion luminescence contribution to the improved photoactivity of erbium doped TiO2 systems
Obregon, S; Colon, GChemical Communications, 48 (2012) 7865-7867
Show abstract ▽
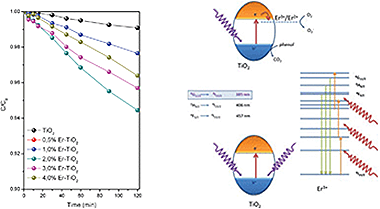
Er3+–TiO2 synthesized by a surfactant free hydrothermal method exhibits good photoactivities under sun-like excitation for the degradation of phenol. The presence of Er3+ does not affect the structural and morphological features of the TiO2 significantly. The best photocatalytic performance was attained for the samples with 2 wt% of Er. Different photocatalytic runs indicated that the incorporation of the Er3+ cation would be responsible for the enhanced photocatalytic activity, which participates in different mechanisms under UV and NIR excitation.
Agosto, 2012 | DOI: 10.1039/C2CC33391K
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Effect of the active metals on the selective H-2 production in glycerol steam reforming
Araque, M; Martinez, LM; Vargas, JC; Centeno, MA; Roger, ACApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 125 (2012) 556-566
Show abstract ▽
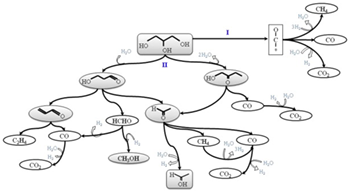
The production of hydrogen by glycerol steam reforming was studied using CeZr(Co, CoRh) catalysts. The effect of Co and Rh presence on the properties of the mixed oxides and the effect on the catalytic behavior were considered. The catalysts were characterized before and after testing by XRD, Raman, TPR, H 2-TPD, TPD-TPO and HRTEM. It was observed that the presence of Co allowed the selective H 2 production related with the presence of a metallic phase at the beginning of the reaction. The presence of Rh favored even more the H 2 production and also increased the stability of the catalyst. For CeZrCoRh, the presence of both metals enhanced the catalyst reduction capacity, a characteristic that significantly improved the catalytic behavior for glycerol steam reforming. The selective H 2 production was related to the capacity of the catalyst to activate H 2O under the reaction conditions. The progressive loss of this capacity decreases the production of H 2, and glycerol decomposition is actually favored over glycerol steam reforming. According to the initial distribution of products, and its evolution with time on stream, two main reaction pathways were proposed.
Agosto, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.06.028
- ‹ anterior
- 325 of 422
- siguiente ›














