Artículos SCI
2012
2012
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Thermal conductivity of high-porosity heavily doped biomorphic silicon carbide prepared from sapele wood biocarbon
Parfen'eva, LS; Orlova, TS; Smirnov, BI; Smirnov, IA; Misiorek, H; Mucha, J; Jezowski, A; Cabezas-Rodriguez, R; Ramirez-Rico, JPhysics of the Solid State, 54 (2012) 1732-1739
Show abstract ▽
The electrical resistivity and thermal conductivity of high-porosity (~52 vol %, channel-type pores) bio-SiC samples prepared from sapele wood biocarbon templates have been measured in the temperature range 5-300 K. An analysis has been made of the obtained results in comparison with the data for bio-SiC samples based on beech and eucalyptus, as well as for polycrystalline β-SiC. The conclusion has been drawn that the electrical resistivity and thermal conductivity of bio-SiC samples based on natural wood are typical of heavily doped polycrystalline β-SiC.
Agosto, 2012 | DOI: 10.1134/S1063783412080240
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Biomimetic mineralization of calcium phosphate on a functionalized porous silicon carbide biomaterial
Dey, A; van den Hoogen, CJ; Rosso, M; Lousberg, N; Hendrix, MMRM; Friedrich, H; Ramirez-Rico, J; Zuilhof, H; de With, G; Sommerdijk, NAJMChemPlusChem, 77 (2012) 694-699
Show abstract ▽
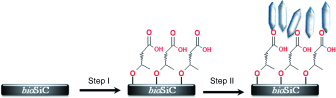
Porous biomorphic silicon carbide (bioSiC) is a structurally realistic, high-strength, and biocompatible material which is promising for application in load-bearing implants. The deposition of an osteoconductive coating is essential for further improvement of its integration with the surrounding tissue. A new strategy towards biomimetic calcium phosphate coatings on bioSiC is described. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis shows that using 10-undecenoic acid methyl ester a covalently bound monolayer can be synthesized on the surface of the bioSiC. After hydrolysis it exposes carboxylic acid groups that promote the selective nucleation and growth of a very well-defined crystalline layer of calcium phosphate. The resulting calcium phosphate coating is characterized by X-ray diffraction and electron microscopy techniques. Further, ion beam imaging is employed to quantify the mineral deposition meanwhile, three-dimensional dual-beam imaging (FIB/SEM) is used to visualize the bioSiC/mineral interface. The monolayer is show to actively induce the nucleation of a well-defined and highly crystalline mixed octacalcium phosphate/hydroxyapatite (OCP/HAP) coating on implantable bioSiC substrates with complex geometry. The mild biomimetic procedure, in principle, allows for the inclusion of bioactive compounds that aid in tissue regeneration. Moreover, the mixed OCP/HAP phase will have a higher solubility compared to HAP, which, in combination with its porous structure, is expected to render the coating more reabsorbable than standard HAP coatings.
Agosto, 2012 | DOI: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cplu.201200118/full
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Effect of the active metals on the selective H-2 production in glycerol steam reforming
Araque, M; Martinez, LM; Vargas, JC; Centeno, MA; Roger, ACApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 125 (2012) 556-566
Show abstract ▽
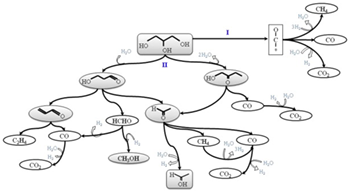
The production of hydrogen by glycerol steam reforming was studied using CeZr(Co, CoRh) catalysts. The effect of Co and Rh presence on the properties of the mixed oxides and the effect on the catalytic behavior were considered. The catalysts were characterized before and after testing by XRD, Raman, TPR, H 2-TPD, TPD-TPO and HRTEM. It was observed that the presence of Co allowed the selective H 2 production related with the presence of a metallic phase at the beginning of the reaction. The presence of Rh favored even more the H 2 production and also increased the stability of the catalyst. For CeZrCoRh, the presence of both metals enhanced the catalyst reduction capacity, a characteristic that significantly improved the catalytic behavior for glycerol steam reforming. The selective H 2 production was related to the capacity of the catalyst to activate H 2O under the reaction conditions. The progressive loss of this capacity decreases the production of H 2, and glycerol decomposition is actually favored over glycerol steam reforming. According to the initial distribution of products, and its evolution with time on stream, two main reaction pathways were proposed.
Agosto, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.06.028
Materiales Coloidales
Aluminum solubility in TiO2 rutile at high pressure and experimental evidence for a CaCl2-structured polymorph
Escudero, A; Langenhorst, F; Muller, WFAmerican Mineralogist, 97 (2012) 1075-1082
Show abstract ▽
Aluminum incorporation into TiO 2 has been studied in the TiO 2-Al 2O 3 system as a function of pressure at temperatures of 900 and 1300 °C using commercial Al 2TiO 5 nanopowder as starting material. A new orthorhombic TiO 2 polymorph with the CaCl 2 structure has been observed in the recovered samples synthesized from 4.5 to 7 GPa and 900 °C and from 2.5 to 7 GPa at 1300 °C. The phase transition to the α-PbO 2 type TiO 2 phase takes place between 7 and 10 GPa at both temperatures. Two mechanisms of Al incorporation in TiO 2 rutile have been observed in the recovered samples. The substitution of Ti 4+ by Al 3+ on normal octahedral sites is dominant at lower pressures. High pressure induces the incorporation of Al 3+ into octahedral interstices of the rutile structure, which is responsible for an orthorhombic distortion of the TiO 2 rutile structure and gives rise to a (110) twinned CaCl 2 type structure. This phase is probably a result of temperature quench at high pressure. Aluminum solubility in TiO 2 increases with increasing pressure. TiO 2 is able to accommodate up to 9.8 wt% Al 2O 3 at 7 GPa and 1300 °C. Temperature has a large effect on the aluminum incorporation in TiO 2, especially at higher pressures. High pressure has a strong effect on both the chemistry and the microstructure of Al-doped TiO 2. Enhanced aluminum concentration in TiO 2 rutile as well as TiO 2 grains with a microstructure consisting of twins are a clear indication of high-pressure conditions.
Julio, 2012 | DOI: 10.2138/am.2012.4049
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Oxidative Dehydrogenation of Ethanol over Au/TiO2 Photocatalysts
Sannino, Diana; Vaiano, Vincenzo; Ciambelli, Paolo; Carmen Hidalgo, M.; Murcia, Julie J.; Antonio Navio, J.Journal of Advanced Oxidation Technologies, 15 (2012) 284-293
Show abstract ▽
Au/TiO2 photocatalysts were used in ethanol oxidative dehydrogenation. Catalysts at gold loading ranging between 0.5-2 wt.% were synthesized by photodeposition (using different deposition times: 15 and 120 min) over an own-prepared TiO2 by sol-gel method. For reference purposes, a commercial 1 wt.% Au/TiO2 catalyst (AUROlite (TM), Strem Chemicals) was also tested. Photocatalytic reactions were carried out in a gas-solid photocatalytic fluidized bed reactor. Catalytic activity depends strongly both on Au loading and on the material properties, such as particle size and distribution of metal on titania surface. Acetaldehyde was the main reaction product, with ethylene, crotonaldehyde and CO2 as by-products. An important improvement of TiO2 photoactivity was achieved for the catalyst with 0.5 wt.% gold prepared with 120 min deposition time. For an ethanol inlet concentration of 0.2 vol% at 60 degrees C, the maximum conversion and acetaldehyde selectivity were 82% and 95%, respectively. These values are considerably higher than those obtained over pristine TiO2 and over the commercial catalyst.
Julio, 2012 | DOI: ---
- ‹ anterior
- 326 of 422
- siguiente ›














