Artículos SCI
2012
2012
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
The effect of nickel on alloy microstructure and electrochemical behaviour of AA1050 aluminium alloy in acid and alkaline solutions
Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Skeldon, P; Thompson, GE; Smith, GCElectrochimica Acta, 75 (2012) 229-238
Show abstract ▽
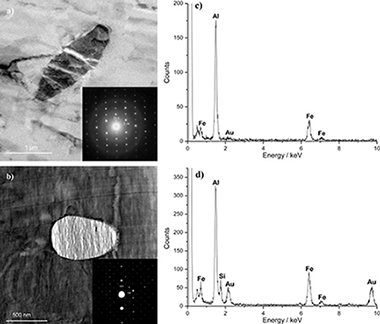
The study investigates the influence of nickel and magnesium additions to AA1050 aluminium alloy on the alloy electrochemical behaviour in sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric solutions under conditions relevant to industries that use alkaline etching as a standard surface treatment procedure and to the lithographic and electronic industries where surface convolution is assisted by pitting in hydrochloric acid. Scanning and transmission electron microscopes were used to characterize the intermetallic particles, and scanning Kelvin probe microscopy was utilised in monitoring the surface potential. Nickel is shown to be incorporated into second phase particles, which mostly consisted of Al3Fe and α-(AlFeSi) phases, resulting in enhanced cathodic activity on the aluminium surface. Consequently, the dissolution rates of the superpure aluminium, alloys without nickel addition and alloy with nickel addition are increased respectively in sodium hydroxide, and increased pitting is respectively promoted in hydrochloric acid. In contrast, the addition of magnesium to the alloy had negligible influence on the etching and pitting behaviour.
Julio, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2012.04.106
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Effect of nanostructured electrode architecture and semiconductor deposition strategy on the photovoltaic performance of quantum dot sensitized solar cells
Samadpour, M; Gimenez, S; Boix, PP; Shen, Q; Calvo, ME; Taghavinia, N; Zad, AI; Toyoda, T; Miguez, H; Mora-Sero, IElectrochimica Acta, 75 (2012) 139-147
Show abstract ▽
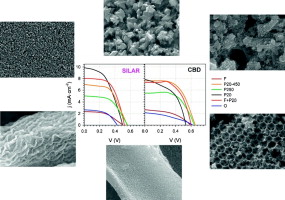
Here we analyze the effect of two relevant aspects related to cell preparation on quantum dot sensitized solar cells (QDSCs) performance: the architecture of the TiO 2 nanostructured electrode and the growth method of quantum dots (QD). Particular attention is given to the effect on the photovoltage, V oc, since this parameter conveys the main current limitation of QDSCs. We have analyzed electrodes directly sensitized with CdSe QDs grown by chemical bath deposition (CBD) and successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR). We have carried out a systematic study comprising structural, optical, photophysical and photoelectrochemical characterization in order to correlate the material properties of the photoanodes with the functional performance of the manufactured QDSCs. The results show that the correspondence between photovoltaic conversion efficiency and the surface area of TiO 2 depends on the QDs deposition method. Higher V oc values are systematically obtained for TiO 2 morphologies with decreasing surface area and for cells using CBD growth method. This is systematically correlated to a higher recombination resistance of CBD sensitized electrodes. Electron injection kinetics from QDs into TiO 2 also depends on both the TiO 2 structure and the QDs deposition method, being systematically faster for CBD. Only for electrodes prepared with small TiO 2 nanoparticles SILAR method presents better performance than CBD, indicating that the small pore size disturb the CBD growth method. These results have important implications for the optimization of QDSCs.Elect
Julio, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2012.04.087
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Novel approaches to flexible visible transparent hybrid films for ultraviolet protection
Calvo, ME; Smirnov, JRC; Miguez, HJournal of Polymer Science Part B-Polymer Physics, 50 (2012) 945-956
Show abstract ▽
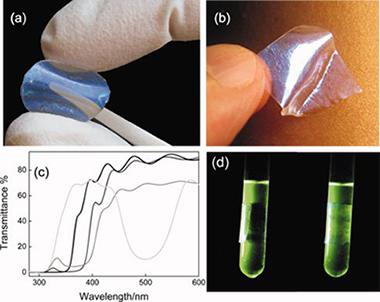
Herein, we present an overview of the most recent achievements and innovations regarding the development of flexible visible transparent films for selective ultraviolet (UV) shielding, with focus on those based on hybrid inorganic-organic materials. The main synthetic paths used nowadays to ensure a high degree of protection are reviewed. Polymers containing organic UV absorbing molecules, hybrid mixtures of polymers and nanoparticles, and the recently introduced series of structures displaying structural color, are identified as the three main types of materials used for this purpose. The use of biocompatible and flexible films to achieve spectrally selective UV protection can find applications in a wide diversity of fields such as photo-treatment of skin diseases, food and beverage packing, and storage of cosmetics. © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. J Polym Sci Part B: Polym Phys, 2012 In this review, the different approaches taken to obtain flexible and transparent films that block ultraviolet radiation based on the use of hybrid materials are covered. The synthetic pathways that lead to films that can shield against UV radiation either by absorption or by interference are described.
Julio, 2012 | DOI: 10.1002/polb.23087
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical Synthesis and Characterization of II-VI Nanocrystals: Challenge for Cytotoxicity Issues
Balaz, P; Jardin, R; Dutkova, E; Sayagues, MJ; Balaz, M; Mojzisova, G; Mojzis, J; Turianicova, E; Fabian, MActa Physica Polonica A, 122 (2012) 224-229
Show abstract ▽
CdSe@ZnS nanocrystals have been prepared by a two-step solid state mechanochemical synthesis. CdSe prepared from elements in the first step is mixed with ZnS synthesized from zinc acetate and sodium sulfide in the second step. The crystallite size of the new type CdSe@ZnS nanocrystals determined by X-ray diffraction Rietveld refined method was 35 nra and 10 Jam for CdSe and ZnS, respectively. Energy dispersive/transmission electron microscopy/energy dispersive spectroscopy methods show good crystallinity of the nanoparticles and scanning electron microscopy elemental mapping illustrate consistent distribution of Cd, Se, Zn and S elements in the bulk of samples. UV-VIS spectra show an onset at 320 urn with calculated bandgap 3.85 eV. This absorption arises from the vibration modes of Zn-S bonds. The nanocrystals show the blue shift from the bandgap of bulk ZnS (3.66 eV). The synthesized CdSe@ZnS nanocrystals have been tested for dissolution, cytotoxicity and L-cysteine conjugation. The dissolution of Cd was less than 0.05 mu g mL(-1) (in comparison with 0.8 mu g mL(-1) which was evidenced for CdSe alone). The very low cytotoxic activity for selected cancer cell lines has been evidenced. CdSe@ZnS nanocrystals coated with L-cysteine are water-soluble and have a great potential in biomedical engineering as fluorescent labels.
Julio, 2012 | DOI: ---
Reactividad de Sólidos
Absence of the core-rim microstructure in TixTa1-xCyN1-y-based cermets developed from a pre-sintered carbonitride master alloy
Chicardi, E; Cordoba, JM; Sayagues, MJ; Gotor, FJInternational Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 33 (2012) 38-43
Show abstract ▽
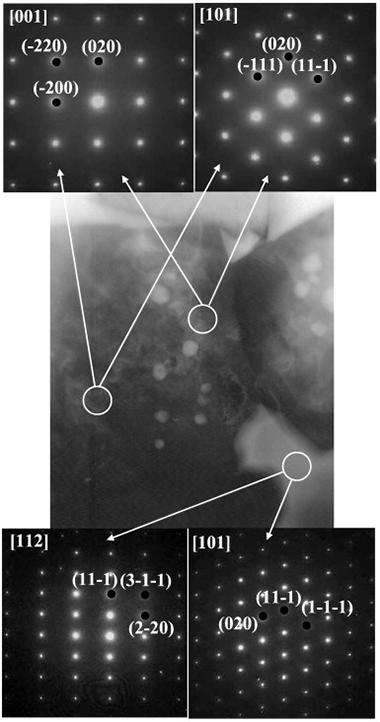
(Ti,Ta)(C,N) solid solution-based cermets with cobalt as the binder phase were synthesised by a two-step milling process. The titanium-tantalum carbonitride solid solution (the ceramic phase) was obtained via a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) process from stoichiometric elemental Ti, Ta, and graphite powder blends in a nitrogen atmosphere. Elemental Co (the binder phase) was added to the ceramic phase, and the mixture was homogenised by mechanical milling (MM). The powdered cermet was then sintered in a tubular furnace at temperatures ranging from 1400°C to 1600°C in an inert atmosphere. The chemical composition and microstructure of the sintered cermets were characterised as ceramic particles grown via a coalescence process and embedded in a complex (Ti,Ta)-Co intermetallic matrix. The absence of the typical core-rim microstructure was confirmed.
Julio, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2012.02.005
- ‹ anterior
- 327 of 422
- siguiente ›














