Artículos SCI
2011
2011
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Aligned TiO(2) nanocolumnar layers prepared by PVD-GLAD for transparent dye sensitized solar cells
Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Gonzalez-Valls, I; Lira-Cantu, M; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AREnergy and Environmental Science, 4 (2011) 3426-3435
Show abstract ▽
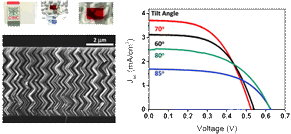
Transparent thin film electrodes made of vertically aligned nanocolumns of TiO2 with well-controlled oblique angles were grown by physical vapor deposition at glancing incidence (PVD-GLAD). For an electrode thickness of 500 nm, we report a 40% variation on solar cell efficiency (from 0.6% to 1.04%) when the deposition angle was modified between 60° and 85°. Transparent thicker films with higher surface area deposited at the optimal angle of 70° were grown with a zigzag morphology which confers high mechanical strength to the thin films. Using this topology, the application of an electrode thickness of 3 m in a DSC resulted in a power conversion efficiency of 2.78% maintaining electrode transparency.
Septiembre, 2011 | DOI: 10.1039/C0EE00489H
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Colored semi-transparent Cu-Si oxide thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering
Gil-Rosta, J; Yubero, F; Fernandez, R; Vilajoana, T; Artus, P; Dursteler, JC; Cotrino, J; Ortega, I; Gonzalez-Elipe, AROptical Material Express, 1 (2011) 1100-1112
Show abstract ▽

Colored semi-transparent Cu-Si oxide thin films have been prepared by reactive magnetron sputtering from a single cathode of copper-silicon composition. Thin films of different composition and optical response were obtained by changing process parameters like the relative amount of copper in the target and the O2/Ar mixture of the reactive plasma gas. The film characteristics were analyzed by several techniques. Their optical properties (refractive index, absorption coefficient, color) have been correlated with the process parameters used in the film preparation as well as with the film stoichiometry and chemistry.
Septiembre, 2011 | DOI: 10.1364/OME.1.001100
Analytical study of Roman and Arabic wall paintings in the Patio De Banderas of Reales Alcazares' Palace using non-destructive XRD/XRF and complementary techniques
Duran, A., Perez-Rodriguez, J.L., Jimenez de Haro, M.C., Franquelo, M.L., Robador, M.D.Journal of Archaeological Science, 38 (2011) 2366-2377
Show abstract ▽
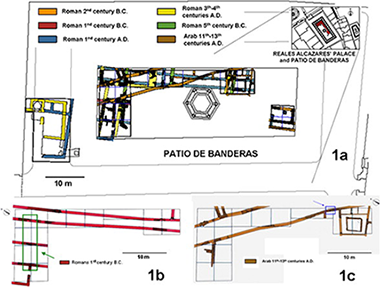
A portable XRD/XRF system and complementary laboratory techniques were employed to improve the knowledge of the procedures used to create Roman and Arabic wall paintings. Integrated physico-chemical investigations were conducted on fragments of artworks collected from the archaeological excavation of the Patio de Banderas in the Reales Alcazares' Palace of Seville (Spain), and a comparative study on the pigments from both historical periods was performed. As a result, pigments such as vermilion, red ochre, yellow ochre, green earth, Egyptian blue, carbon and phosphor-based black pigments were detected in Roman samples; however, in the Arabic fragments, only haematite was observed. In addition, the size and shape of the particles of the wall paintings were studied with an XRD 2-dimensional detector and SEM-EDX.
Septiembre, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jas.2011.04.021
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
CO oxidation at low temperature on Au/CePO4: Mechanistic aspects
Romero-Sarria, F., Domínguez, M.I., Centeno, M.A., Odriozola, J.A.Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 107 (2011), 268-273
Show abstract ▽
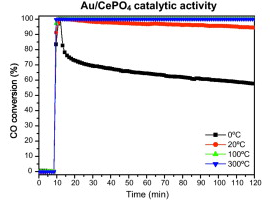
This work reports the synthesis and characterization of a cerium phosphate supported gold catalyst as well as its catalytic activity for the oxidation of CO. A precipitation method in the presence of an organic modifier followed by a hydrothermal treatment was used for the support synthesis, resulting in high surface area nanometric particles. Gold/cerium phosphate catalyst with a 1% (w/w) nominal gold content was characterized using XRF, XRD, N2 adsorption-desorption measurements, TEM and DRIFTS-MS. The catalyst shows good catalytic activity at low temperature. The activity is related to the generation of oxygen vacancies in the support caused by the elimination of structural oxygen. In situ studies revealed that the reaction of the oxygen vacancies with gaseous oxygen resulted in the formation of peroxo species. These species are responsible for the activity detected at room temperature in both the catalyst and the support. Moreover, the presence of carbonate and hydrogen carbonate acting as reaction intermediates have been observed.
Septiembre, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.07.022
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity of Bi-doped TiO2 photocatalysts under simulated solar irradiation
Murcia-López, S., Hidalgo, M.C., Navío, J.A.Applied Catalysis A: General, 404 (2011) 59-67
Show abstract ▽
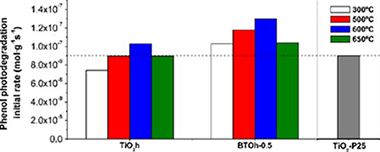
A series of Bi3+-doped TiO2 catalysts with a doping concentration up to 2 wt% were prepared by a sol-gel hydrothermal method. The prepared photocatalysts were characterized by different techniques to determine their structure, morphology and light absorption properties. The activities were evaluated in the photocatalytic oxidation of phenol in aqueous solution under UV-vis illumination. The experimental results indicate that the presence of Bi3+ in TiO2 catalysts enhances the photocatalytic reaction of phenol degradation, although the efficiency of the process markedly depends on the nominal content of the Bi3+ and on the calcination temperature. It was found that the optimal dosage of 0.5 wt% Bi3+ in TiO2 and calcinations at 600 °C 4 h achieved the fastest reaction of phenol degradation under the experimental conditions. From the comparison of the initial rates of the photocatalytic degradation of phenol between home prepared undoped and Bi3+-doped TiO2 with commercial TiO2 Degussa P25, it can be inferred that home prepared TiO 2 calcined at temperatures above 500 °C clearly exceed the photocatalytic performance of P25. When bismuth is incorporated, the reaction rate values are even higher, especially at 600 °C. Even when Bi 3+-doped TiO2 (0.5 wt% Bi3+) calcined at 600 °C has almost the same BET surface than P25, its activity is better. In particular, the reaction rate for the sample with a 0.5% mass content of Bi 3+ calcined at 600 °C not only present higher value with respect to the other series but also a degree of mineralization close to 100%.
Septiembre, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2011.07.008
- ‹ anterior
- 348 of 422
- siguiente ›














